
As we saw in Section 21.2, the reduction of iron oxides is accomplished by using carbon monoxide as a reducing agent. Starting with coke in a blast furnace, the following equilibrium plays a key role in the extraction of iron:
Use the data in Appendix 2 to calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and 1000°C. Assume ΔH° and ΔS° to be independent of temperature.
Appendix 2
Inorganic Substances
Interpretation:
For the given reaction, the equilibrium constant at
Concept Introduction:
Equilibrium constant:
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of the concentration of product and the concentration of the reactant at equilibrium.
It can be calculated using the relationship between Gibb’s free energy and rate constant:
Where,
Gibbs free energy: Gibbs free is a thermodynamic parameter, which can be defined as the amount of energy available with the system to perform a useful work.
Gibbs free energy Equation:
Where,
T– is Temperature in K.
The change in standard entropy can be calculated as follows:
The change in standard enthalpy can be calculated as follows:
Answer to Problem 22.104QP
For the given reaction,
The equilibrium constant at
The equilibrium constant at
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
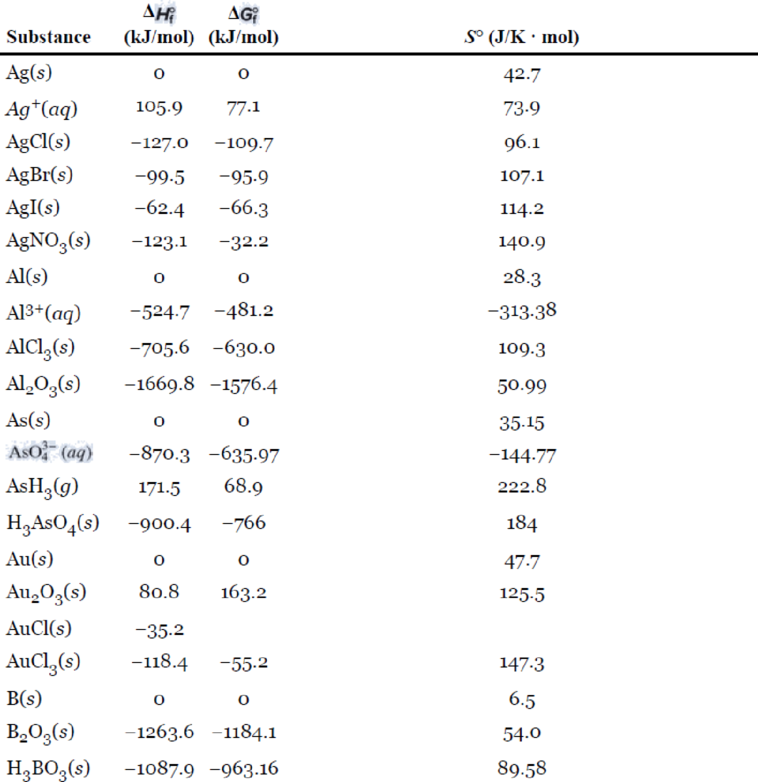
The following table gives the data of standard enthalpy of formation and standard entropy values for the reactants and products which are extracted from the appendix 2.
| Reactant/Product | Substance | ||
| Reactant | 0 | 5.69 | |
| Reactant | -393.5 | 213.6 | |
| Product | -110.5 | 197.9 |
Converting the temperature from
The change in standard enthalpy can be calculated as follows:
Converting it into
The change in standard entropy can be calculated as follows:
Calculating the Gibb’s free energy at
Calculating the equilibrium constant for the given reaction at
Thus, the equilibrium constant at
Calculating the Gibb’s free energy at
Calculating the equilibrium constant for the given reaction at
Thus, the equilibrium constant at
For the given reaction, the equilibrium constants at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry
- Briefly state the electrocapillary equation for ideally polarized electrodes.arrow_forwardWhat is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forward
- The molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forwardGiven the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forward
- At 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





