
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
10th Edition
ISBN: 2818440034374
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.31P
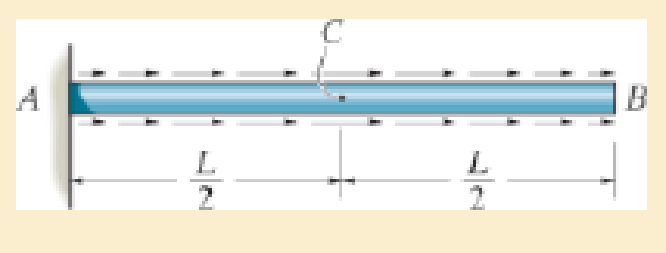
The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in the shaft that can be expressed as εx = ksin (
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2. Figure 2 shows a device for lifting bricks and concrete blocks. It comprises two compo-
nents ABC and BD, with a frictionless pin at B. Determine the minimum coefficient of friction
required at A and D if the device is to work satisfactorily.
W
all dimensions in inches
Figure 2
D
1. The shaft AD in Figure 1 supports two pulleys at B and C of radius 200 mm and 250 mm
respectively. The shaft is supported in frictionless bearings at A and D and is rotating clockwise
(when viewed from the right) at a constant speed of 300 rpm. Only bearing A can support thrust.
The tensions T₁ = 200 N, T₂ = 400 N, and T3 = 300 N. The distances AB = 120 mm, BC = 150
mm, and CD120 mm. Find the tension 74 and the reaction forces at the bearings.
A
T
fo
Figure 1
5. Figure 5 shows a two-dimensional idealization of the front suspension system for a car.
During cornering, the road exerts a vertical force of 5 kN and a leftward horizontal force of 1.2
kN on the tire, which is of 510 mm diameter. Draw free-body diagrams of each component and
determine the forces transmitted between them.
250
A
-320
B
170
D
170
-220-220-
all dimensions in mm.
Figure 5
Chapter 2 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8. The force F in Figure 8 is 120 lb and the angle 0 = 25°. Find the axial force N, the shear force V and the bending moment M at the point K which is midway between B and C and illustrate their directions on a sketch of the segment KCD. E -0 B K అ D H 7 A- all dimensions in inches Figure 8 Ꮎ G Farrow_forward6. Determine the coordinates x, y of the centroid of the area shaded in Figure 6. y y=x³ Figure 6 3arrow_forward3. Use the method of sections to determine the forces in the members BD, CD, CE in the struc- ture of Figure 3. A B D 4 kN 6 kN all dimensions in meters. Figure 3arrow_forward
- A pipeline engineer is considering alternative natural gas pipeline routings. The first route is mostly over land and the second is primarily undersea. Both pipelines will need some valve and fitting replacements in year 25. Cost data for each route is shown in Table P2.21. Notice that the undersea route has a higher initial cost due to higher installation costs and extra corrosion protection for the pipeline. However, the undersea route has cheaper security and maintenance costs which substantially reduces annual costs. The MARR for the project is 15%. Determine which route should be pursued based on a present worth analysis.arrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T₂ = -14.00 kpsi. What is the maximum shear stress for this case? The maximum shear stress is kpsi. = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi,arrow_forwardThe initial cost of a proposed heat recovery system is $375,000. The annual operation andmaintenance costs are projected to be $12,000. The salvage value of the system at the end of itsuseful life (projected to be 30 years) is $60,000. The annual savings in fuel costs resulting fromthis system are estimated to be $55,000 per year.a. Assuming annual compounding, determine the rate of return for this heat recovery system.b. If management has set the MARR to be 15% for a heat recovery system like this, what is themaximum initial cost that can be spent on the system (assuming that all other costs and incomesare the same)?arrow_forward
- The initial cost of a machine for a production facility is $225,000. The machine is expected tolast for 10 years with no salvage value. The company’s tax rate is 49% and SLD is used todepreciate the machine. For this type of depreciation, the tax life of the machine is considered 8years and its salvage value is $5,000. The after-tax rate of return is 14.3%. Determine the uniformannual before-tax cash flow.arrow_forwardThree alternatives are being considered for an air cleaning system. All three systems have a lifeof 10 years with no salvage value. System A has an initial cost of $29,000. During the first fiveyears of operation, the annual costs to operate system A are $5,000. During the second five years,the annual cost of system A increases to $16,000. System B has an initial cost of $43,000. Theannual cost to operate system B is $4,000, however, after the first year, this cost increases by$1,600 per year. System C has an initial cost of $58,000 with an annual cost of $2,400. System Crequires two upgrades: one during year 4 which costs $6,000, and the other during year 8 whichcosts $3,000. The MARR for this project is 17%. Determine which air cleaning system should beinstalled based on an economic analysis.arrow_forwardShow all work as much as you can and box out answersarrow_forward
- Show as much work as possible and box out answers pleasearrow_forwardon-the-job conditions. 9 ±0.2- 0.5 M Application questions 1-7 refer to the drawing above. 1. What does the flatness tolerance labeled "G" apply to? Surface F A. B. Surfaces E and F C. Surfaces D, E, H, and I D. The derived median plane of 12 +0.2 0.5 0.5 CF) 20 ±0.2 0.1 7. O 12 ±0.2- H 0.3 ASME Y14.5-2009arrow_forwardelements, each with a length of 1 m. Determine the temperature on node 1, 2, 3, 4. 3. Solve the strong form analytically (you may choose Maple, MATLAB or Mathematica to help you solve this ODE). Compare the FE approximate temperature distribution through the block against the analytical solution. 1 (1) 200 °C 2 (2) 3 m 3 (3)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY