
(a)
Interpretation:
The types of
Concept introduction:
Functional groups:
The functional group is defined as an atom or group of atoms combined in a specific manner that gives the chemical properties of the organic compound and they are the main reason for the chemical reactivity of the compound. Compounds having similar functional groups undergoes similar type of reactions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of chiral centres present in estrone that has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Chiral centre:
Chiral centre is defined as an atom bonded to four different chemical species. It is a stereo centre that holds the atom in such way that the structure may not be superimposable to its mirror image. They give optical isomerism.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the compounds
Concept introduction:
Structural formula:
The structural formula of a compound can be defined as a graphic representation of the molecular structure showing how the atoms are arranged and the
Retrosynthetic approach:
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique for planning a synthesis mainly for complex organic molecules where the complex target molecule is reduced into a sequence of progressively simpler structures along a pathway which ultimately leads to the identification of a simple starting molecule or easily available from which the synthesis can be developed.
During retrosynthetic analysis the target molecule is symmetrically broken down by a combination of functional group interconversion and disconnection. This disconnection is related to breaking of carbon-carbon bond of a molecule to generate simpler fragments. The complete set of disconnections and functional group interconversions for a specified target molecule is what constitutes a retrosynthetic plan.
Heck reaction:
The Heck reaction is the
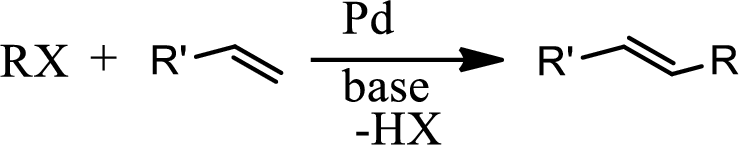
(d)
Interpretation:
The pathway of converting compounds
Concept introduction:
Heck reaction:
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in presence of a base and palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. The reaction is as follows,
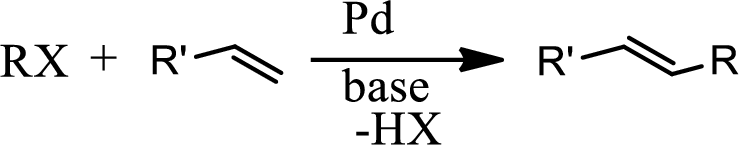
(e)
Interpretation:
The stereochemistry of compound
Concept introduction:
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in presence of a base and palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. The reaction is as follows,
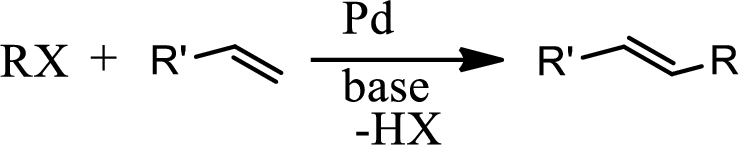
(f)
Interpretation:
The pathway of conversion of tertiary butyl ether to acetone to form estrone from compound
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of secondary alcohol:
Oxidation of alcohol to carbonyl is very difficult as the reaction is so fast that it always ends up by giving acid. Hence for secondary alcohol to get oxidised to carbonyl selectively PCC is used.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- 8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forward
- о но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

