
Equity as an Option and
a. What is the value of the firm’s equity and debt if Project A is undertaken? If Project B is undertaken?
b. Which project would the stockholders prefer? Can you reconcile your answer with the NPV rule?
c. Suppose the stockholders and bondholders are, in fact, the same group of investors. Would this affect your answer to (b)?
d. What does this problem suggest to you about stockholder incentives?
a.
To compute: Value of the firm’s equity and debt under project A and project B.
Option Pricing:
Option pricing helps in determining correct or fair price in the market. It is the value of one share on the basis of which option is traded. Black-Scholes is one of the pricing methods. Further, equity is also used as an option.
Explanation of Solution
Project A
Given,
Stock price is
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $22,900 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Substitute $22,900 as value of firm and $9,019.78 as value of equity.
Project B
Given,
Stock price is $21,700.
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
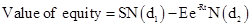
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $21,700 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Substitute $21,700 as value of firm and $4,285.82 as value of equity.
Working Note:
Formula to calculate
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Formula to calculate
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Hence, for Project A the value of firm’s equity is $9,019.78, value of firm’s debt is$13,880.22 and for Project B the value of firm’s equity is $4,285.82 and value of firm’s debt is $17,414.18.
b.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders.
Answer to Problem 22QP
- Here, equity’s value is higher in Project A than Project B.
- Project A does not create more bondholders.
Explanation of Solution
- If Project A is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,200.
- If Project B is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- NPV rules say Project B should be accepted, but value of equity is more in the case of Project A rather than Project B, which shows that Project A has less of bondholders.
- Thus, Project A is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project A.
c.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders if both stockholders and bondholders are same.
Answer to Problem 22QP
As Project B adds more value to the firm, this would be a good option.
Explanation of Solution
- If stockholders and bondholder would be the same, in that case their interest would also be the same and they can get benefits equally.
- Since Project A increases the firm’s assets to$1,200 and Project B increases the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- Thus, Project B is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project B.
d.
To explain: The effect on stockholders incentives.
Answer to Problem 22QP
In case of leveraged firm, stockholders would definitely prefer those projects, which would increase value of equity.
Explanation of Solution
- Reason for opting equity source is that in the case of debt source, risk is borne by the bondholders and benefits are limited to their debt value, which is not happening in the case of equity sources.
- All benefits after paying the debt, goes to the stockholders pocket.
- Thus, the stockholders incentive would relate to the project that adds more value to the equity.
Hence, stockholder’s incentives are more related with the project that contains equity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- Scenario three: If a portfolio has a positive investment in every asset, can the expected return on a portfolio be greater than that of every asset in the portfolio? Can it be less than that of every asset in the portfolio? If you answer yes to one of both of these questions, explain and give an example for your answer(s). Please Provide a Referencearrow_forwardHello expert Give the answer please general accountingarrow_forwardScenario 2: The homepage for Coca-Cola Company can be found at coca-cola.com Links to an external site.. Locate the most recent annual report, which contains a balance sheet for the company. What is the book value of equity for Coca-Cola? The market value of a company is (# of shares of stock outstanding multiplied by the price per share). This information can be found at www.finance.yahoo.com Links to an external site., using the ticker symbol for Coca-Cola (KO). What is the market value of equity? Which number is more relevant to shareholders – the book value of equity or the market value of equity?arrow_forward
- FILE HOME INSERT Calibri Paste Clipboard BIU Font A1 1 2 34 сл 5 6 Calculating interest rates - Excel PAGE LAYOUT FORMULAS DATA 11 Α΄ Α΄ % × fx A B C 4 17 REVIEW VIEW Alignment Number Conditional Format as Cell Cells Formatting Table Styles▾ Styles D E F G H Solve for the unknown interest rate in each of the following: Complete the following analysis. Do not hard code values in your calculations. All answers should be positive. 7 8 Present value Years Interest rate 9 10 11 SA SASA A $ 181 4 $ 335 18 $ 48,000 19 $ 40,353 25 12 13 14 15 16 $ SA SA SA A $ Future value 297 1,080 $ 185,382 $ 531,618arrow_forwardB B Canning Machine 2 Monster Beverage is considering purchasing a new canning machine. This machine costs $3,500,000 up front. Required return = 12.0% Year Cash Flow 0 $-3,500,000 1 $1,000,000 2 $1,200,000 3 $1,300,000 4 $900,000 What is the value of Year 3 cash flow discounted to the present? 5 $1,000,000 Enter a response then click Submit below $ 0 Submitarrow_forwardFinances Income Statement Balance Sheet Finances Income Statement Balance Sheet Materia Income Statement Balance Sheet FY23 FY24 FY23 FY24 FY23 FY24 Sales Cost of Goods Sold 11,306,000,000 5,088,000,000 13,206,000,000 Current Current Assets 5,943,000,000 Other Expenses 4,523,000,000 5,283,000,000 Cash 211,000,000 328,600,000 Liabilities Accounts Payable 621,000,000 532,000,000 Depreciation 905,000,000 1,058,000,000 Accounts 502,000,000 619,600,000 Notes Payable 376,000,000 440,000,000 Earnings Before Int. & Tax 790,000,000 922,000,000 Receivable Interest Expense 453,000,000 530,000,000 Total Current Inventory 41,000,000 99,800,000 997,000,000 972,000,000 Taxable Income 337,000,000 392,000,000 Liabilities Taxes (25%) 84,250,000 98,000,000 Total Current 754,000,000 1,048,000,000 Long-Term Debt 16,529,000,000 17,383,500,000 Net Income Dividends 252,750,000 294,000,000 Assets 0 0 Fixed Assets Add. to Retained Earnings 252,750,000 294,000,000 Net Plant & 20,038,000,000 21,722,000,000…arrow_forward
- Do you know what are Keith Gill's previous projects?arrow_forwardExplain why long-term bonds are subject to greater interest rate risk than short-term bonds with references or practical examples.arrow_forwardWhat does it mean when a bond is referred to as a convertible bond? Would a convertible bond be more or less attractive to a bond holder than a non-convertible bond? Explain in detail with examples or academic references.arrow_forward
- Alfa international paid $2.00 annual dividend on common stock and promises that the dividend will grow by 4% per year, if the stock’s market price for today is $20, what is required rate of return?arrow_forwardgive answer general accounting.arrow_forwardGive me answers in general financearrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





