
Concept explainers
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:
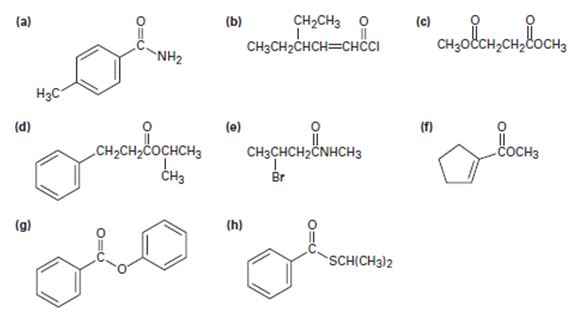
a)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
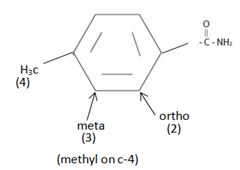
The IUPAC name of the given compound is p-methyl phenyl acet amide.
Explanation of Solution
The compound given is an unsubstituted amide that can be represented by the general formula 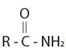 ; since the amide nitrogen in NH2 is not substituted by R1 an alkyl group.
; since the amide nitrogen in NH2 is not substituted by R1 an alkyl group.
The R alkyl group attached to carbonyl carbon is phenyl, which has a para-substituted methyl with the 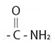 substituent. ie
substituent. ie
The IUPAC system of naming an amide unsubstituted follows this rule:
Replace the –oic acid or ic acid ending with amide and use the R alkyl group before this. Thus p-methyl-phenyl acetic acid to
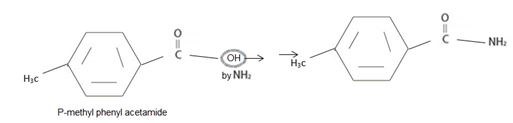
Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is p-methyl phenyl acet amide.
b)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
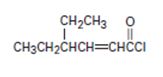
Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is 4-ethyl-2-hexenoyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is consistent with 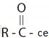 , an acyl chloride.
, an acyl chloride.
The IUPAC system names an acyl chloride by first identifying the alkyl component R by its IUPAC name. [the parent hydro carbon residue]. Obviously this given the name of the parent carboxylic acid itself. Follow this name by replacing the -ic acid ending with oyl and finally add the halide suffix.
For the given compound the parent hydrocarbon R is a six-carbon unsaturated hydrocarbon chain as.
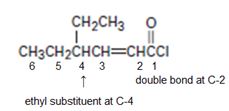
Thus this chain (longest chain) is named 4-ethyl-hexene-(2) [oic - acid] and the halide substituent chloride. We replace –oic acid by –oyl chloride. This leads to 4-ethyl-2 hexenoyl chloride or 4-ethyl-hexene-2-oyl chloride (from 4-ethyl-hexene-2-oic acid or 4 ethyl-2-hexenoic acid). The parent carboxylic acid.
Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is 4-ethyl-2-hexenoyl chloride.
c)
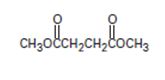
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The IUPAC name of the given compound is thus dimethyl succinate.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
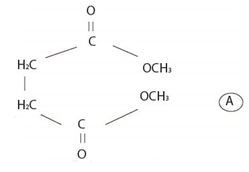
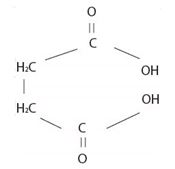
The structural formula A, of the given compound shows it to be the ester derivative of the dicarboxylic acid succinic acid is
The IUPAC system prescribes the following rule to name an ester derivative of a carboxylic acid thus:
First, identify the two alkyl group attached to each carboxylic oxygen (for two carboxylic acid groups in the given dicarboxylic acid). Then name the ester by starting with the name of their alkyl group (S) and adding the suffix–ate to replace the ending–ic acid.
Thus, combining these two rules, the given ester is named by IUPAC system as dimethyl succinate (from succinic acid) (for two CH3 groups) attached to carboxyl-groups)
The IUPAC name of the given compound is thus dimethyl succinate.
d)
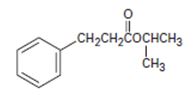
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
Thus, the IUPAC isopropyl-3 phenyl pro panoate name of the given compound is isopropyl–3 phenyl propanoate.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for the given compound is consistent with the general formula for an ester derivative of a mono carboxylic acid is 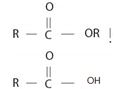 for the ester and for the parent acid the IUPAC system prescribes the following rules to name such an ester derivative is:
for the ester and for the parent acid the IUPAC system prescribes the following rules to name such an ester derivative is:
1) First, identify and name the alkyl group R1, attached to the carboxyl oxygen. For the given compound, it is isopropyl
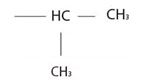
This corner in the prefix, first in the name of the parent carboxylic acid and also in the ester derivative.
2) Second, identify the R alkyl chain residue of the carboxylic acid. This for the given compound is the 3 carbon propanoic acid with a phenyl substituent at C-3 ie
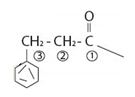
3) Combining these two rules, finally the use the suffix–ate to replace the–ic acid ending. This given.
Thus, the IUPAC isopropyl-3 phenyl pro panoate name of the given compound is isopropyl–3 phenyl propanoate.
e)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
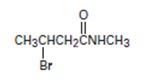
The IUPAC name of the given compound is N-methyl-4 bromo butanamide.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula given for the compound is
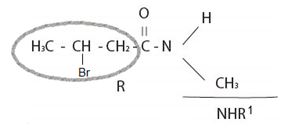
Consistent with the general formula for an amide derivative of a carbonylic acid is 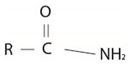 with the amide bring further alkyl, R1, substituted at the amide nitrogen ie NHR1 or
with the amide bring further alkyl, R1, substituted at the amide nitrogen ie NHR1 or 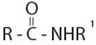 the IUPAC system prescribes the following ruler to name such substituted amides.
the IUPAC system prescribes the following ruler to name such substituted amides.
1) First, identify the N-alkyl substituent. In the given compound it is N-methyl-(mono substituted).
2) Next identify and name by the IUPAC system, the R, ie alkyl hydrocarbon chain component attached to the carbonyl carbon.
For the given compound, R is,
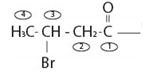
or remembering that carbonyl carbon is C-1, it is four carbon (longest hydro carbon chain) with a bromine at carbon-C-3. Thus, the name of this residue is 4-bromo butan–(derivative).
Finally, combining these two aspects, replace the–ic acid ending for the parent 4-bromobutanoic acid by –amide. This leads to N-methyl-4-bromo butanamide.
Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is N-methyl-4 bromo butanamide.
f)
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
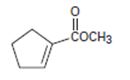
The IUPAC name for the given compound methyl-1-cyclopentene carboxylate.
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC system prescribes the following rules to name such compounds is:
a) First, identify and name the R1, compound of the ester oxygen OR1. This, in the given compounds is methyl –OCH3.
b) Next identify the parent hydro carbon residue R attached the carbonyl carbon. For the given compound it is an unsaturated cyclopentene (5 carbon closed cyclic hydro carbon) with a double bond at C-1, which holds the carboxyl carbon. ie
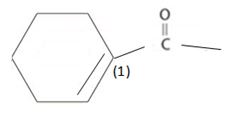
Thus, this residue R is 1-cyclopentene for the parent acid 1-cyclopentene carboxylic acid. Finally, combining these two rules, replace the –ic acid ending by –ate ie carboxylate. Thus, the name of the ester is methyl-1-cycopentene carboxylate.
Thus the IUPAC name for the given compound methyl-1-cyclopentene carboxylate.
g)
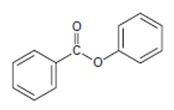
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The IUPAC name of the given compound is phenyl-benzoate.
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC system prescribes the following rules to name such esters is:
1) First identify and name the alkyl residue R1 of the ester oxygen. This, in the given compound is phenyl Ph or 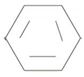 (unsubstituted)
(unsubstituted)
2) Second, identify and name by the IUPAC system the alkyl residue R attached to carbonyl carbon. This, in the given compound is
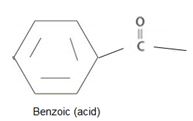
Finally combining these two rules, replace the –ic acid ending with the suffix –ate; the R1 alkyl name is the prefix. This leads to phenyl-benzoate.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the given compound is phenyl-benzoate.
h)
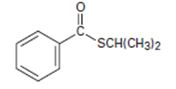
Interpretation:
To identify the given compound by introspecting its structural formula and name it by the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 45AP
Thus the IUPAC name for the given compound is isopropyl-phenyl since it is a thio ester carbothioate.
Explanation of Solution
The IUPAC system prescribes the following rules to name such thiol derivatives (sulphur) is:
1) First, identify and name by the IUPAC system, the alkyl residue, R1 attached to the –SR1 function. For the given compound this is the iso-propyl function ie
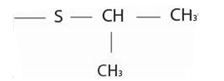
2) Next, identify and name the alkyl R residue attached to the carbonyl carbon. This is, for the given compound
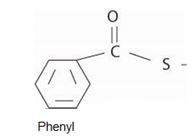
The parent carboxylic acid is thus phenyl carboxylic acid or
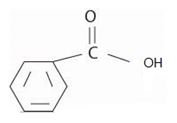
Finally, combining these two aspects, recall that the general ester of this carboxylic acid is the IUPAC name
Phenyl carboxylate for the this ester function, substitute the carboxylate ending by carbothioate. These the IUPAC name is, Isopropyl-phenyl carbothioate.
Thus the IUPAC name for the given compound is isopropyl-phenyl since it is a thio ester carbothioate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forward
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward

 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



