
Concept explainers
Preparing an operating budget—sales, production, direct materials, direct labor,
The Irwin Batting Company manufactures wood baseball bats Irwin’s two primary products are a youth bat, designed for children and young teens, and an adult bat, designed for high school and college-aged players. Irwin sells the bats to sporting goods stores, and all sales are on account. The youth bat sells for $35; the adult bat sells for $50. Irwin’s highest sales volume is in the first three months of the year as retailers prepare for the spring baseball season. Irwin’s
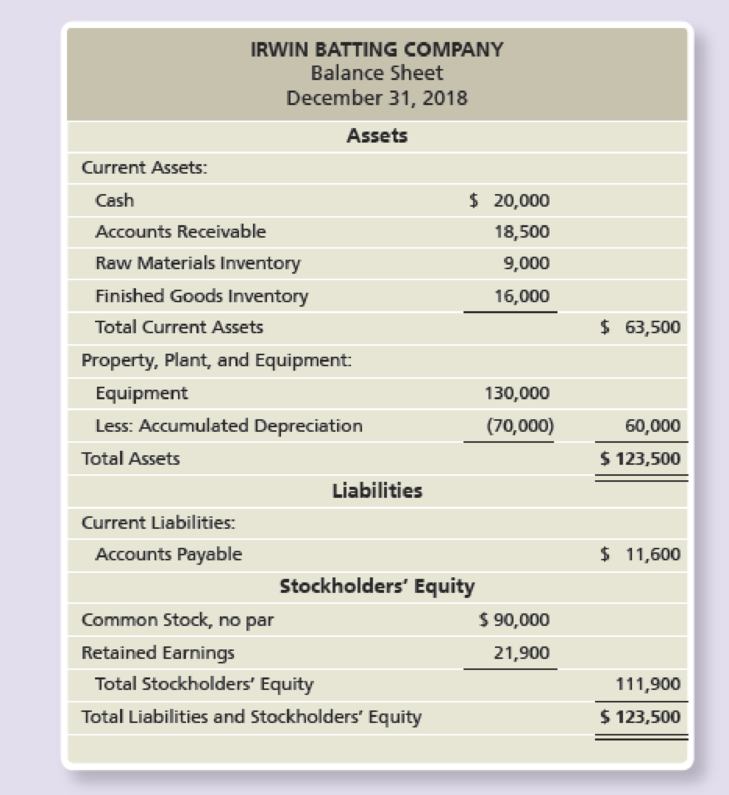
Other data for Irwin Batting Company for the first quarter of 2019:
- a. Budgeted sales are 1,400 youth bats and 3,300 adult bats.
- b. Finished Goods Inventory on December 31, 2018, consists of 700 youth bats at $15 each and 550 adult bats at $10 each.
- c. Desired ending Finished Goods Inventory is 220 youth bats and 300 adult bats; FIFO inventory costing method is used.
- d. Direct materials requirements are 40 ounces of wood for youth bats and 70 ounces of wood for adult bats. The cost of wood is $0.10 per ounce.
- e. Raw Materials Inventory on December 31, 2018, consists of 90,000 ounces of wood at $0.10 per ounce.
- f. Desired ending Raw Materials Inventory is 90,000 ounces (indirect materials are insignificant and not considered for budgeting purposes).
- g. Each bat requires 0.4 hours of direct labor; direct labor costs average $26 per hour.
- h. Variable manufacturing overhead is $0.30 per bat.
- i. Fixed manufacturing overhead includes $1,300 per quarter in
depreciation and $14,977 per quarter for other costs, such as insurance and property taxes. - j. Fixed selling and administrative expenses include $13,000 per quarter for salaries; $3,500 per quarter for rent; $1,400 per quarter for insurance; and $450 per quarter for depreciation.
- k. Variable selling and administrative expenses include supplies at 1% of sales.
Requirements
- 1. Prepare Irwin’s sales budget for the first quarter of 2019.
- 2. Prepare Irwin’s production budget for the first quarter of 2019.
- 3. Prepare Irwin’s direct materials, direct labor budget, and manufacturing overhead budget for the first quarter of 2019. Round the predetermined overhead allocation rate to two decimal places. The overhead allocation base is direct labor hours.
- 4. Prepare Irwin’s cost of goods sold budget for the first quarter of 2019.
- 5. Prepare Irwin’s selling and administrative expense budget for the first quarter of 2019.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Managerial Chapters (6th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Foundations of Financial Management
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
- The Fantastic Ice Cream Shoppe sold 9,000 servings of ice cream during June for $4 per serving. The shop purchases the ice cream in large tubs from the Dream Ice Cream Company. Each tub costs the shop $9 and has enough ice cream to fill 20 ice cream cones. The shop purchases the ice cream cones for $0.10 each from a local warehouse club. Located in an outdoor mall, the rent for the shop space is $2,050 per month. The shop expenses $290 a month for the depreciation of the shop's furniture and equipment. During June, the shop incurred an additional $2,700 of other operating expenses (75% of these were fixed costs).arrow_forwardHello tutor please provide correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardRobinson Manufacturing discovered the following information in its accounting records: $519,800 in direct materials used, $223,500 in direct labor, and $775,115 in manufacturing overhead. The Work in Process Inventory account had an opening balance of $72,400 and a closing balance of $87,600. Calculate the company’s Cost of Goods Manufactured.arrow_forward
- Sanjay would like to organize HOS (a business entity) as either an S corporation or as a corporation (taxed as a C corporation) generating a 16 percent annual before-tax return on a $350,000 investment. Sanjay’s marginal tax rate is 24 percent and the corporate tax rate is 21 percent. Sanjay’s marginal tax rate on individual capital gains and dividends is 15 percent. HOS will pay out its after-tax earnings every year to either its members or its shareholders. If HOS is taxed as an S corporation, the business income allocation would qualify for the deduction for qualified business income (assume no limitations on the deduction). Assume Sanjay does not owe any additional Medicare tax or net investment income tax. Required 1. For each scenario, C corporation and S corporation, calculate the total tax (entity level and owner level). 2. For each scenario, C corporation and S corporation, calculate the effective tax rate. C Corporation S Corporation 1. Total tax…arrow_forwardI need correct solution of this general accounting questionarrow_forwardHii expert please given correct answer general accountingarrow_forward
- Markowis Corp has collected the following data concerning its maintenance costs for the pest 6 months units produced Total cost July 18,015 36,036 august 37,032 40,048 September 36,036 55,055 October 22,022 38,038 November 40,040 74,575 December 38,038 62,062 Compute the variable coot per unit using the high-low method. (Round variable cost per mile to 2 decimal places e.g. 1.25) Compute the fixed cost elements using the high-low method.arrow_forwardUse the following data to determine the total dollar amount of assets to be classified as current assets. Marigold Corp. Balance Sheet December 31, 2025 Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable Inventory $67000 Accounts payable $126000 86500 Salaries and wages payable 11100 149000 Bonds payable 161500 Prepaid insurance 83000 Total liabilities 298600 Stock investments (long-term) 193000 Land 199500 Buildings $226000 Common stock 309400 Less: Accumulated depreciation (53500) 172500 Retained earnings 475500 Trademarks 133000 Total stockholders' equity 784900 Total assets $1083500 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $1083500 ○ $269100 $385500 ○ $236500 ○ $578500arrow_forwardShould the machine be replaced?arrow_forward
- Using the following balance sheet and income statement data, what is the total amount of working capital? Current assets $39700 Net income $52100 Current liabilities 19800 Stockholders' equity 96700 Average assets 198400 Total liabilities 52100 Total assets 148800 Average common shares outstanding was 18600. ○ $9900 ○ $39700 ○ $19900 ○ $12400arrow_forwardSuppose that Old Navy has assets of $4265000, common stock of $1018000, and retained earnings of $659000. What are the creditors' claims on their assets? ○ $2588000 ○ $3906000 ○ $1677000 ○ $4624000arrow_forwardBrody Corp. uses a process costing system. Beginning inventory for January consisted of 1,400 units that were 46% completed. 10,300 units were started during January. On January 31, the inventory consisted of 550 units that were 77% completed. How many units were completed during the period?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

