
MCAT-Style Passage Problems
Lightbulb Failure
You’ve probably observed that the most common time for an incandescent lightbulb to fail is the moment when it is turned on. Let’s look at the properties of the bulb’s filament to see why this happens.
The current in the tungsten filament of a lightbulb heats the filament until it glows. The filament is so hot that some of the atoms on its surface fly off and end up sticking on a cooler part of the bulb. Thus the filament gets progressively thinner as the bulb ages. There will certainly be one spot on the filament that is a bit thinner than elsewhere. This thin segment will have a higher resistance than the surrounding filament. More power will be dissipated at this spot, so it won’t only be a thin spot, it also will be a hot spot.
Now, let’s look at the resistance of the filament. The graph in Figure P22.70 shows data for the current in a lightbulb as a function of the potential difference across it. The graph is not linear, so the filament is not an ohmic material with a constant resistance. However, we can define the resistance at any particular potential difference ∆V to be R = ∆V/I. This ratio, and hence the resistance, increases with ∆V and thus with temperature.
Figure P22. 70
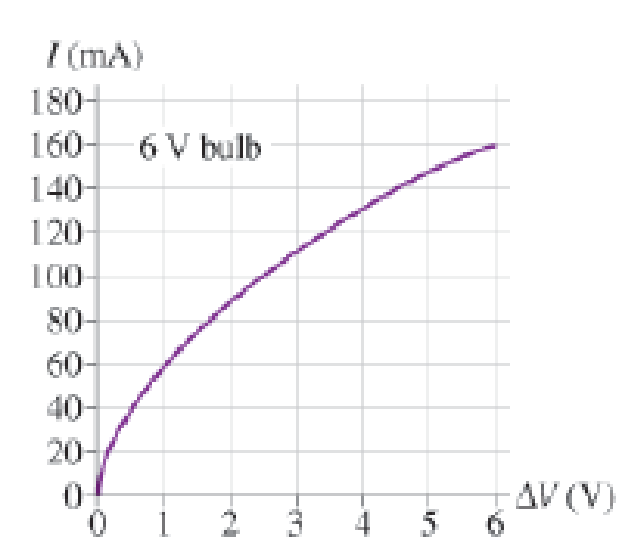
When the bulb is turned on, the filament is cold and its resistance is much lower than during normal, high-temperature operation. The low resistance causes a surge of higher-than-normal current lasting a fraction of a second until the filament heats up. Because power dissipation is I2R, the power dissipated during this first fraction of a second is much larger than the bulb’s rated power. This current surge concentrates the power dissipation at the high-resistance thin spot, perhaps melting it and breaking the filament.
There are devices to put in a light socket that control the current through a lightbulb, thereby increasing its lifetime. Which of the following strategies would increase the lifetime of a bulb without making it dimmer?
A. Reducing the average current through the bulb
B. Limiting the maximum current through the bulb
C. Increasing the average current through the bulb
D. Limiting the minimum current through the bulb
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





