
Each type of cost for all three jobs.
Answer to Problem 41A
Job 1:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Job 2:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Job 3:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manufacturing cost consists of labor costs, material cost and overhead cost. Total manufacturing cost for job
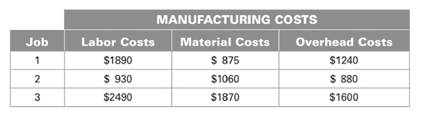
Calculation:
Components of manufacturing cost is given as below.
| Job | Labor Cost | Material cost | Overhead cost | Total cost |
Now we need to find the individual cost percentage for each job. Total cost will be base and individual costs will be percentage.
As we know the proportion to find percentage is given as
Job 1:
Labor cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the labor cost percentage is
Similarly,
Material cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the material cost percentage is
Again,
Overhead cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the Overhead cost percentage is
Job 2:
Labor cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the labor cost percentage is
Similarly,
Material cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the material cost percentage is
Again,
Overhead cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the Overhead cost percentage is
Job 3:
Labor cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the labor cost percentage is
Similarly,
Material cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the material cost percentage is
Again, Overhead cost
Putting these value in standard proportion,
Hence, the overhead cost percentage is
Thus,
Job 1:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Job 2:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Job 3:
Labor cost percentage is
Material cost percentage is
Overhead cost percentage is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Mathematics for Machine Technology
- [) Hwk 29 SUBMIT ANSWEK Hwk 30 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X - Mind Tap Cengage Learning ☑ MA244-03_Syllabus_Spring, 20 × b Answered: [) 90% Hwk 29 Hwk X Rotation of Axes Example - Elimi X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=36606609 B שי 90% 2. [-/3 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.4.003. Use the age transition matrix L and age distribution vector X1 to find the age distribution vectors X2 and x3. 0 34 x2 = X3 = L = ↓ ↑ 1 0 0 x1 = 1 0 0 2 20 20 20 Then find a stable age distribution vector. x = t ↓ 1 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER 3. [-/3 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.4.004. Use the age transition matrix L and age distribution vector X1 to find the age distribution vectors x2 and ×3. ill { ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHERarrow_forward[) Hwk 29 SUBMIT ANSWER Hwk 29 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X - Mind Tap Cengage Learning ☑ MA244-03_Syllabus_Spring, 20 × b Answered: ( Homework#8 | ba X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36606608&tags=autosave#question3706218_2 2. [-/2.85 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.3.003. Prove that the symmetric matrix is diagonalizable. (Assume that a is real.) 0 0 a A = a 0 a 0 0 Find the eigenvalues of A. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. Do not list the same eigenvalue multiple times.) λ= Find an invertible matrix P such that P-1AP is diagonal. P = Which of the following statements is true? (Select all that apply.) ☐ A is diagonalizable because it is a square matrix. A is diagonalizable because it has a determinant of 0. A is diagonalizable because it is an anti-diagonal matrix. A is diagonalizable because it has 3 distinct eigenvalues. A is diagonalizable because it has a nonzero determinant. A is diagonalizable because it is a symmetric…arrow_forwardUse the method of undetermined coefficients to solve the given nonhomogeneous system. x-()*+(5) = 1 3 3 1 X+ t +3 -1 -2t 1 x(t) = º1 1 e +021 e +arrow_forward
- Find the general solution of the given system. 6 -(-1)x x' = -6 11 x(t) = x(t) = e5t)*[(c1 + c2(t− 1/6))(c1 + c2t)] Your answer cannoarrow_forward(c) Describe the distribution plan and show the total distribution cost. Optimal Solution Amount Cost $ 2000 Southern-Hamilton 200 Southern-Butler $ Southern-Clermont 300 4500 Northwest-Hamilton 200 $2400 Northwest-Butler 200 $3000 Northwest-Clermont $ Total Cost ક (d) Recent residential and industrial growth in Butler County has the potential for increasing demand by 100 units. (i) Create an updated distribution plan assuming Southern Gas becomes the preferred supplier. Distribution Plan with Southern Gas Amount Southern-Hamilton $ Cost × Southern-Butler x $ Southern-Clermont 300 $ 4500 Northwest-Hamilton 64 x Northwest-Butler $ × Northwest-Clermont 0 $0 Total Cost $ (ii) Create an updated distribution plan assuming Northwest Gas becomes the preferred supplier. Distribution Plan with Northwest Gas Southern-Hamilton Southern-Butler 0 Southern-Clermont Northwest-Hamilton Northwest-Butler Northwest-Clermont Total Cost Amount × x x +7 $0 Cost × $ × $ × +4 $ -/+ $ × ×arrow_forwardThe distribution system for the Herman Company consists of three plants, two warehouses, and four customers. Plant capacities and shipping costs per unit (in $) from each plant to each warehouse are as follows. Warehouse Plant Capacity 1 2 1 4 7 450 2 8 5 600 3 5 6 380 Customer demand and shipping costs per unit (in $) from each warehouse to each customer are as follows. Customer Warehouse 1 2 3 1 6 4 8 2 3 6 7 7 Demand 300 300 300 400 (a) Develop a network representation of this problem. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. (b) Formulate a linear programming model of the problem. (Let Plant 1 be node 1, Plant 2 be node 2, Plant 3 be node 3, Warehouse 1 be node 4, Warehouse 2 be node 5, Customer 1 be node 6, Customer 2 be node 7, Customer 3 be node 8, and Customer 4 be node 9. Express your answers in the form x;;, where x,; represents the number of units shipped from node i to node j.) Min 4x14+8x24+5x34+7x15 +5x25…arrow_forward
- A linear programming computer package is needed. Hanson Inn is a 96-room hotel located near the airport and convention center in Louisville, Kentucky. When a convention or a special event is in town, Hanson increases its normal room rates and takes reservations based on a revenue management system. A large profesional organization has scheduled its annual convention in Louisville for the first weekend in June. Hanson Inn agreed to make at least 50% of its rooms available for convention attendees at a special convention rate in order to be listed as a recommended hotel for the convention. Although the majority of attendees at the annual meeting typically request a Friday and Saturday two-night package, some attendees may select a Friday night only or a Saturday night only reservation. Customers not attending the convention may also request a Friday and Saturday two-night package, or make a Friday night only or Saturday night only reservation. Thus, six types of reservations are…arrow_forward25.2. Find the Laurent series for the function 1/[z(z-1)] in the follow- ing domains: (a). 0<|z|< 1, (b). 1<|z, (c). 0arrow_forward25.5. Find the Laurent series for the function 1/[(z - 1)(-2)(z - 3)] in the following domains: (a). 0 3. شهریarrow_forward25.1. Expand each of the following functions f(z) in a Laurent series on the indicated domain: (a). z² - 2z+5 (2-2)(z² + 1)' (c). Log za 2 b (z - موجود 11, 29, where b>a> 1 are real, |z| > b.arrow_forward25.3. Find the Laurent series for the function z/[(22 + 1)(z² + 4)] in the following domains (a). 02.arrow_forward25.2. Find the Laurent series for the function 1/[z(z-1)] in the follow- ing domains: (a). 0<|z|< 1, (b). 1 <|z|, (c). 0<|z1|< 1, (d). 1< |z1|, (e). 1<|z2|<2.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





