
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 65PQ
A Figure P23.65 shows two identical
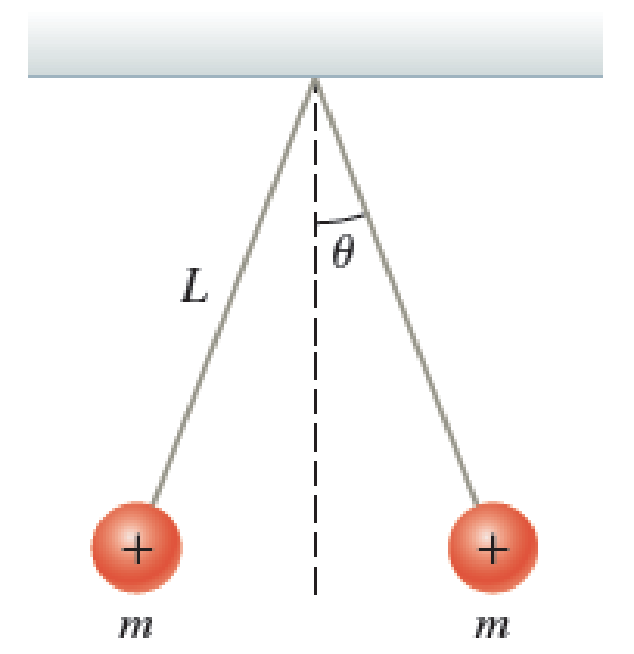
Figure P23.65
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
E1
R₁
w
0.50
20 Ω
12
R₁₂
ww
ΒΩ
R₂
60
E3
C
RA
w
15 Ω
E2
0.25
E4
0.75 Ω
0.5 Ω
Solve plz
Solve plz
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 23.2 - Initially a glass rod and a piece of silk are...Ch. 23.3 - a. In Figure 23.8, why are there three plus signs...Ch. 23.3 - When wool is rubbed against amber, the wool...Ch. 23.3 - Prob. 23.4CECh. 23.4 - The following scenarios involve a metal ball and a...Ch. 23.4 - Prob. 23.6CECh. 23 - What is the difference between a contact force and...Ch. 23 - Many textbooks claim Franklin decided that moving...Ch. 23 - An object has a charge of 35 nC. How many excess...Ch. 23 - As part of a demonstration, a physics professor...
Ch. 23 - A single coulomb represents a large amount of...Ch. 23 - A sphere has a net charge of 8.05 nC, and a...Ch. 23 - A glass rod is initially neutral. After it is...Ch. 23 - After an initially neutral glass rod is rubbed...Ch. 23 - A 50.0-g piece of aluminum has a net charge of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 10PQCh. 23 - A silk scarf is rubbed against glass, and a wool...Ch. 23 - CASE STUDY A person in Franklins time may have...Ch. 23 - Prob. 13PQCh. 23 - Prob. 14PQCh. 23 - A charge of 36.3 nC is transferred to a neutral...Ch. 23 - Prob. 16PQCh. 23 - Prob. 17PQCh. 23 - An electrophorus is a device developed more than...Ch. 23 - Prob. 19PQCh. 23 - An electroscope is a device used to measure the...Ch. 23 - Two particles with charges of +5.50 nC and 8.95 nC...Ch. 23 - Particle A has a charge of 34.5 nC, and particle B...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23PQCh. 23 - Prob. 24PQCh. 23 - Particle A has charge qA and particle B has charge...Ch. 23 - Two charged particles are placed along the y axis....Ch. 23 - A 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin...Ch. 23 - A 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin...Ch. 23 - Two particles with charges q1 and q2 are separated...Ch. 23 - An electron with charge e and mass m moves in a...Ch. 23 - Two electrons in adjacent atomic shells are...Ch. 23 - Two small, identical metal balls with charges 5.0...Ch. 23 - Two identical spheres each have a mass of 5.0 g...Ch. 23 - One end of a light spring with force constant k =...Ch. 23 - Two 25.0-g copper spheres are placed 75.0 cm...Ch. 23 - Three charged particles lie along a single line....Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles shown...Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles in...Ch. 23 - Given the arrangement of charged particles in...Ch. 23 - Three charged metal spheres are arrayed in the xy...Ch. 23 - Charges A, B, and C are arrayed along the y axis,...Ch. 23 - Three identical conducting spheres are fixed along...Ch. 23 - Charges A, B, and C are arranged in the xy plane...Ch. 23 - Prob. 44PQCh. 23 - A particle with charge q is located at the origin,...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.46 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 23 - Prob. 47PQCh. 23 - Two metal spheres of identical mass m = 4.00 g are...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.49 shows two identical small, charged...Ch. 23 - Two small spherical conductors are suspended from...Ch. 23 - Four equally charged particles with charge q are...Ch. 23 - Four charged particles q, q, q, and q are Fixed...Ch. 23 - A metal sphere with charge +8.00 nC is attached to...Ch. 23 - Prob. 54PQCh. 23 - Three small metallic spheres with identical mass m...Ch. 23 - How does a negatively charged rubber balloon stick...Ch. 23 - How many electrons are in a 1.00-g electrically...Ch. 23 - Prob. 58PQCh. 23 - Prob. 59PQCh. 23 - Prob. 60PQCh. 23 - Three charged particles are arranged in the xy...Ch. 23 - A We saw in Figure 23.16 that a neutral metal can...Ch. 23 - Prob. 63PQCh. 23 - A Figure P23.65 shows two identical conducting...Ch. 23 - Two helium-filled, spherical balloons, each with...Ch. 23 - Two small metallic spheres, each with a mass of...Ch. 23 - A Two positively charged spheres with charges 4e...Ch. 23 - Prob. 69PQCh. 23 - Three charged spheres are at rest in a plane as...Ch. 23 - Prob. 71PQCh. 23 - Three particles with charges of 1.0 C, 1.0 C, and...Ch. 23 - A Two positively charged particles, each with...Ch. 23 - Prob. 74PQCh. 23 - Eight small conducting spheres with identical...Ch. 23 - Prob. 76PQCh. 23 - Prob. 77PQCh. 23 - Prob. 78PQCh. 23 - Prob. 79PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)arrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forward
- An ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forwardThe outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forward
- The heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forwardL₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY