
a)
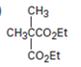
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
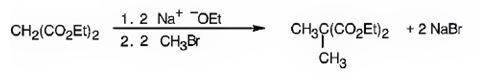
Explanation of Solution
The compound shown is a derivative of carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The acid has two methyl groups attached to the carbon adjacent to ester groups. It can be prepared by replacing the two hydrogens on the active methylene group of malonic ester by two methyl groups. This is achieved by treating the ester with two equivalents of sodium ethoxide and two equivalents of methyl bromide.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
b)
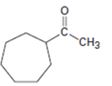
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
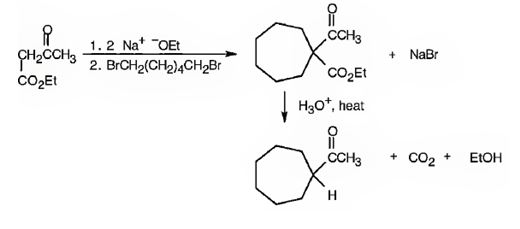
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
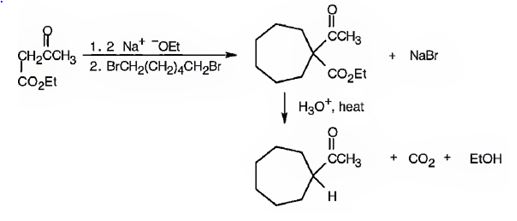
Explanation of Solution
: The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,6- dibromohexane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted acetoacetic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield methyl cycloheptyl ketone.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
c)
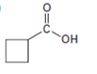
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
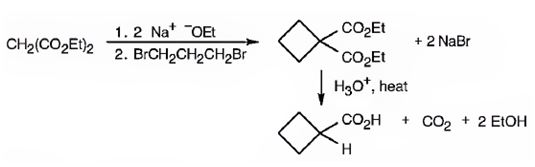
Explanation of Solution
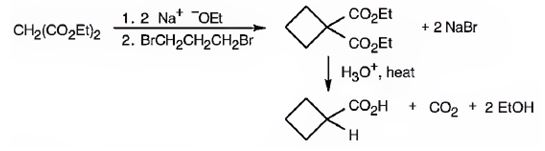
The compound shown is a carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of malonic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,3- dibromopropane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted malonic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic diester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester groups get hydrolyzed to give a dicarboxylic acid. The dicarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield cyclobutylcarboxylic acid.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
d)
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
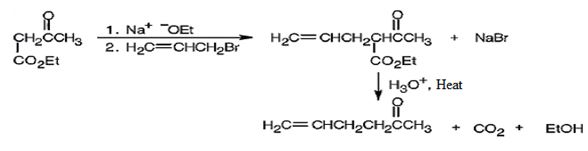
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
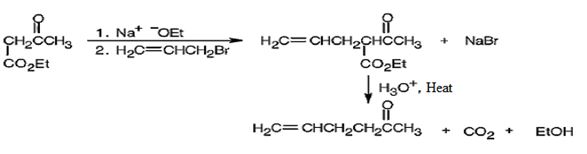
Explanation of Solution
The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on allyl bromide displaces the bromide ion to produce α- allylsubstituted acetoacetic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield hex-5-ene-2-one.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


