
Concept explainers
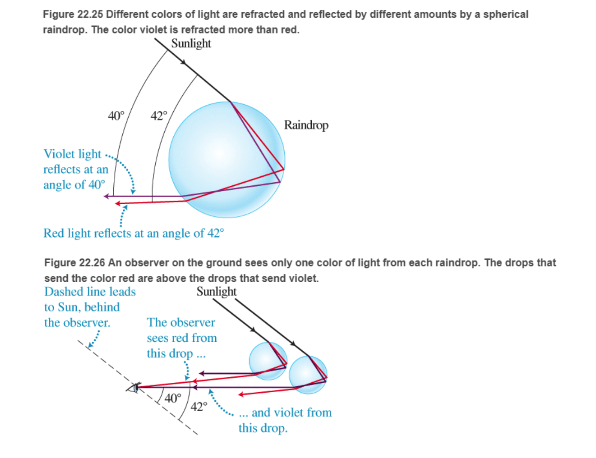
Rainbows How is a rainbow formed? Recall that the index of refraction of a medium is slightly different for different colors. When white light from the Sun enters a spherical raindrop, as shown in Figure 22.25, the light is refracted, or bent. After reflecting off the back surface of the drop, the light is refracted again as it leaves the front surface.

Each drop separates the colors of light. An observer on the ground with her back to the Sun sees at most one color of light coming from a particular drop (see Figure 22.26). If the observer sees rod light from a drop (for example, the top drop in Figure 22.26), the violet light for that same drop is deflected above her head. However, if she sees violet light coming from a drop lower in the sky, the red light from that drop is deflected below her eyes onto the ground. She sees red light when her line of view makes an angle of
Why is violet light refracted more than red light?
a. The violet light travels a shorter distance in the drop than the red light.
b. The red light travels more slowly than the violet light.
c. The refractive index of water for violet light is greater than that for red light.
d. All of the above.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Pearson eText for College Physics: Explore and Apply -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Lab Assignment #3 Vectors 2. Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in cables A and B. 30° 30° 300KN 3. Determine the forces in members A and B of the following structure. 30° B 200kN Name: TA: 4. Determine the resultant of the three coplanar forces using vectors. F₁ =500N, F₂-800N, F, 900N, 0,-30°, 62-50° 30° 50° F₁ = 500N = 900N F₂ = 800Narrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors Name: TA: 1. With the equipment provided in the lab, determine the magnitude of vector A so the system is in static equilibrium. Perform the experiment as per the figure below and compare the calculated values with the numbers from the spring scale that corresponds to vector A. A Case 1: Vector B 40g Vector C 20g 0 = 30° Vector A = ? Case 2: Vector B 50g Vector C = 40g 0 = 53° Vector A ? Case 3: Vector B 50g Vector C 30g 0 = 37° Vector A = ?arrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 20.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between q1 and q2 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (A). Let q1=-1.30 µC, q2=-4.20µC, and q3= +4.30 µC. __________________ N/Carrow_forward
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forwardI do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forwardRank the six combinations of electric charges on the basis of the electric force acting on 91. Define forces pointing to the right as positive and forces pointing to the left as negative. Rank in increasing order by placing the most negative on the left and the most positive on the right. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) [most negative 91 = +1nC 92 = +1nC 91 = -1nC 93 = +1nC 92- +1nC 93 = +1nC -1nC 92- -1nC 93- -1nC 91= +1nC 92 = +1nC 93=-1nC 91 +1nC 92=-1nC 93=-1nC 91 = +1nC 2 = −1nC 93 = +1nC The correct ranking cannot be determined. Reset Help most positivearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





