
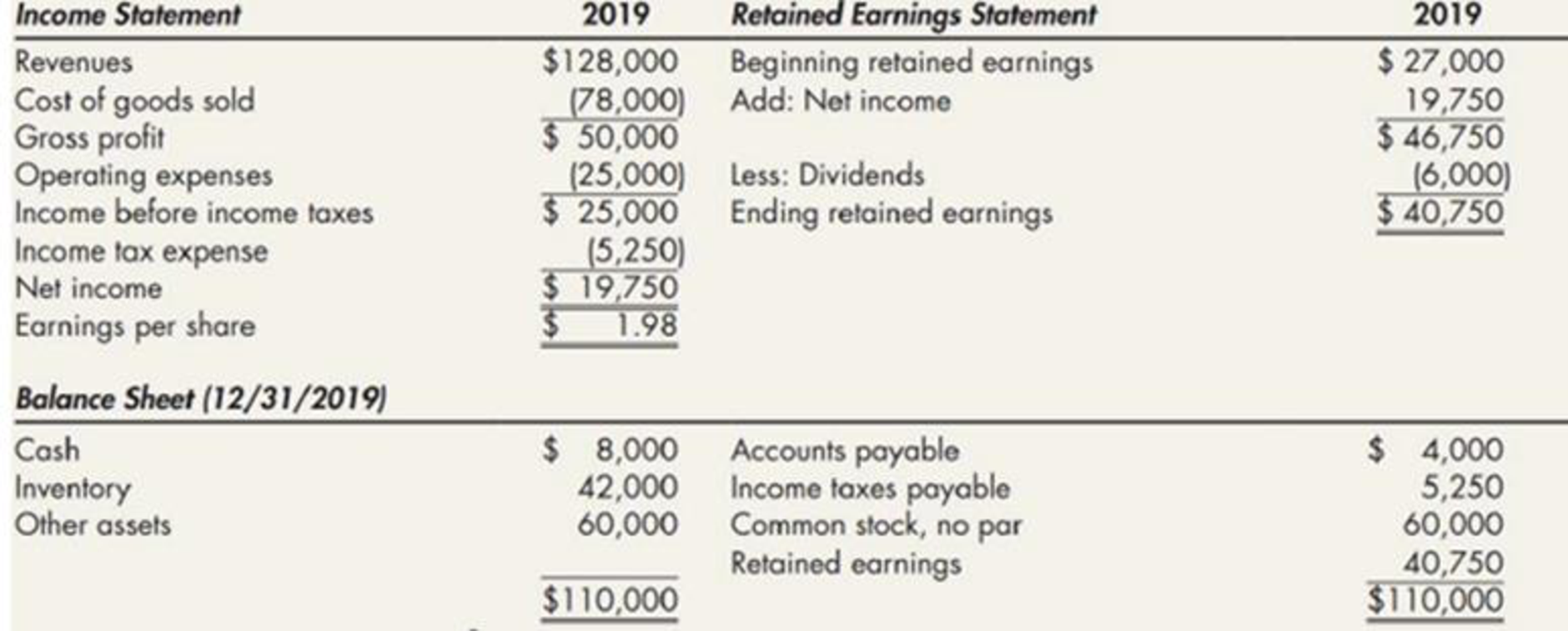
Schmidt Company began operations on January 1, 2018, and used the LIFO inventory method for both financial reporting and income taxes. However, at the beginning of 2020, Schmidt decided to switch to the average cost inventory method for financial and income tax reporting. It had previously reported the following financial statement information for 2019:
An analysis of the accounting records discloses the following cost of goods sold under the LIFO and average cost inventory methods:
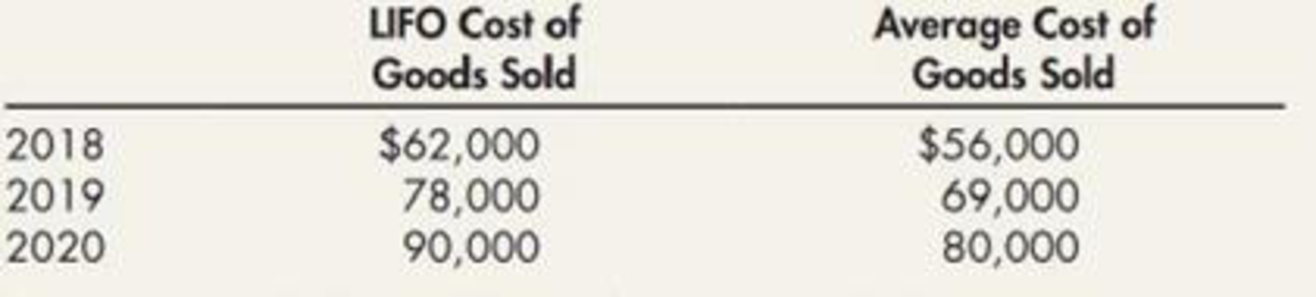
There are no indirect effects of the change in inventory method. Revenues for 2020 total $130,000; operating expenses for 2020 total $30,000. Schmidt is subject to a 21% income tax rate in all years; it pays all income taxes payable in the next quarter. Assume that any
Required:
- 1. Prepare the
journal entry to reflect the change in method at the beginning of 2020. Show supporting calculations. - 2. Prepare the 2020 financial statements. Notes to the financial statements are not necessary. Show supporting calculations.
1.
Journalize the cumulative effect of the retrospective adjustment on Company S’s prior year income that would be reported in 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the cumulative effect of the retrospective adjustment on Company S’s prior year income that would be reported in 2020.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Inventory | 15,000 | |||||
| Deferred Tax Liability | 3,150 | |||||
| Retained Earnings | 11,850 | |||||
| (Record the cumulative effect of pretax income due to change from LIFO to average cost) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Inventory is an asset account. Since the cumulative difference has increased due to change from LIFO to average cost, inventory has increased, the asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Deferred Tax Liability is a liability account. The obligation to pay taxes has increased on saved income taxes, due to increase in cumulative difference. The liability increased and an increase in liability is credited.
- Retained Earnings is an equity account. Since earnings increased due to increase in pretax income due to increase in cumulative difference out of the change from LIFO to average cost, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the deferred tax liability amount.
Compute retained earnings amount.
2.
Prepare comparative financial statements for Company S for the year 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations, and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare comparative income statements of Company S for the year 2020.
| Company S | ||
| Comparative Income Statements | ||
| For the Years Ended December 31 | ||
| 2020 |
2019 (As Adjusted) | |
| Revenues | $130,000 | $128,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | (80,000) | (69,000) |
| Gross profit | 50,000 | 59,000 |
| Operating expenses | (30,000) | (25,000) |
| Income before income taxes | 20,000 | 14,000 |
| Income tax expense | (4,200) | (7,140) |
| Net income | $15,800 | $26,860 |
| Earnings per share: | ||
| Net income | $1.58 | $2.69 |
Table (2)
Working Notes:
Compute the income tax expense for 2020.
Compute the income tax expense for 2019.
Compute the earnings per share (EPS) for 2020.
Compute the earnings per share (EPS) for 2019.
Statement of retained earnings: This statement reports the beginning retained earnings and all the changes which led to ending retained earnings. Net income from income statement is added to and dividends is deducted from beginning retained earnings to arrive at the end result, ending retained earnings.
Prepare comparative statements of retained earnings of Company S for the year 2020.
| Company S | ||
| Comparative Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the Years Ended December 31 | ||
| 2020 | 2019 | |
| Beginning unadjusted retained earnings | $40,750 | $27,000 |
| Plus: Adjustment for the cumulative effect on prior years of retrospectively applying the average cost inventory method (net of taxes) | 11,850 | 4,740 |
| Adjusted beginning retained earnings | 52,600 | 31,740 |
| Add: Net income | 15,800 | 26,860 |
| 68,400 | 58,600 | |
| Less: Dividends | (10,000) | (6,000) |
| Ending retained earnings | $58,400 | $52,600 |
Table (3)
Working Notes:
Compute the adjustment value for 2020.
Compute the adjustment value for 2019.
Prepare comparative balance sheets of Company S for the year 2020.
| Company S | ||
| Comparative Balance Sheets | ||
| December 31 | ||
| 2020 |
2019 (As Adjusted) | |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $15,600 | $8,000 |
| Inventory | 34,000 | 57,000 |
| Other assets | 76,000 | 60,000 |
| Total assets | $125,600 | $125,000 |
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | ||
| Accounts payable | $3,000 | $4,000 |
| Income taxes payable | 4,200 | 5,250 |
| Deferred tax liability | 0 | 3,150 |
| Common stock, no par | 60,000 | 60,000 |
| Retained earnings | 58,400 | 52,600 |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $125,600 | $125,000 |
Table (4)
Working Notes:
Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of income tax expense, which is the income taxes payable in 2020, and Table (1) for value and computation of deferred tax liability in 2019.
Compute adjusted inventory value for 2019.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Poonam's material quantity variance is favorable or unfavorablearrow_forward??arrow_forwardPoonam has a standard of 1.5 pounds of materials per unit, at S6 per pound. In producing 2,000 units, Poonam used 3,100 pounds of materials at a total cost of $18,135. Poonam's material quantity variance is favorable or unfavorable?arrow_forward
- General Accountingarrow_forwardSubject: General Accountingarrow_forwardThe following information describes a company's usage of direct labor in a recent period: Actual direct labor hours used 32,500 Actual rate per hour $18.00 Standard rate per hour $16.50 Standard hours for units produced 32,000 How much is the direct labor efficiency variance? Answer: $8,250 unfavorablearrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning


