
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The distinguishing tests for the pair of given compounds are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
舧 Chair conformations: It is the most stable conformation, which accurately shows the spatial arrangement of atoms.
舧 Equatorial bonds are parallel to the average plane of the ring, while axial bonds are perpendicular to the average plane of the ring.
舧 The conformation having bonds at the equatorial positions are more stable than those with bonds at the axial position.
舧 On flipping the cyclohexane ring, axial bonds become equatorial bonds and equatorial bonds becomes axial bond.
舧 Bulkier group acquires equatorial positions to form stable conformer due to steric factors.
舧 The most stable configuration of aldopyranoses is when the
舧 Stereochemistry: The equatorial orientation refers to the spatial arrangement of
舧 The anomeric effect is lowest for sugars with equatorial orientation, which results in lower energetic state, and consequently this type of orientation confers higher stability.
舧 The anomeric effect is highest for sugars with axial orientation, which results in higher energetic state, and consequently this type of orientation confers lower stability.
舧 A carbohydrate is a
舧
舧 Carbohydrates are oxidized by
舧 Aldaric acids are carbohydrates having two carboxylic acids. They are formed due to oxidation reaction of aldoses with dilute
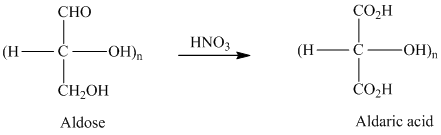
舧 Monosaccharides containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group are called aldohexoses.
舧 Alditols are compounds produced from aldoses or ketoses on reduction with certain reagents such as sodium borohydride (
舧 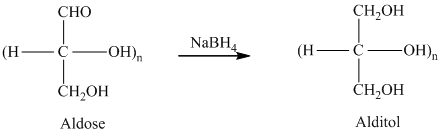
舧 Compounds formed by the reaction of reducing sugars with excess of phenyl hydrazine are called osazones. Osazones are products of oxidation and are produced by all reducing sugars.
舧 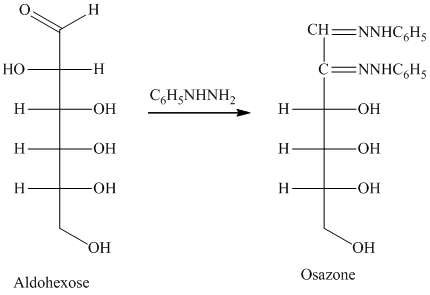
舧 Fischer projection is a way of representing the structural formulae of compounds through cross formulation of their open chain structures.
舧. Bromine water is an effective reagent that selectively oxidizes the
舧 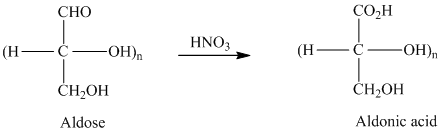
Tollen’s (
舧 Compounds that have plane of symmetry tend to form meso compounds. A meso form arises when the two stereoisomers produce superimposable (achiral) images, and hence, compounds having meso are optically inactive. Chiral (or non-superimposable) molecules are optically active.
舧
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL) W/WILEYPLUS NEXT
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning




