
Concept explainers
(a)
To describe: The chemical transformation which is required to convert glutamate to (2S)-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyrate (AHBA).
Introduction:
Glutamate comes under the category of non-essential amino acid and it contains two carboxyl groups. It is an acidic amino acid which is important part of the neurotransmission process. AHBA (4-amino-2-bydoxy butyrate) it is main component of many antibiotics.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows formation of AHBA from glutamate.
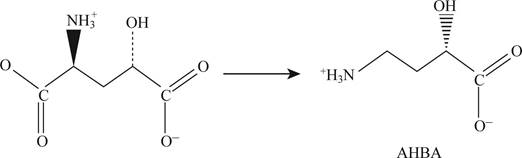
Fig.1: Formation of AHBA from glutamate.
Explanation:
AHBA (4-amino-2-bydoxy butyrate) is formed from the glutamate by the process of decarboxylation. When there is a removal of α-carboxyl group from the glutamate and addition of one –OH group to the γ-carbon then AHBA is formed which is given in Fig. 1.
(b)
To determine: How Btrl can act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A prosthetic group.
Introduction:
Coenzyme A is important in the synthesis and oxidation of the fatty acids and it also help in the citric acid cycle during the oxidation of the pyruvate.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Btrl and acyl carrier proteins have similarities in terms of their sequences. When this compound incubated in CoA conditions it increases its molecular weight. It is because CoA molecule can bind to Btrl molecule when CoA is added to the serine residue (any one) with the replacement of the hydroxyl group with a 4’-phosphopantertheine group
The molecular weight of the CoA is 17;
And the molecular weight of 4’phosphopantetheine is 356;
Molecular mass of purified Btrl protein is 11,812.
So, the overall molecular weight of the Btrl which could act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A would be as follows:
This calculated molecular weight is very much close to the observed molecular weight 12,153.
Conclusion:
Btrl can act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A because the expected molecular weight is very close to the calculated value of molecular weight which is 12,153.
(c)
To determine: The structures which are consistent with the proposed structure of γ-glutamyl-S-Btrl.
Introduction:
Alpha carboxyl group is any organic molecule group that contains basic amino group and acidic carboxyl group which is very unique to each amino acid.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig. 2 shows glutamyl-S-Btrl.
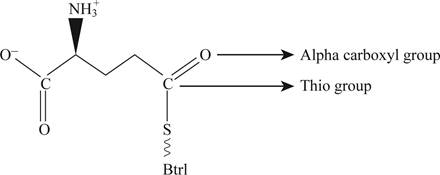
Fig.2: Glutamyl-S-Btrl
Explanation:
One more structure which is consistent is that a thio-ester could formed with the α-carboxyl group which is represented in the Fig. 2. Thio-ester is the compound which has
(d)
To determine: The chemical basis of the γ-glutamyl-S-Btrl can be correct because the alpha carboxyl group might be removed at some stage in the process.
Introduction:
Organic molecule group such as alpha carboxyl group that contains basic amino group and acidic carboxyl group and it is very unique to each amino acid.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
The process of removal of a carboxyl group from a compound is termed as decarboxylation. In many reactions, carboxyl group should be in a free state for an amino acid to be removed. It is very difficult to imagine that decarboxylation process can occur with a carboxyl group in its thio-ester form.
(e)
To determine: The most likely structure of the BtrK species
Introduction:
Decarboxylation is a
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig 3 shows most likely structure of the BtrK
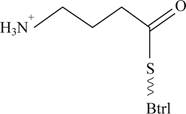
Fig 3: Most likely structure of the BtrK
Explanation:
The molecular species of Mr is 12,240 when the γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl is incubated with purified Btrl.
The molecular species of Mr is 12,281 of γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl.
Therefore,
Due to decarboxylation of the BtrK, carboxyl group would be deleted from the structure and only
(f)
To determine: The molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Introduction:
A pure substance is made from molecules with the average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representations: Fig 4 shows expected molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
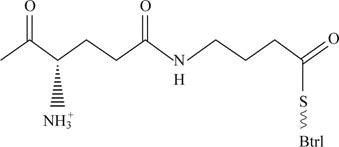
Fig 4: Expected molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Explanation:
The Molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370 is represented in the figure 4. The molecular species of Mr is 12,240 when the γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl is incubated with purified Btrl. The Molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Therefore,
This molecular structure would have free amino group and alpha carboxyl group and thio group will remain in the new species.
(g)
To propose: The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA with the help of enzymes that catalyze each step and any kind of cofactors and substrate required during the pathway.
Introduction:
In the plausible pathways different kind of enzyme and cofactor and substrate are used with the help of these factors a useful product can be synthesized.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.5 shows the plausible pathway for t.he synthesis of AHBA
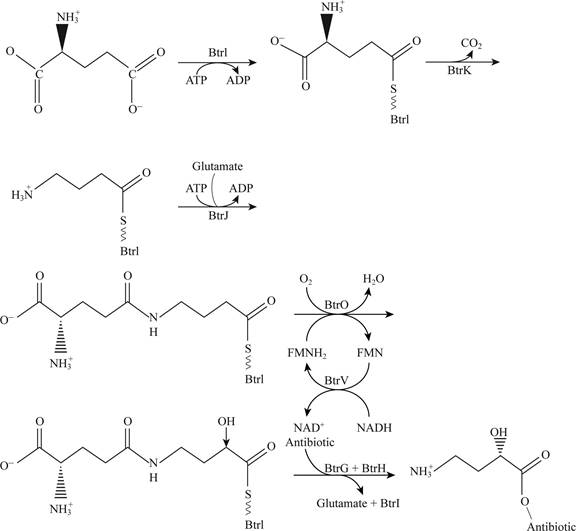
Fig.5: The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA
Explanation:
The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA and respective addition of antibiotics is represented in the Fig. 5. This pathway includes the involvement of co-factor such as ATP, NAD and glutamate amino acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Lehninger Principles Of Biochemistry 7e & Study Guide And Solutions Manual For Lehninger Principles Of Biochemistry 7e
- Draw the reaction between sphingosine and arachidonic acid. Draw out the full structures.arrow_forwardDraw both cis and trans oleic acid. Explain why cis-oleic acid has a melting point of 13.4°C and trans-oleic acid has a melting point of 44.5°C.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the mixed triacylglycerol formed by the reaction of glycerol and the fatty acids arachidic, lauric and trans-palmitoleic. Draw the line structure.arrow_forward
- Draw out the structure for lycopene and label each isoprene unit. "Where is lycopene found in nature and what health benefits does it provide?arrow_forwardWhat does it mean to be an essential fatty acid? What are the essential fatty acids?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast primary and secondary active transport mechanisms in terms of energy utilisation and efficiency. Provide examples of each and discuss their physiological significance in maintaining ionic balance and nutrient uptake. Rubric Understanding the key concepts (clearly and accurately explains primary and secondary active transport mechanisms, showing a deep understanding of their roles) Energy utilisation analysis ( thoroughly compares energy utilisation in primary and secondary transport with specific and relevant examples Efficiency discussion Use of examples (provides relevant and accurate examples (e.g sodium potassium pump, SGLT1) with clear links to physiological significance. Clarity and structure (presents ideas logically and cohesively with clear organisation and smooth transition between sections)arrow_forward
- 9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate? 요요. 1. NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 3. A OCH2CH3 2. ethyl acetoacetate ii A 3. H3O+ OH B C D Earrow_forward7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. Which one is it? Ph کہ A B C D Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forward
- what is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forwardFour distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





