
A long, thin steel wire is cut in half, and each half is connected to a different terminal of a light bulb. An
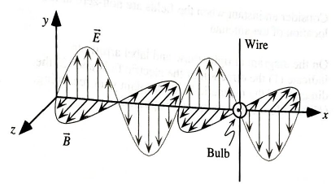
-
a. In what direction is the wave propagating? Explain your reasoning.
The direction of the propagation of the wave.
Answer to Problem 1aTH
The direction of the propagation of the wave is along positive x axis.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
An electromagnetic wave is shown graphically as below:
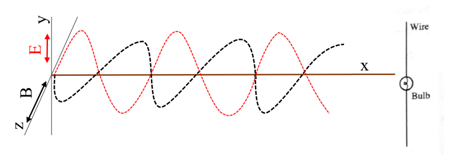
Figure 1: An electromagnetic wave
The given electric field is in the form of sinusoidal wave form is:
According to the above equation, the direction of oscillating electrical field is along y and the direction of the wave propagation is along x direction. The corresponding magnetic field is given as below:
The magnetic field (black dotted sine wave) and electric field (red dotted sine wave) are shown in Figure 1.
The direction of the electromagnetic wave can be determined by the argument of the function, here is the Sin function which is
Derivative of this equation 1
The speed
Conclusion:
The direction of the propagation of the wave is along positive x axis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- The electric part of an electromagnetic wave is given by E(x, t) = 0.75 sin (0.30x t) V/m in SI units. a. What are the amplitudes Emax and Bmax? b. What are the angular wave number and the wavelength? c. What is the propagation velocity? d. What are the angular frequency, frequency, and period?arrow_forwardThe electric field of an electromagnetic wave traveling in vacuum is described by the following wave function: E =(5.00V/m)cos[kx(6.00109s1)t+0.40] j where k is the wavenumber in rad/m, x is in m, t s in Find the following quantities: (a) amplitude (b) frequency (c) wavelength (d) the direction of the travel of the wave (e) the associated magnetic field wavearrow_forwardFigure P24.13 shows a plane electromagnetic sinusoidal wave propagating in the x direction. Suppose the wavelength is 50.0 m and the electric field vibrates in the xy plane with an amplitude of 22.0 V/m. Calculate (a) the frequency of the wave and (b) the magnetic field B when the electric field has its maximum value in the negative y direction. (c) Write an expression for B with the correct unit vector, with numerical values for Bmax, k, and , and with its magnitude in the form B=Bmaxcos(kxt) Figure P24.13 Problems 13 and 64.arrow_forward
- If the electric field of an electromagnetic wave is oscillating along the z-axis and the magnetic field is oscillating along the x-axis, in what possible direction is the wave traveling?arrow_forwardThe magnetic field of a wave propagating through a certain nonmagnetic material in the positive y direction has an amplitude of 30 mA/m and a frequency of- 10 Hz . If the wave is polarized on the positive z direction and its wavelength is 12.6 meter, find the equation of the instantaneous Electric field. Assume the initial phase is 0. Select one: O a. E(y, t) = -2.4īcos(10°t – y) V/m 12.6 O b. E(y, t) = 2400žcos(2710°t – 12.6y) V/m O c. E(y, t) = 2.4ricos(10*t – y) V/m 12.6 O d. E(z, t) = 2.4jcos(10°t - z) mv/m 12.6 O e. E(y, t) = 1.6žcos(t – 2.10®ry) v/m O f. E(y, t) = 30žcos(10°t + y) mv/m 27 12.6arrow_forwardThe electric field for a plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the +y direction is shown. Ē 11₁ 个个 Consider a point where E is in the +z direction. The B field is: in the +x direction and in phase with the E field in the +x direction and one-fourth of a cycle out of phase with the E field in the +z direction and in phase with the E field in the -x direction and in phase with the E field in the +z direction and one-fourth of a cycle out of phase with the E fieldarrow_forward
- Question 1: For a plane electromagnetic wave, the magnetic field at a point x and time t is B (x, t) = [1.2 × 10-7 sin (0.5 × 103 x + 1.5 × 1011 t) k] T. The instantaneous electric field E corresponding to B is: (speed of light c = 3 × 108 ms–1) 1) E (x, t) = [36 sin (1 × 103 x + 1.5 × 1011t) i] V / m 2) E (x, t) = [36 sin (0.5 × 103 x + 1.5 × 1011t) k] V / m 3) E (x, t) = [36 sin (1 × 103 x + 0.5 × 1011t) j] V / m 4) E (x, t) = [- 36 sin (0.5 × 103 x + 1.5 × 1011t) j] V / marrow_forwardA flat, sine-shaped electromagnetic wave propagating in an insulating material with a fixed isolation of 2 = K. If the value of the angular frequency of this wave is equal to w = 3 x 10^7 rad / sec. Calculate the following: (1) the characteristic impedance of this wave Z (2) its wave number K (3) the velocity of the wave in this dielectric medium 0 1)arrow_forwardThe magnetic field in a plane monochromatic electromagnetic wave with wavelength λ = 683 nm, propagating in a vacuum in the z-direction is described by B = (B₁ sin(kz – wt)) (î+ ĵ) where B₁ = 5.3 X 10-6 T, and i-hat and j-hat are the unit vectors in the +x and +y directions, respectively. 1) What is k, the wavenumber of this wave? 0 2) What is Zmax, the distance along the positive z-axis to the position where the magnitude of the magnetic field is a maximum at t = 0? 0 m¹ Submit 0 3) What is Emax, the amplitude of the electric field oscillations? nm Submit 0 V/m Submit 4) What is Ey, the y-component of the electric field at (x = 0, y-0, z = Zmax) at t = 0? V/m Submit + +arrow_forward
- The intensity of solar radiation near the earth is 1.4 kW/m2. What force is exerted by solarradiation impinging normally on a 5.0 m2 perfectly reflecting panel of an artificial satelliteorbiting the earth? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4pi × 10^-7 T · m/A,E0 = 8.85 × 10^-12 C2/N · m2)arrow_forwardA plane electromagnetic wave has the magnetic field given by B~ (x, y, z, t) = B0 sin (x + y)k√2+ ωtˆk where k is the wave number and ˆi, ˆj and ˆk are the Cartesian unit vectors in x, yand z directions, respectively.The electric field E~ (x, y, z, t) corresponding to the above wave is given byarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave E = (2) sin (2π (8.1910 x 105 GHz) t- z+ (0.5000 rad)) travels along z-axis of a right-handed system of coordinates. Angle between the x-axis and the positive (+) direction of electric field oscillation is 0 = 0.9817 rad. What are the electric field strength and x,y,z- components of the electric field vector at position t = 6 fs and when z = 602 nm ? E * Z What is the electric field strength? E=1 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 1 What is the x-component of the electric field vector? E₂ = 1 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 1 What is the y-component of the electric field vector? E₂ = 1 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 1 What is the z-component of the electric field vector? E₂=1 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 1 Do not leave any fields blank. If you don't know the answer, insert 1 for example. Insert the answer with 3 significant digits without rounding the answer. Unit Constant Value c 2.9979 × 10 Quantity…arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


