
(a)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of
(a)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomer is vinyl fluoride. It is an
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is vinyl fluoride. It is an addition polymer whose structure is shown in Figure 1.
The structure of the monomer is,
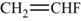
Figure 1
The polymer contains a repeating chain of vinyl fluoride, which on adding polymerization forms a polymer known as polyvinyl fluoride. Hence, the monomer is vinyl fluoride.
(b)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
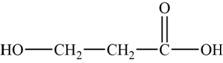
Figure 2
The polymer contains a repeating chain of
(c)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(c)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomers are
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomers are
The structures of the monomers are,
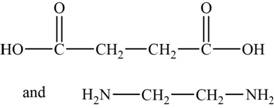
Figure 3
The polymer chain consists of the repeating units of ethane on which carboxylic group is present on carbon 1 and 2 respectively indicates that one monomer is
(d)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(d)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
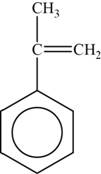
Figure 4
The repeating unit of polymer has
(e)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(e)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
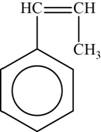
Figure 5
The repeating unit of polymer has
(f)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(f)
Answer to Problem 78E
Answer
The monomer are
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer are and
The structures of the monomers are,
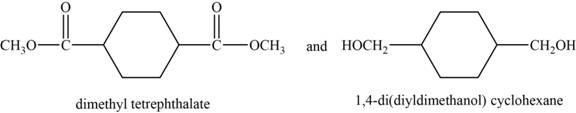
Figure 6
DMT is an organic compound. It is the diester formed from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry (Instructor's)
- Rank the labeled protons (Ha-Hd) in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic. НОН НЬ OHd Онсarrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? ? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C :0 T Add/Remove step Garrow_forwardThe following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forward
- A covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forward
- All of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





