
Concept explainers
Complete this concept map to summarize the key concepts concerning the body’s defenses.
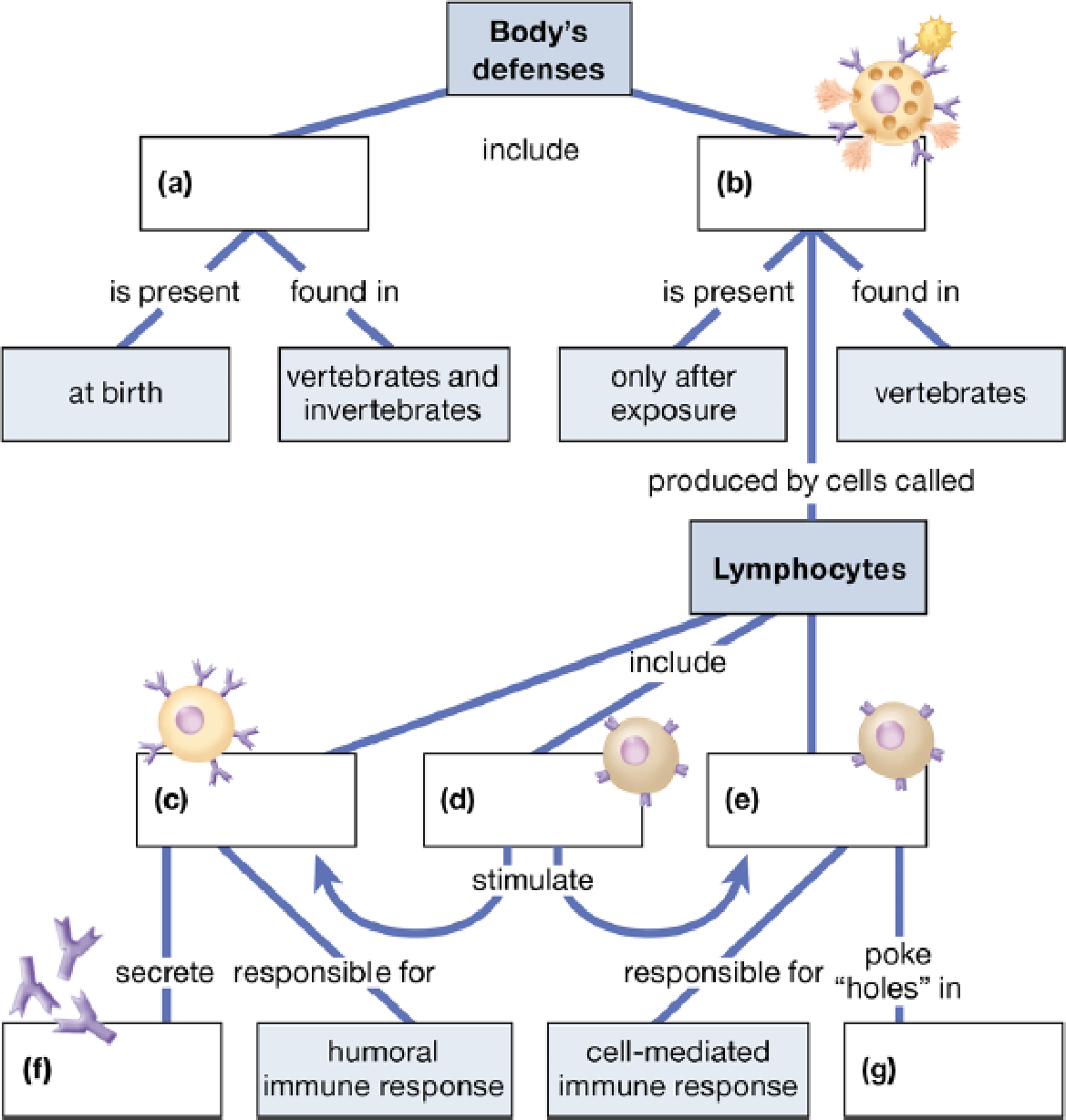
To complete: The given concept map and to summarize the key concepts concerning body’s defense.
Introduction:
The immune system of the human body is divided into two main branches, namely the innate immunity and the adaptive immunity. Innate or the body’s first defense mechanism is present since birth and this defense mechanism are non-specific, which means it acts as a barrier in for every foreign body irrespective of its structure. Adaptive immunity of the body comes in later stages, when the body is introduced to pathogens. It is a specific type of defense mechanism.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: A concept map explaining immune defense mechanisms of body is presented in Fig.1.
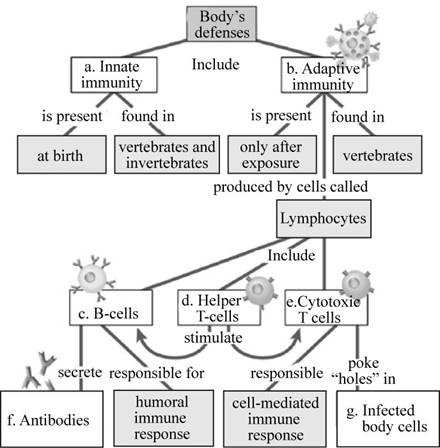
Fig. 1: Map depicting the concept of body’s defenses
Explanation of Solution
a)
Correct answer: Innate immunity.
Explanation:
Innate immunity is the immunity present in the body since birththat helps in protecting the body from infection. Hence the correct answer is innate immunity.
(b)
Correct answer: Adaptive immunity.
Explanation:
Adaptive immunity is the immunity that is acquired by the body when the body comes in contact with the foreign agent. Hence the correct answer is adaptive immunity.
(c)
Correct answer: B-cells.
Explanation:
B-cells are the immune cells that help in the protecting the body from infection and is a part of the humoral immunity. Hence the correct answer is B-cells.
(d)
Correct answer: Helper T-cells.
Explanation:
Helper T-cells helps in the recognizing the foreign antigen and instigate the release of antibodies. Hence the correct answer is helper T-cells
(e)
Correct answer: Cytotoxic T cells.
Explanation:
Cytotoxic T-cells help in neutralizing the antigen carrying cell by attaching to it and releasing degenerative enzymes. Hence the correct answer is cytotoxic T cells.
(f)
Correct answer: Antibodies.
Explanation:
Antibodies are protein molecules that help in the recognizing foreign antigen and eliciting an immune response. Hence the correct answer is antibodies.
(g)
Correct answer: Infected body cells.
Explanation:
Infected body cells are the host’s cells that are penetrated by the infectious agent. Hence the correct answer is infected body cells.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Which of the following is not true about the life-cycle of Fucus. a. 8 eggs per oogonium b. 64 sperm per antheridium c. eggs are flagellated d. sperm are flagellatedarrow_forwardGreen Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forwardCertain toxic terpenoids in this group is thought to deter herbivory but may also have some anti-tumor activity? a. green algae b. brown algae c. red algae d. golden algae e. none of thesearrow_forward
- In the cellular slime molds, the most common phase is: a. plasmodium b. pseudoplasmodial c. single cells as myxamoebae d. moundingarrow_forwardWhich of the following descriptive terms does not describe Hydrodictyon? a. colonial b. nonmotile c. 1 large reticulated chloroplast in each cell d. all of these describe Hydrodictyonarrow_forwardWhich of the following does not apply to Chara? a. "stoneworts" b. isogamous c. calcified walls d. apical growth with an axis and branchesarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning





