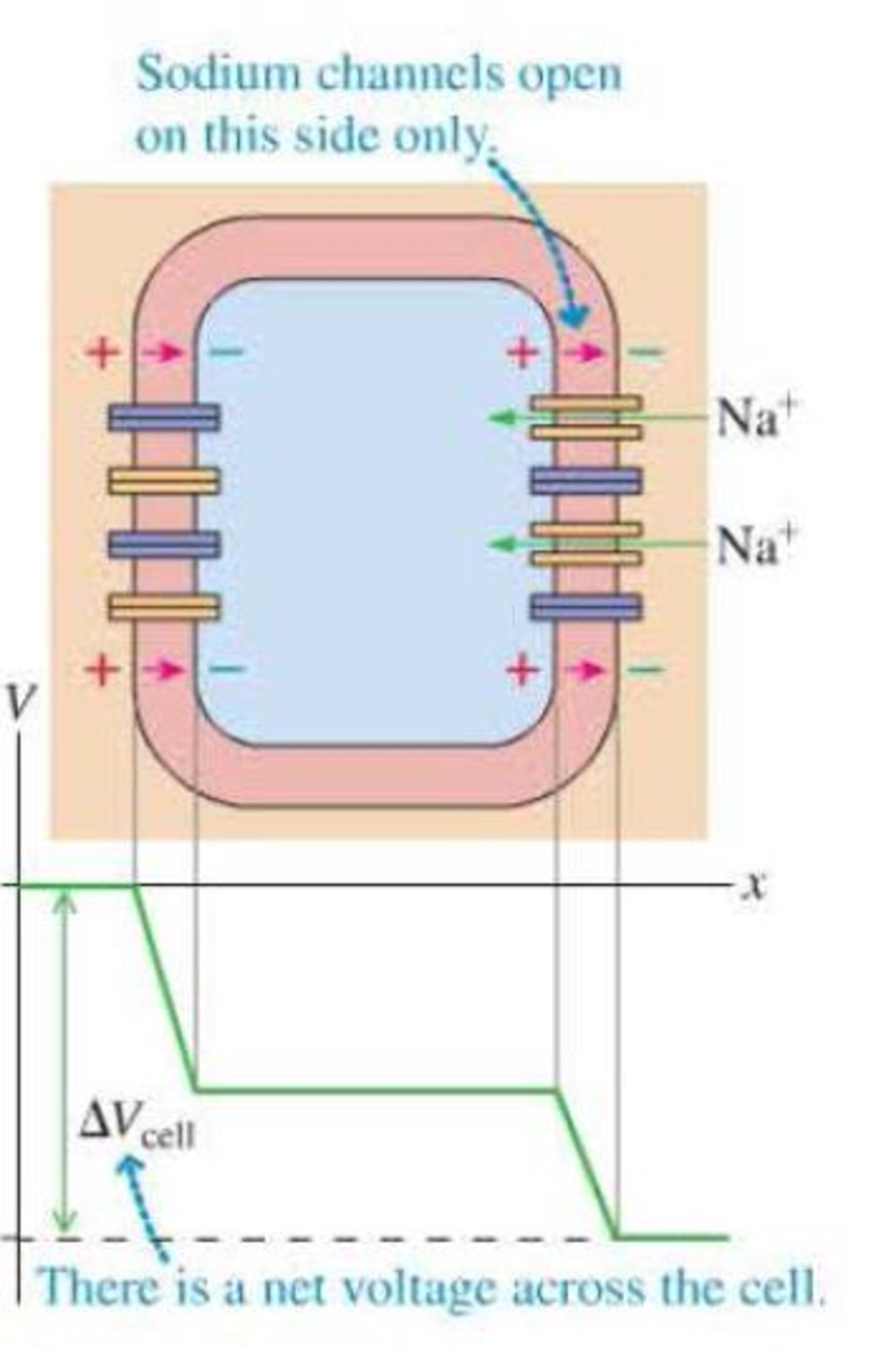
The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle cell is quite small, but there are many species of fish that use multiple action potentials in series to produce significant voltages. The electric organs in these fish are composed of specialized disk-shaped cells called electrocytes. The cell at rest has the usual potential difference between the inside and the outside, but the net potential difference across the cell is zero. An electrocyte is connected to nerve fibers that initially trigger a depolarization in one side of the cell but not the other. For the very short time of this depolarization, there is a net potential difference across the cell, as shown in Figure P23.86. Stacks of these cells connected in series can produce a large total voltage. Each stack can produce a small current; for more total current, more stacks are needed, connected in parallel.
Figure P23.86
Electric eels live in fresh water. The torpedo ray is an electric fish that lives in salt water. The electrocytes in the ray are grouped differently than in the eel; each stack of electrocytes has fewer cells, but there are more stacks in parallel. Which of the following best explains the ray’s electrocyte arrangement?
A. The lower resistivity of salt water requires more current but lower voltage.
B. The lower resistivity of salt water requires more voltage but lower current.
C. The higher resistivity of salt water requires more current but lower voltage.
D. The higher resistivity of salt water requires more voltage but lower current.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- A 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forwardReport on the percentage errors (with uncertainty) between the value of 'k' from the F vs displacement plot and each of the values of 'k' from the period measurements. Please comment on the goodness of the results. Value of k = Spring constant k = 50.00 N/m Each of the values of k from period measurements: Six Measurements of time for 5 osccilations: t1 = 7.76s, t2=8.00s, t3=7.40s, t4=7.00s, t5=6.90s, t6=7.10s (t1-tavg)^2 = (7.76-7.36)^2 = 0.16%(t2-tavg)^2 =(8.00-7.36)^2 = 0.4096%(t3-tavg)^2 =(7.40-7.36)^2 = 0.0016%(t4-tavg)^2 =(7.00-7.36)^2 = 0.1296%(t5-tavg)^2 =(6.90-7.36)^2 = 0.2116%(t6-tavg)^2 =(7.10-7.36)^2 = 0.0676arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Based on the two periods (from hand timed and ultrasonic sensor), find the value of 'k' they suggest from the physics and from the value of the hanging mass. hand time period is 1.472s and ultrasonic sensor time period is 1.44sarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardExperimental Research Report Template Title: Paper Airplane Flight. Materials: Paper, ruler, tape Procedure: Fold paper into different airplane designs, such as dart, glider, or classic. Measure and record the distances each design flies when thrown with the same force. Discuss aerodynamics and the factors that affect flight distance. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the…arrow_forward
- Title: Studying the Relationship Between Drop Height and Bouncing Height of a Ball: You can drop balls of different materials (e.g., rubber, plastic, ping pong) from various heights onto a flat surface and measure the height of their bounce using a ruler. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the lab: tables, charts, graphs, sketches, etc.) Data Analysis: (Explain you…arrow_forwardA traveler at an airport takes an escalator up one floor as in the figure below. The moving staircase would itself carry him upward with vertical velocity component v between entry and exit points separated by height h. However, while the escalator is moving, the hurried traveler climbs the steps of the escalator at a rate of n steps/s. Assume that the height of each step is hs. (a) Determine the amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy by the traveler's leg muscles during his escalator ride given that his mass is m. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) energy = (b) Determine the work the escalator motor does on this person. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) work =arrow_forwardWhich of the following is part of the interior of the Sun? photosphere the corona sunspots radiation zonearrow_forward
- Most craters on the surface of the Moon are believed to be caused by which of the following? faults asteroids volcanoes meteoroidsarrow_forwardAn object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes? y (m) C B (5.00, 5.00) A x (m) © (a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O ] (b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation? ○ The force of friction is a conservative force. ○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done by the applied force. ] (b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table. ] (c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. ] (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. ]arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





