
a)
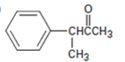
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared is to be given.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of aTo give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
b)
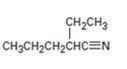
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of a ketone, ester or nitrile by a SN2 reaction of the enolate ion with an alkyl halide. Thus by looking at α- carbon of the product the alkyl halide to be used in the reaction can be identified. The enolate ion can be produced by using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
To give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
c)
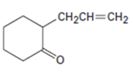
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of a ketone, ester or nitrile by aSN2reaction of the enolate ion with an alkyl halide. Thus by looking at α- carbon of the product the alkyl halide to be used in the reaction can be identified. The enolate ion can be produced by using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
To give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
d)
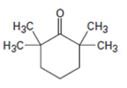
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of a ketone, ester or nitrile by a SN2 reaction of the enolate ion with an alkyl halide. Thus by looking at α- carbon of the product the alkyl halide to be used in the reaction can be identified. The enolate ion can be produced by using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
To give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
e)
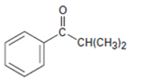
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of a ketone, ester or nitrile by a SN2 reaction of the enolate ion with an alkyl halide. Thus by looking at α- carbon of the product the alkyl halide to be used in the reaction can be identified. The enolate ion can be produced by using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
To give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
f)
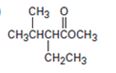
Interpretation:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how the compound shown can be prepared.
Concept introduction:
An alkylation reaction is used to introduce a methyl or a primary alkyl group in α- position of a ketone, ester or nitrile by a SN2 reaction of the enolate ion with an alkyl halide. Thus by looking at α- carbon of the product the alkyl halide to be used in the reaction can be identified. The enolate ion can be produced by using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
To give:
Using an alkylation reaction as the key step how to prepare the compound shown.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardConsider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forward
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

