
Interpretation:
A mechanism for the dehydration of 4-methylcyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
A dehydration reaction takes place after the removal of water molecule/s from the reactant molecule. In the mechanism of any organic reaction, negative charge always attacks on the positive center, and removal of good leaving group takes place. The stability of a leaving group depends on the stability of the molecule which can be shown by inductive, hyperconjugation or resonance effect.
Explanation of Solution
Below is the mechanism for the dehydration of 4-methyl cyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid:
In the first step, lone pair of electrons attack on the H atom which results in the formation positive charge on the O of the -OH group of 4-methyl cyclohexanol.
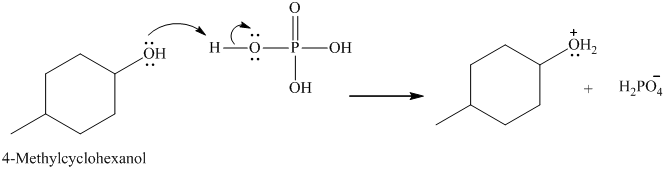
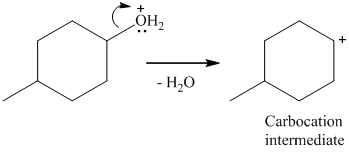
Here, the good leaving group is H2O. The derivative of hydronium ion removes a water molecule to form a carbocation intermediate.
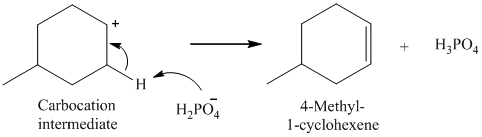
The nucleophile (H2PO4-) abstracts a proton from adjacent carbon of carbocation to form 4-methyl-1-cyclohexene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
A Small Scale Approach to Organic Laboratory Techniques
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


