
Concept explainers
Sustainable Use of Horseshoe Crabs Horseshoe crab blood clots immediately upon exposure to bacterial toxins, so it can be used to test injectable drugs for the presence of dangerous bacteria. To keep horseshoe crab populations stable, blood is extracted from captured animals, which are then returned to the wild. Concerns about the survival of animals after bleeding led researchers to do an experiment. They compared survival of animals captured and maintained in a tank with that of animals captured, bled, and kept in a similar tank. FIGURE 24.28 shows the results.
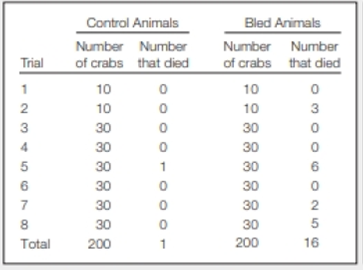
FIGURE 24.28 Mortality of young male horseshoe crabs kept in tanks during the 2 weeks after their capture. Half the animals were bled on the day of their capture. Control animals were handled, but not bled. This procedure was repeated 8 times with different sets of horseshoe crabs.
In which trial did the most control crabs die? In which did the most bled crabs die?
To explain: The trial in which the most control crabs died.
Introduction: Horseshoe crabs belong to the Phylum Arthropod. They are normally found around shallow ocean waters. Horseshoe crabs are living fossils. The horseshoe crabs though they look like crustaceans are marine arachnids.
Explanation of Solution
The uniqueness of horseshoe crabs is that they clot upon encountering bacteria. Therefore, they are used in experiments where highly virulent bacteria are involved. The blood of horseshoe crabs is taken and then let out in their habitat in order to conserve their population, but this might also lead to their death. Therefore, experiments were conducted to check their survival after taking their blood.
In trial 5, the number of control crabs is 30, and 1 crab died out of it.
The trial group 5 marked the highest number of control crabs that died.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (Looseleaf)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physical Universe
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- examples of synamtomorphy.arrow_forwardE. Bar Graph Use the same technique to upload the completed image. We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CO2 data (Fig A1.6.2) 1. Calculate the average rate of increase in COz concentration per year for the time intervals 1959-1969, 1969- 1979, etc. and write the results in the spaces provided. The value for 1959-1969 is provided for you as an example. 2. Plot the results as a bar graph. The 1959-1969 is plotted for you. 3. Choose the graph that looks the most like yours A) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CU, data (rig. nive). Average Yearly Rate of Observatory, Hawall interval Rate of increase per year 1959-1969 0.9 1969-1979 1979-1989 1989-1999 1999-2009 Figure A1.6.2 1999-2009 *- mrame -11- -n4 P2 جية 1989-1999 1979-1989 1969-1979 1959-1969 This bar drawn for you as an example 1.0 CO, Average Increase/Year (ppmv) B) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive…arrow_forwardUse the relationships you just described to compute the values needed to fill in the blanks in the table in Fig A1.4.1 depth (a) 1.0 cml 0.7 cml cm| base dimensions (b, c)| 1.0 cm| 1.0 cm| 1.0 cm 1.0 cm| 1.0 cm| 1.0 cm volume (V) 1.0_cm' cm'| cm'| density (p) 1.0 g/cm'| 1.0 g/cm 1.0 g/cm' mass (m)| 0.3 g Column 1: depth at 1.0 cm volume mass Column 2: depth at 0.7 cm volume mass Column 3: unknown depth depth volumearrow_forward
- San Andreas Transform Boundary Plate Motion The geologic map below of southern California shows the position of the famous San Andreas Fault, a transform plate boundary between the North American Plate (east side) and the Pacific Plate (west side). The relative motion between the plates is indicated by the half arrows along the transform plate boundary (i.e., the Pacific Plate is moving to the northwest relative to the North American Plate). Note the two bodies of Oligocene volcanic rocks (labeled Ov) on the map in the previous page located along either side of the San Andreas Fault. These rocks are about 23.5 million years old and were once one body of rock. They have been separated by displacement along the fault. 21. Based on the offset of these volcanic rocks, what is the average annual rate of relative plate motion in cm/yr? SAF lab 2.jpg Group of answer choices 0.67 cm/yr 2 cm/yr 6.7 cm/yr 1.5 cm/yr CALIFORNIA Berkeley San Francisco K Os Q San Andreas Fault Ov…arrow_forwardThese are NOT part of any graded assignment. Are there other examples of synapomorphy. What is it called when the traits retained are similar to ancestors?arrow_forwardPlease hand draw everying. Thank you! Draw a gram positive bacterial cell below. Your cell should have the following parts, labeled: A coccus shape A capsule The gram positive cell wall should have the peptidoglycan labeled, as well as its component parts (NAM, NAG, and teichoic acid) A cell membrane Fimbriae A nucleoid Ribosomes Inclusionsarrow_forward
- Draw a gram negative bacterial cell below. Your cell should have the following parts, labeled: A bacillus shape Fimbriae Amphitrichous flagella 2 membranes (outer and inner) The outer membrane should have lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with lipid A and O antigens Periplasmic space The thin peptidoglycan cell wall between the 2 membranes A nucleoid Ribosomes Inclusionsarrow_forwardBacterial species Cell wall type Example: S. mitis Gram positive S. epidermidis H. pylori M. bovis S. marcescens Shape and arrangement Coccus, streptococcus Drawing 0000000arrow_forwardDraw a gram positive bacterial cell below. Your cell should have the following parts, labeled: A coccus shape A capsule The gram positive cell wall should have the peptidoglycan labeled, as well as its component parts (NAM, NAG, and teichoic acid) A cell membrane Fimbriae A nucleoid Ribosomes Inclusionsarrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





