
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663987
Author: Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 24.48AP
Consider a plane surface in a uniform electric field as in Figure P24.48, where d = 15.0 cm and θ = 70.0°. If the net flux through the surface is 6.00 N · find the magnitude of the electric field.
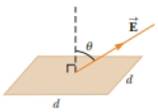
Figure P24.48
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a closed triangular box resting within a horizontal electric field of magnitude E = 7.80 X 104 N/C as shown in Figure P24.4. Calculate the electric flux through (a) the vertical rectangular surface, (b) the slanted surface, and (c) the entire surface of the box.
Could you solve the question in the picture shown?
a circular surface with a radius of 0.061 m is exposed to a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.88E4 N/C. The electric flux through the surface is 77 Nm^2/C. What is the angle between the diraction of the electric field and the normal to the surface
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 24 - Suppose a point charge is located at the center of...Ch. 24 - If the net flux through a gaussian surface is...Ch. 24 - A cubical gaussian surface surrounds a long,...Ch. 24 - A coaxial cable consists of a long, straight...Ch. 24 - In which of the following contexts ran Gausss law...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge q is located inside a...Ch. 24 - Charges of 3.00 nC, -2.00 nC, -7.00 nC, and 1.00...Ch. 24 - A large, metallic, spherical shell has no net...Ch. 24 - Two solid spheres, both of radius 5 cm. carry...Ch. 24 - A uniform electric field of 1.00 N/C is set up by...
Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius 5 cm carries...Ch. 24 - A cubical gaussian surface is bisected by a large...Ch. 24 - Rank the electric fluxes through each gaussian...Ch. 24 - Consider an electric field that is uniform in...Ch. 24 - A cubical surface surrounds a point charge q...Ch. 24 - A uniform electric field exists in a region of...Ch. 24 - If the total charge inside a closed surface is...Ch. 24 - Explain why the electric flux through a closed...Ch. 24 - If more electric field lines leave a gaussian...Ch. 24 - A person is placed in a large, hollow, metallic...Ch. 24 - Consider two identical conducting spheres whose...Ch. 24 - A common demonstration involves charging a rubber...Ch. 24 - On the basis of the repulsive nature of the force...Ch. 24 - The Sun is lower in the sky during the winter than...Ch. 24 - A flat surface of area 3.20 m2 is rotated in a...Ch. 24 - A vertical electric field of magnitude 2.00 104...Ch. 24 - A 40.0-cm-diameter circular loop is rotated in a...Ch. 24 - Consider a closed triangular box resting within a...Ch. 24 - An electric field of magnitude 3.50 kN/C is...Ch. 24 - A nonuniform electric field is given by the...Ch. 24 - An uncharged, nonconducting, hollow sphere of...Ch. 24 - Find the net electric flux through the spherical...Ch. 24 - The following charges are located inside a...Ch. 24 - The electric field everywhere on the surface of a...Ch. 24 - Four closed surfaces, S1 through S4 together with...Ch. 24 - A charge of 170 C is at the center of a cube of...Ch. 24 - In the air over a particular region at an altitude...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge of 12.0 C is placed at the...Ch. 24 - (a) Find the net electric flux through the cube...Ch. 24 - (a) A panicle with charge q is located a distance...Ch. 24 - An infinitely long line charge having a uniform...Ch. 24 - Find the net electric flux through (a) the closed...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q = 5.00 C is located at...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located at the center...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located a small...Ch. 24 - Figure P23.23 represents the top view of a cubic...Ch. 24 - In nuclear fission, a nucleus of uranium-238,...Ch. 24 - The charge per unit length on a long, straight...Ch. 24 - A 10.0-g piece of Styrofoam carries a net charge...Ch. 24 - Determine the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 24 - A large, flat, horizontal sheet of charge has a...Ch. 24 - Suppose you fill two rubber balloons with air,...Ch. 24 - Consider a thin, spherical shell of radius 14.0 cm...Ch. 24 - A nonconducting wall carries charge with a uniform...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged, straight filament 7.00 m in...Ch. 24 - Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each...Ch. 24 - Consider a long, cylindrical charge distribution...Ch. 24 - A cylindrical shell of radius 7.00 cm and length...Ch. 24 - A solid sphere of radius 40.0 cm has a total...Ch. 24 - Review. A particle with a charge of 60.0 nC is...Ch. 24 - A long, straight metal rod has a radius of 5.00 cm...Ch. 24 - Why is the following situation impossible? A solid...Ch. 24 - A solid metallic sphere of radius a carries total...Ch. 24 - A positively charged panicle is at a distance R/2...Ch. 24 - A very large, thin, flat plate of aluminum of area...Ch. 24 - In a certain region of space, the electric field...Ch. 24 - Two identical conducting spheres each having a...Ch. 24 - A square plate of copper with 50.0-cm sides has no...Ch. 24 - A long, straight wire is surrounded by a hollow...Ch. 24 - A thin, square, conducting plate 50.0 cm on a side...Ch. 24 - A solid conducting sphere of radius 2.00 cm has a...Ch. 24 - Consider a plane surface in a uniform electric...Ch. 24 - Find the electric flux through the plane surface...Ch. 24 - A hollow, metallic, spherical shell has exterior...