
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553582
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 23, Problem 32P
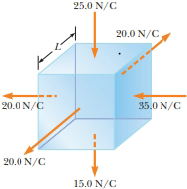
Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge L = 1.00 m in Figure P23.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric flux through the cube and (b) the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge he a single point charge?
Figure P23.32
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge L = 1.00 m in Figure P23.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric flux through the cube and (b) the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge he a single point charge?
The electric field everywhere on the surface of a thin, spherical shell of radius 0.745 m is of magnitude 915 N/C and points radially toward the center of the sphere.
(a) What is the net charge within the sphere's surface?
nC
(b) What is the distribution of the charge inside the spherical shell?
O The negative charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution.
O The positive charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution.
O The positive charge has an asymmetric charge distribution.
O The negative charge has an asymmetric charge distribution.
The electric field everywhere on the surface of a thin, spherical shell of radius 0.800 m is of magnitude 892 N/C and points radially toward the center of the sphere.
(a) What is the net charge within the sphere's surface?
nC
(b) What is the distribution of the charge inside the spherical shell?
O The negative charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution.
O The positive charge has an asymmetric charge distribution.
O The positive charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution.
O The negative charge has an asymmetric charge distribution.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
Ch. 23.2 - Suppose a point charge is located at the center of...Ch. 23.3 - If the net flux through a gaussian surface is...Ch. 23 - A negatively charged rod of finite length carries...Ch. 23 - A positively charged disk has a uniform charge per...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged ring of radius 10.0 cm has a...Ch. 23 - The electric field along the axis of a uniformly...Ch. 23 - Example 23.3 derives the exact expression for the...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged rod of length L and total...Ch. 23 - A continuous line of charge lies along the x axis,...Ch. 23 - A thin rod of length and uniform charge per unit...
Ch. 23 - (a) Consider a uniformly charged, thin-walled,...Ch. 23 - A vertical electric field of magnitude 2.00 104...Ch. 23 - A flat surface of area 3.20 m2 is rotated in a...Ch. 23 - A nonuniform electric field is given by the...Ch. 23 - An uncharged, nonconducting, hollow sphere of...Ch. 23 - Find the net electric flux through the spherical...Ch. 23 - Four closed surfaces, S1 through S4 together with...Ch. 23 - A charge of 170 C is at the center of a cube of...Ch. 23 - (a) Find the net electric flux through the cube...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge of 12.0 C is placed at the...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge Q = 5.00 C is located at...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge Q is located at the center...Ch. 23 - (a) A panicle with charge q is located a distance...Ch. 23 - Find the net electric flux through (a) the closed...Ch. 23 - Figure P23.23 represents the top view of a cubic...Ch. 23 - Determine the magnitude of the electric field at...Ch. 23 - In nuclear fission, a nucleus of uranium-238,...Ch. 23 - Suppose you fill two rubber balloons with air,...Ch. 23 - A large, flat, horizontal sheet of charge has a...Ch. 23 - A nonconducting wall carries charge with a uniform...Ch. 23 - A uniformly charged, straight filament 7.00 m in...Ch. 23 - You are working on a laboratory device that...Ch. 23 - Consider a long, cylindrical charge distribution...Ch. 23 - Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each...Ch. 23 - A solid sphere of radius 40.0 cm has a total...Ch. 23 - A cylindrical shell of radius 7.00 cm and length...Ch. 23 - You are working for the summer at a research...Ch. 23 - You are working for the summer at a research...Ch. 23 - Find the electric flux through the plane surface...Ch. 23 - Three solid plastic cylinders all have radius 2.50...Ch. 23 - A line of charge starts at x = +x0 and extends to...Ch. 23 - Show that the maximum magnitude Emax of the...Ch. 23 - A line of positive charge is formed into a...Ch. 23 - A very large conducting plate lying in the xy...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R = 1.00 m surrounds a particle...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R surrounds a particle with...Ch. 23 - A slab of insulating material has a nonuniform...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius 2a is made of a nonconducting...Ch. 23 - An infinitely long insulating cylinder of radius R...Ch. 23 - A particle with charge Q is located on the axis of...Ch. 23 - Review. A slab of insulating material (infinite in...Ch. 23 - Identical thin rods of length 2a carry equal...Ch. 23 - A solid insulating sphere of radius R has a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A total charge Q is distributed uniformly on a metal ring of radius R. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the center of the ring at point O (Fig. P24.61)? b. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the point A lying on the axis of the ring a distance R from the center O (same length as the radius of the ring)? FIGURE P24.61arrow_forwardThe question is in the picture.arrow_forwardThe electric field everywhere on the surface of a charged sphere of radius 0.273 m has a magnitude of 520 N/C and points radially outward from the center of the sphere. (a) What is the net charge on the sphere? nC (b) What can you conclude about the nature and distribution of charge inside the sphere?arrow_forward
- The electric field on the axis of a uniformly charged ring has magnitude 400 kN/C at a point 6 cm from the ring center. The magnitude 15 cm from the center is 125 kN/C; in both cases the field points away from the ring. a. Find the rings radius b. find the rings chargearrow_forwardA particle with charge Q is located on the axis of a circle of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the circle (as shown). Show that if one-fourth of the electric flux from the charge passes through the circle, then R = √(3b).arrow_forward. A charge q located at the center of a regu- +5.80 µC is lar tetrahedron (a four-sided surface) as in Figure P15.50. Find (a) the total electric flux through the tetrahedron and (b) the electric flux through one face of the tetrahedron. Figure P15.50arrow_forward
- The electric field everywhere on the surface of a thin, spherical shell of radius 0.775 m is of magnitude 897 N/C and points radially toward the center of the sphere. (a) What is the net charge within the sphere's surface? X If the net charge inside the sphere is moved to the center of the sphere would this change the value of the electric field on the surface? nC (b) What is the distribution of the charge inside the spherical shell? O The negative charge has an asymmetric charge distribution. O The positive charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution. The negative charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution. O The positive charge has an asymmetric charge distribution. 4arrow_forwardAn infinite sheet charge of has a charge density of +44.81 pC/m2 and covers the entire x-y plane. A second infinite sheet of charge has a charge density of −53.2 pC/m2 covers the entire y-z plane. What is the magnitude of the electric field at any point not on either surface?arrow_forward32. Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge1.00 m in Figure P24.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric lux through the cube and ( the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge be a single point charge? ON/C 200 N/C 200 N/C 850N/C 200N/C 5.ON/Carrow_forward
- We have a nonconducting solid sphere of radius 2.9 cm carrying a uniformly distributed positive charge of 4.3 nC. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 1 cm from the center of the sphere? b) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere? c) Now consider a conducting sphere with the same radius and total charge. In this situation, what is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere?arrow_forwardWe have a nonconducting solid sphere of radius 3.4 cm carrying a uniformly distributed positive charge of 7.6 nC. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 1.6 cm from the center of the sphere? b) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere?arrow_forwardA semicircle of radius a is in the first and Figure second quadrants, with the cen- ter of curvature at the origin. Positive charge +Q is distrib- uted uniformly around the left half of the semicircle, and nega- tive charge -Q is distributed uniformly around the right half of the semicircle (Fig. P21.86). What are the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the origin produced by this distribution of charge? +Qarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY