
As we saw in Section 21.2, the reduction of iron oxides is accomplished by using carbon monoxide as a reducing agent. Starting with coke in a blast furnace, the following equilibrium plays a key role in the extraction of iron:
Use the data in Appendix 2 to calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and 1000°C. Assume ΔH° and ΔS° to be independent of temperature.
Appendix 2
Inorganic Substances
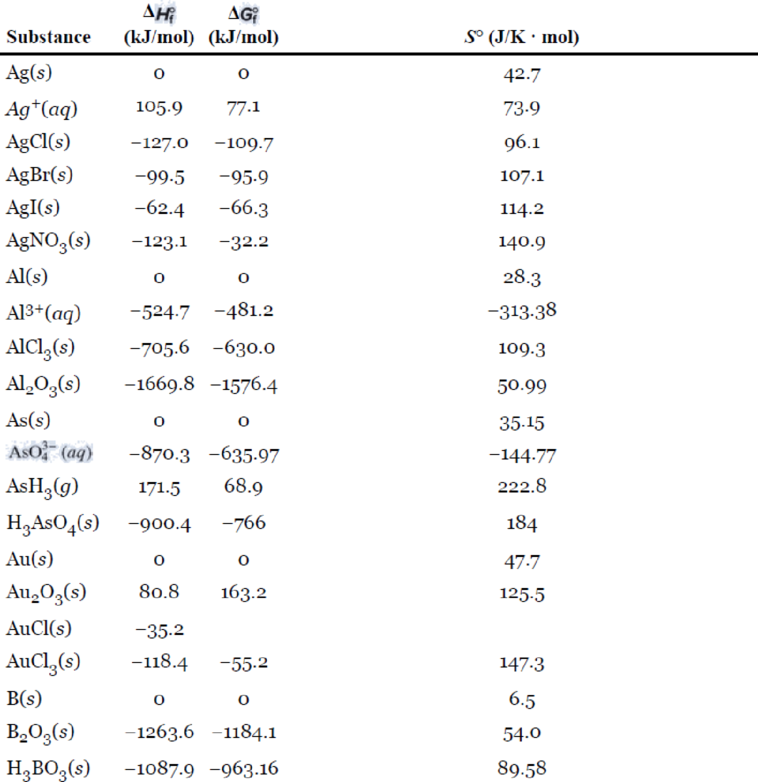
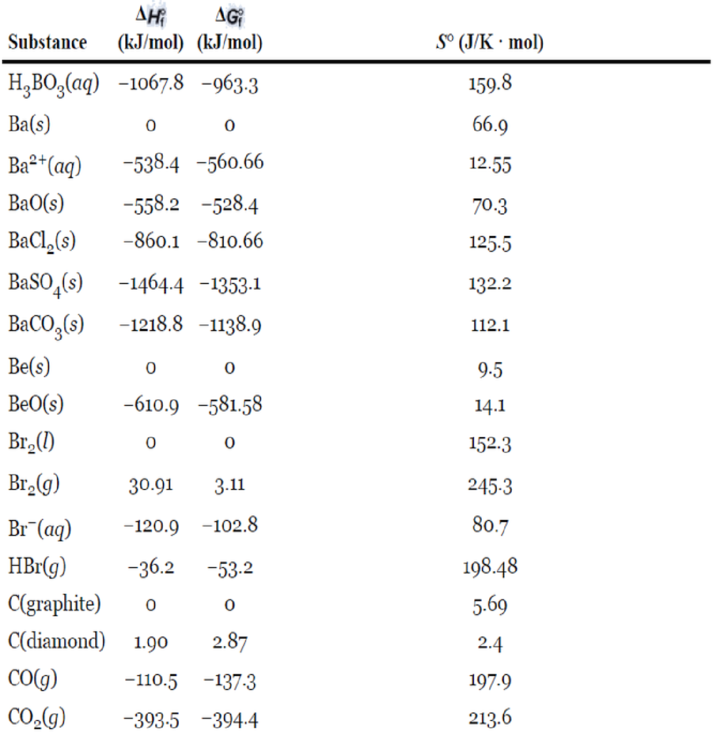
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the equilibrium constant at
Concept Introduction:
Equilibrium constant:
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of the concentration of product and the concentration of the reactant at equilibrium.
It can be calculated using the relationship between Gibb’s free energy and rate constant:
Where,
Gibbs free energy: Gibbs free is a thermodynamic parameter, which can be defined as the amount of energy available with the system to perform a useful work.
Gibbs free energy Equation:
Where,
T– is Temperature in K.
The change in standard entropy can be calculated as follows:
The change in standard enthalpy can be calculated as follows:
Answer to Problem 22.104QP
For the given reaction,
The equilibrium constant at
The equilibrium constant at
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
The following table gives the data of standard enthalpy of formation and standard entropy values for the reactants and products which are extracted from the appendix 2.
| Reactant/Product | Substance | ||
| Reactant | 0 | 5.69 | |
| Reactant | -393.5 | 213.6 | |
| Product | -110.5 | 197.9 |
Converting the temperature from
The change in standard enthalpy can be calculated as follows:
Converting it into
The change in standard entropy can be calculated as follows:
Calculating the Gibb’s free energy at
Calculating the equilibrium constant for the given reaction at
Thus, the equilibrium constant at
Calculating the Gibb’s free energy at
Calculating the equilibrium constant for the given reaction at
Thus, the equilibrium constant at
For the given reaction, the equilibrium constants at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ALEKS 360; 18WKS F/ GEN. CHEMISTRY >I<
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
- Which of the following oxyacids is the weakest? Group of answer choices H2SeO3 Si(OH)4 H2SO4 H3PO4arrow_forwardAdd conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformation. + More... If you need to write reagents above and below the arrow that have complex hydrocarbon groups in them, there is a set of standard abbreviations you can use. More... T H,N NC Datarrow_forwardIndicate the order of basicity of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





