
Concept explainers
In GWAS analysis, because of the existence of LD blocks (or haplotype blocks), it is not necessary to genotype a person for every one of the 50 million known SNPs. Haplotype blocks are stretches of DNA containing particular SNP variants that tend to be inherited together (as a block) because recombination within the region is rare. In the accompanying figure, three different SNP loci are shown at top (SNP10, SNP11, and SNP12), each with two alleles among the world’s population of humans.
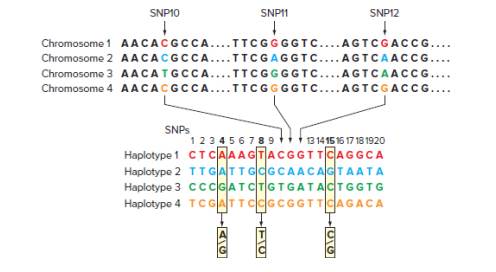
Only four of all the possible combinations of these SNP alleles are found in human genomes, as shown in the four chromosome types pictured. These three SNPs are part of a larger block of 20 SNPs that are usually inherited in one of the four configurations, or haplotypes, shown. Because these 20 SNPs are inherited as haplotype blocks, genotyping any individual for the three so-called Tag SNPs (SNP4, SNP8, and SNP15 shown in bold) should be sufficient to predict that individual’s alleles for the other 17 SNPs.
| a. | How many configurations of the three SNPs shown at the top of the diagram (SNPs 10, 11, and 12) are theoretically possible? |
| b. | How many haplotype variants are theoretically possible considering all 20 SNPs in the haplotype block, and assuming that each of them has two possible alleles? |
| c. | Given that humans are diploid, every individual has two copies of every (autosomal) haplotype block, one on each homolog. Does heterozygosity for the haplotype blocks interfere with genotyping individuals using the Tag SNPs shown in the diagram? Explain? |
| d. | In part (c), you saw that the three Tag SNPs shown in the diagram are sufficient to type any individual for this particular haplotype block. Is this the only set of three Tag SNPs that could be used? |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
GENETICS(LL)-W/CONNECT >CUSTOM<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- Briefly state the physical meaning of the electrocapillary equation (Lippman equation).arrow_forwardExplain in a small summary how: What genetic information can be obtained from a Punnet square? What genetic information cannot be determined from a Punnet square? Why might a Punnet Square be beneficial to understanding genetics/inheritance?arrow_forwardIn a small summary write down:arrow_forward
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