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius R = 1.00 m surrounds a particle...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius R surrounds a particle with...Ch. 24 - A very large conducting plate lying in the xy...Ch. 24 - A solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius a = 5.00 cm...Ch. 24 - Two infinite, nonconducting sheets of charge are...Ch. 24 - For the configuration shown in Figure P24.45,...Ch. 24 - An insulating solid sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged spherical shell with positive...Ch. 24 - An insulating solid sphere of radius a has a...Ch. 24 - A slab of insulating material has a nonuniform...Ch. 24 - Prob. 24.62CPCh. 24 - A dosed surface with dimensions a = b= 0.400 111...Ch. 24 - A sphere of radius 2a is made of a nonconducting...Ch. 24 - A spherically symmetric charge distribution has a...Ch. 24 - A solid insulating sphere of radius R has a...Ch. 24 - An infinitely long insulating cylinder of radius R...Ch. 24 - A particle with charge Q is located on the axis of...Ch. 24 - Review. A slab of insulating material (infinite in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can someone please explain it to me ASAP??!!!arrow_forwardA particle with charge Q is located a small distance δ immediately above the center of the flat face of a hemisphere of radius R as shown in Figure P24.21. What is the electric flux (a) through the curved surface and (b) through the flat face as δ → 0?arrow_forwardFind the electric flux (in units of N.m2/C) through the surface of the rectangle ( 30 cm x 40 cm) in the figure given that E = 399.7 N/C. Normal E 0-30arrow_forward
- A flat sheet is in the shape of a rectangle with sides of lengths 0.2 m and 1.7 m . The sheet is immersed in a uniform electric field of magnitude 65.0 N/C that is directed at 65.0 o from the plane of the sheet . Find the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet. O 20.0 Nm² /C O 13.0 Nm²/C O 2.6 Nm2/C O 240.4 Nm? /C O 44.1 Nm2/Carrow_forwardA square that has 10 cm long edges is centered on the x axis in a region where there exists a uniform electric field given by E = (2.00 kN/c)î. (a) What is the electric flux of this electric field through the surface of a square if the normal to the surface is in the +x direction? N. m2/c (b) What is the electric flux through the same square surface if the normal to the surface makes a 70° angle with the y axis and an angle of 90° with the z axis? N. m2/carrow_forward(a) Find the net electric flux through the cube shown in Figure P24.15. (b) Can you use Gaussslaw to find the electric field on the surface of this cube? Explain.arrow_forward
- A 3.7 cm × 4.0 cm rectangle lies in the xy-plane. What is the electric flux through the rectangle if E (vector) =(120ı^−240k^)N/C? What is the electric flux through the rectangle if E (vector) =(120ı^−240ȷ^)N/C?arrow_forwardA circular surface with a radius of 0.066 m is exposed to a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.90 × 104 N/C. The electric flux through the surface is 52 N·m2/C. What is the angle between the direction of the electric field and the normal to the surface?arrow_forwardWe have an electric flux of magnitude 141 Nm2/ C passing through a flat horizontal surface with an area of 0.58 m2. The flux is due to a uniform electric field, which points 14.4 degrees above the horizontal. Find the magnitude of the electric field.arrow_forward
- A flat sheet is in the shape of a rectangle with sides of lengths 0.400 m and 0.600 m. The sheet is immersed in a uniform electric field of magnitude 95.0 N/C that is directed at 200 from the plane of the sheet. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet.arrow_forwardA uniform electric field of magnitude 5.7 x 104 N/C is at an angle of 10° to a square sheet with sides 5.5 m long. What is the electric flux through the sheet? Hint Electric flux is E N.m²/C.arrow_forwardAn insulating solid sphere of radius R = 6.0cm has a total positive charge Q uniformly distributed throughout its volume. The electric flux through a spherical Gaussian surface of radius r = 3.0cm is 2.26x105N.m2/C. How much charge (in units of μC) is enclosed by the Gaussian surface of radius r =3.0cm? What is the magnitude ( in units of 106N/C) of the E-field at the Gaussian surface of part (1)? What is the magnitude (in units of 106N/C) of the E-field at surface of the sphere?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY