
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The mechanism that will increase or decrease insulin secretion by pancreatic
Introduction:
Insulin is the peptide hormone that is secreted by pancreas; insulin is produced naturally in the body of an organism. Insulin is required by the cells to use glucose as energy source. Glyburide is an antidiabetic drug that has sulfonylureas that close relation with sulfonamide antibiotics.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig 1: represent the pathway of glyburide:
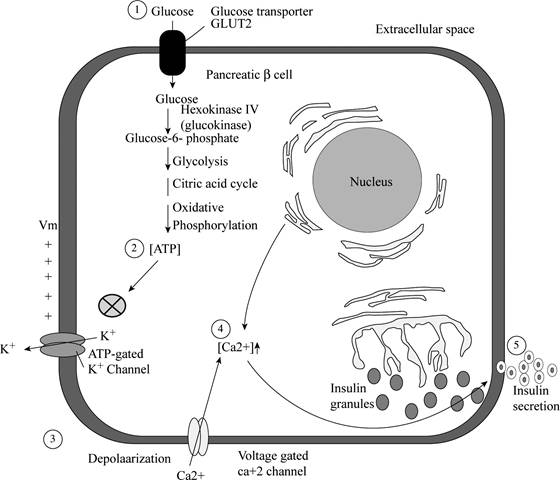
Fig.1: the pathway of glyburide
Explanation:
Treatment of diabetes with glyburide leads to the rapid secretion of insulin from the
Conclusion:
Glyburide will increase the secretion of insulin by shutting down the ATP-gated
(b)
To determine: The treatment process with glyburide that will reduce the symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Introduction:
Glyburide is an antidiabetic drug that has sulfonylureas that has close relation with sulfonamide antibiotics. Type 2 diabetes is a severe case of diabetes that can be reversed by changing diet and lifestyle. To treat type 2 diabetes insulin is taken as injections..
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Glyburide drug will reduce the symptoms of type 2 diabetes because diabetes is a disease, which is cause due to the improper level of insulin. Glyburide will increase the secretion of insulin, and increased insulin level will reduces the symptoms of diabetes.
Conclusion:
Glyburide will reduce the symptoms of type 2 diabetes by increasing the insulin level in the body.
(c)
To determine: The reason that glyburide can be used to treat type 1 diabetes with explanation.
Introduction:
Glyburide is an antidiabetic drug that has sulfonylureas that close relation with sulfonamide antibiotic. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which immune system immune system remain active.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Type 1, diabetes is caused by the defect in pancreatic cells. The glyburide drug is not useful for the Type 1 diabetes patients, because glyburide act on pancreatic cell to produce insulin, which maintain the level of glucose in the body.
Conclusion:
Type 1 diabetes occurs due to the defect in pancreatic cell. Glyburide drug is not useful for its treatment.
(d)
To determine: The importance of iodinated glyburide that has same binding characteristic with unaltered glyburide.
Introduction:
Insulin is the peptide hormone that is secreted by pancreas; insulin is produced naturally in the body of organism. Insulin is required by the cells to use glucose as energy source. Glyburide is an antidiabetic drug that has sulfonylureas that close relation with sulfonamide antibiotics.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig1: Represent the Iodinated glyburide:
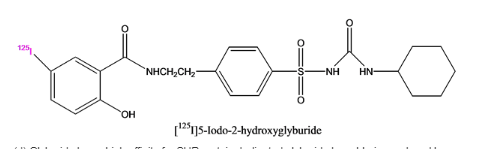
Explanation:
Glyburide show high affinity for SUR protein. Chlorine of glyburide is replaced by iodinated glyburide. Iodinated glyburide will not bind to SUR as glyburide does. If binding will not occur then wrong protein is cloned. This is required to differentiate iodinated glyburide with glyburide.
Conclusion:
Iodinated glyburide is required to differentiate iodinated glyburide with glyburide.
(e)
To determine: The reason for the requirement of antibody binding step.
Introduction:
Antibodies are also known as immunoglobulins, which are made up of proteins. These proteins will protect the living organism from the foreign substances. Glyburide is an antidiabetic drug that has sulfonylureas that close relation with sulfonamide antibiotics
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
To purify the desired protein from a mixture of different proteins antibody-binding step is required. Antibody-binding step efficiently is used to separate desired protein from the mixture of different protein.
Conclusion:
Antibody binding step will separate out the desired protein from the mixture of different proteins.
(f)
To determine: The importance of putative SUR
Introduction:
Hybridization is the method that is used for the interbreeding of an individual from different population to produce hybrid. SUR subunit has 17 subunits that have 17 transmembrane domain.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
It is important to include putative SUR
Conclusion:
Hybridization step is important because cloned genes may code same sequences in another protein.
(g)
To determine: The name of
Introduction:
Gene cloning is the method by which similar copies of particular genes are produced. DNA cloning is a molecular technique that is used to make identical copies of the target gene.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
The following table represents the
| Experiment | Cell type | Added Putative SUR
|
Added excess unlabeled glyburide |
|
| 1 | HIT | No | No | +++ |
| 2 | HIT | No | Yes | - |
| 3 | No | No | - | |
| 4 | Yes | No | +++ | |
| 5 | Yes | Yes | - |
From the given table, the
Conclusion:
In the second experiment
(h)
To determine: The information from the given table to argue that
Introduction:
Gene cloning is the method by which similar copies of particular genes are produced. DNA cloning is a molecular technique that is used to make identical copies of the target gene.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
The
Conclusion:
The weight of cloned gene encodes SUR protein and weight as the SUR that is obtained from
(i)
To enlist: The extra information that is required to prove that SUR gene is cloned.
Introduction:
Gene cloning is the method by which similar copies of particular genes are produced. DNA cloning is a molecular technique that is used to make identical copies of the target gene.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
To prove that SUR gene is cloned following information are required:
1) Check whether the transformed cells have ATP- gated
2) ATP- gated
3) Check whether these organisms are able to produce insulin by introducing mutants of the putative SUR gene.
Conclusion:
To prove that SUR gene is cloned, ATP-gated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Lehninger Principles Of Biochemistry 7e & Study Guide And Solutions Manual For Lehninger Principles Of Biochemistry 7e
- Draw the reaction between sphingosine and arachidonic acid. Draw out the full structures.arrow_forwardDraw both cis and trans oleic acid. Explain why cis-oleic acid has a melting point of 13.4°C and trans-oleic acid has a melting point of 44.5°C.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the mixed triacylglycerol formed by the reaction of glycerol and the fatty acids arachidic, lauric and trans-palmitoleic. Draw the line structure.arrow_forward
- Draw out the structure for lycopene and label each isoprene unit. "Where is lycopene found in nature and what health benefits does it provide?arrow_forwardWhat does it mean to be an essential fatty acid? What are the essential fatty acids?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast primary and secondary active transport mechanisms in terms of energy utilisation and efficiency. Provide examples of each and discuss their physiological significance in maintaining ionic balance and nutrient uptake. Rubric Understanding the key concepts (clearly and accurately explains primary and secondary active transport mechanisms, showing a deep understanding of their roles) Energy utilisation analysis ( thoroughly compares energy utilisation in primary and secondary transport with specific and relevant examples Efficiency discussion Use of examples (provides relevant and accurate examples (e.g sodium potassium pump, SGLT1) with clear links to physiological significance. Clarity and structure (presents ideas logically and cohesively with clear organisation and smooth transition between sections)arrow_forward
- 9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate? 요요. 1. NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 3. A OCH2CH3 2. ethyl acetoacetate ii A 3. H3O+ OH B C D Earrow_forward7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. Which one is it? Ph کہ A B C D Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forward
- what is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forwardFour distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





