
Concept explainers
Complete the following concept map to review some of the concepts of gas exchange.
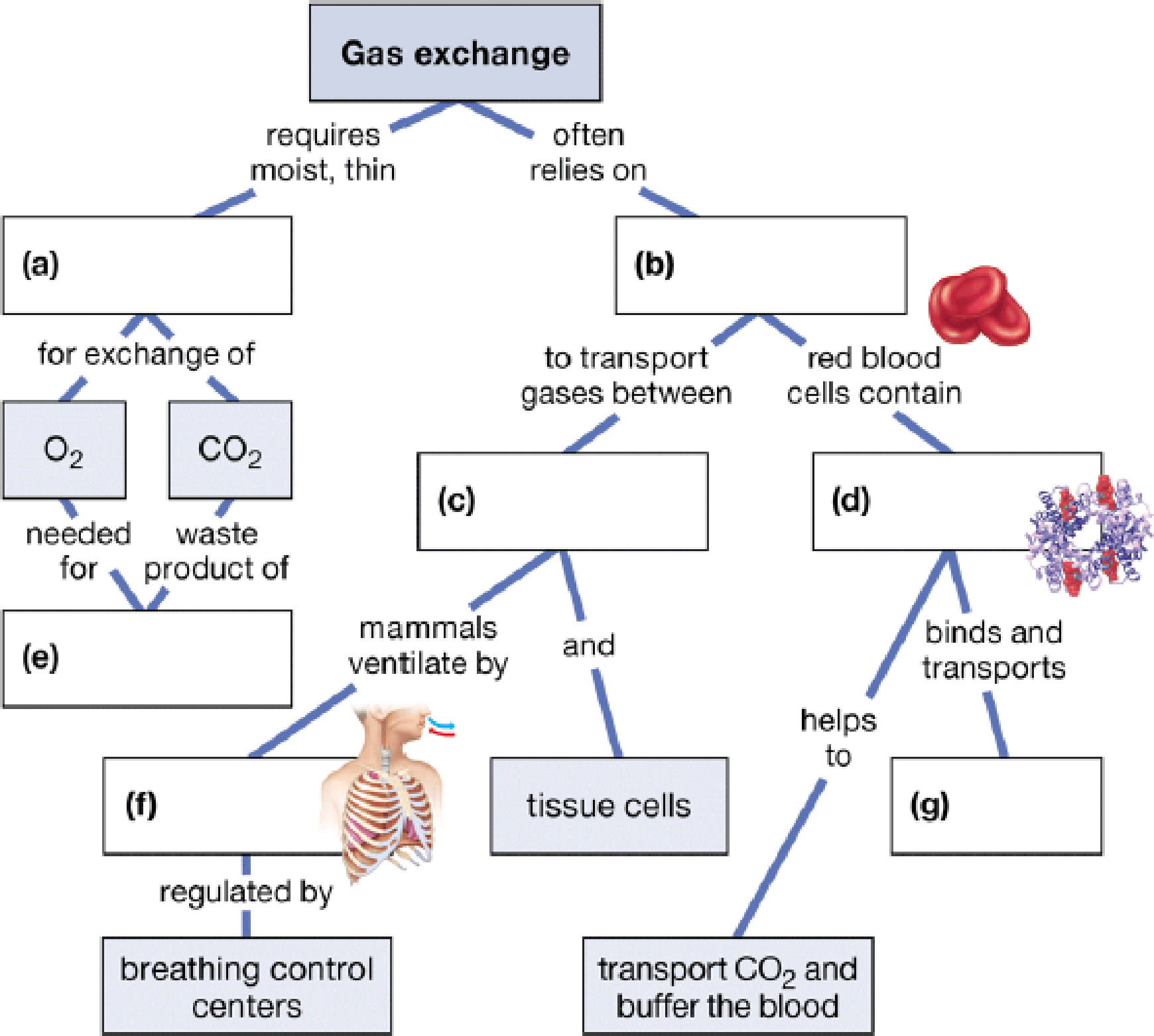
To complete: The given map to review some of the concepts of gas exchange.
Introduction:
The respiratory system is a biological system that ensures the transport of air by the process of inhalation and exhalation, that is, in and out the body with the help of the lungs.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Fig.1 shows the completed map to review some of the concepts of gas exchange.
Pictorial representation: Some of the concepts related to gas exchange are presented in the concept map given in Fig.1.
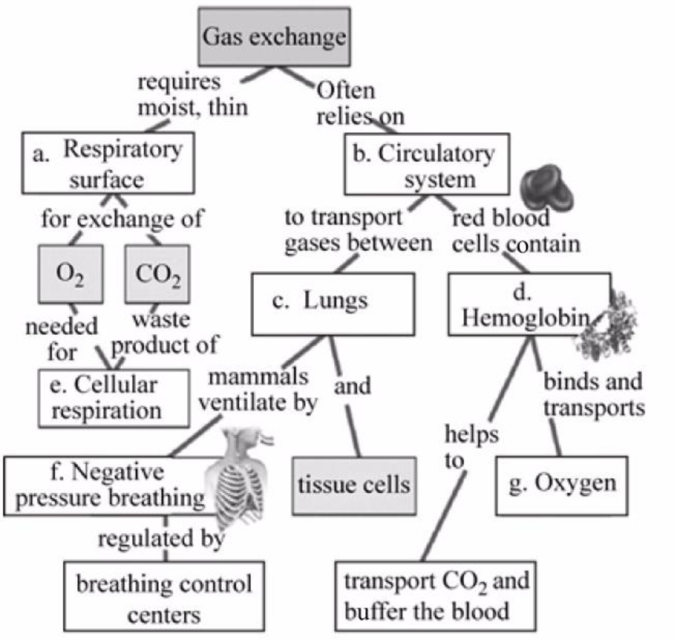
Fig.1: Concepts of gas exchange.
Explanation of Solution
a.
Correct answer: Respiratory surface.
For gas exchange to occur, the respiratory surface should be thin and moist. Hence, the correct answer is the respiratory surface.
b.
Correct answer: Circulatory system.
Gas exchange relies on the circulatory system as the exchanged oxygen and carbon dioxide travel in the blood to the heart and different body cells. Hence, the correct answer is the circulatory system.
c.
Correct answer: Lungs
It is the main organ for the exchange of gases consisting of air sacs that carry out gaseous exchange and the blood carries the exchanged gas to the tissue cells. Hence, the correct answer is the lungs.
d.
Correct answer: Hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is a blood pigment present inside the red blood cell, which helps in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide by binding with it and also maintains the pH of the blood. Hence, the correct answer is hemoglobin.
e.
Correct answer: Cellular respiration.
In cellular respiration, oxygen is used to convert glucose into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP. Hence, the correct answer is cellular respiration.
f.
Correct answer: Negative pressure breathing.
This type of breathing is regulated by the “breathing control center of the brain”. In negative pressure breathing, the air pressure inside the lungs drops during the contraction of the diaphragm, and the lower portion of the chest cavity rises; this allows the movement of air from outside to inside. Hence, the correct answer is negative pressure breathing.
g.
Correct answer: Oxygen.
Hemoglobin pigment in the blood binds with the oxygen present in the lungs, and this oxygen is utilized to form energy. Hence, the correct answer is oxygen.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Identify the indicated cavity (Fucus). a. antheridia b. conceptacel c. receptacle d. oogonium e. none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure (Saprolegnia). a. antheridium O b. oospore c.sperm d. auxospore e. tetraspore Of. zygosporearrow_forwardUsing information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding? Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions. Details: You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons. Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…arrow_forward
- Using information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding? Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions. Details: You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons. Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…arrow_forwardNow draw a rough sketch of what the control data might look like if in addition to the specific binding, there was also a considerable amount of nonspecific binding (again using a normal dose/response curve) (do % total bound ligand vs concentration)arrow_forwardWhat are functions of cuboidal cells in the kidney? Select all that apply. Concentration of gases Dilution of chemicals Secretion of molecules Nutrition to tissues Support of tissues Absorption of moleculesarrow_forward
- question1 In plants, epithelial tissue is only found as the outermost cell layer and acts as a barrier. In humans, epithelial tissue is found inside the body as well as on the surface. What function(s) does/do epithelial tissue carry out in humans? Select all that apply. Waste storage Filtration Oxygen transport Protection Diffusion Osmosis Absorptionarrow_forwardWhat words best describes this organism? a. Unicellular/nonmotile Ob. unicellular/motile c. colonial/nonmotile d. colonial/motile e. multicelluar O f. siphonous g. none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the phylum or class. a. Euglenophyta b. Dinoflagellata c. Bacillariophyceae d. Oomycetes e. Phaeophyceae O f. Myxomycota g. Xanthophyceae ○ h. Chrysophyceae i. Dictyosteliomycota O j. Rhodophyta Ok. Chlorophyceaens I. Charophyceaensarrow_forward
- Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





