
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given
Concept introduction:
The alkene, on reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.19P
The given diol is
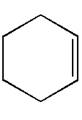
Explanation of Solution
The given diol is
The given diol is
It is determined that the diol can be produced using reagents, either
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given diol can be produced from an alkene using either
Concept introduction:
The alkene, on reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.19P
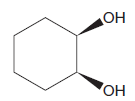
The given diol is not a
Explanation of Solution
The given diol is
The given diol is not a
It is determined that the diol cannot be produced using reagents either
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the given diol can be produced from an alkene using either
Concept introduction:
The alkene, on reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.19P
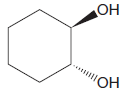
The given diol is not a
Explanation of Solution
The given diol is
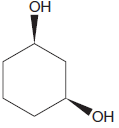
The given diol is not a
It is determined that the diol cannot be produced using reagents either
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the given diol can be produced from an alkene using either
Concept introduction:
The alkene, on reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.19P
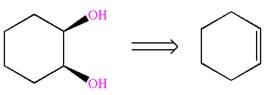
The given diol is
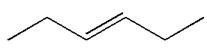
Explanation of Solution
The given diol is
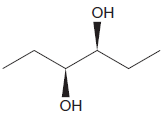
The given diol is
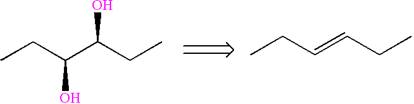
It is determined that the diol can be produced using reagents either
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the given diol can be produced from an alkene using either
Concept introduction:
The alkene, on reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.19P
The given diol is
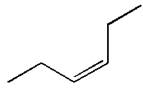
Explanation of Solution
The given diol is
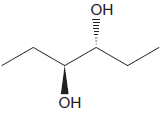
The given diol is
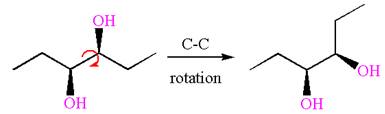
The alkene that can be used to produce this diol is identified by replacing the hydroxyl groups and placing the double bond between those carbons. Therefore, the structure of the alkene is
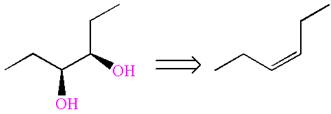
It is determined that the diol can be produced using reagents either
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Draw the structure of the product of the reaction given the IR and MS data. Spectral analysis of the product reveals: MS: M 150, M-15, M-43 CH.COCI AICI, IR: 3150-3000 cm, 2950-2850 cm and 1700 cmarrow_forwardPart II. Identify whether the two protons in blue are homotopic, enantiopic, diasteriotopic, or heterotopic. a) HO b) Bri H HH c) d) H H H Br 0arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Choose the option that is decreasing from biggest to smallest. Group of answer choices: 100 m, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100000 um, 10000000 nm 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100 m 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100 m 100 m, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100000 um, 10000000 nmarrow_forwardQ1. (a) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH3. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement. (b) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH4*. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement.arrow_forwardWhich is NOT the typical size of a bacteria? 1000 nm 0.001 mm 0.01 mm 1 umarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





