
Concept explainers
Subpart (a):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
When the wants and needs of a human are unlimited and the budget of an individual is limited, it will lead to a constraint of needs and this constraint raised is due to the limited budget is known as the budget constraint of an individual. Thus, the budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given
Here, the income of the person is given as $60, the price of one meal at dining hall is $6, and the price of cup 'o soup is $1.5. Thus, when the consumer spends her entire income on the meal in dining hall, the quantity that she receives can be calculated by dividing the income by the per meal price as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on meal from dining hall, she can buy 10 meals. When she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can receive 40 cup 'o soup meals.
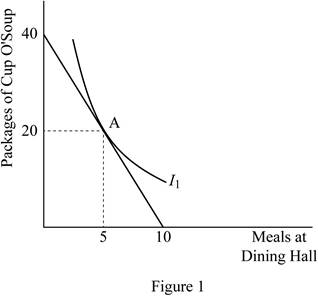
The budget constraint represents all the combinations of these two goods ranging between 10 dining hall meals and no cup 'o soup meal to no dining hall meals and 40 cup 'o soup meals. However in this case, the consumer spends her income equally on both of the commodities. Thus, she spends $30 each on dining hall meals and cup 'o soup meals. Thus, when the consumer spends $30 on the meal in dining hall, the quantity that she receives can be calculated by dividing the income by per meal price as follows:
Thus, when she spends $30 of her income on meal from dining hall, she can buy 5 meals. When she spends $30 of her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends $30 of her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can receive 20 cup 'o soup meals. This will be the point of her consumption, when the income is equally spent on both commodities. The graphical representation shows this combination at point A and it is represented as follows:
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (b):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
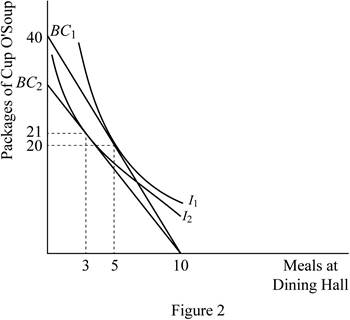
When the price of the cup o' soup increases to $2 from $1.5, the vertical intercept of the student's budget constraint will shift downwards; this will flatten the budget constraint curve. When she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can only receive 30 cup 'o soup meals. This flattens the budget constraint curve.
It is also said that at present she only spends 30 percent of her income on the dining hall meal, which means that the income spent on dining hall meal is only $18 and that spend on cup o' soup is $42. At this income spending distribution, she can purchase 3 units of dining hall meals and 21 units of cup o' soup meals. This new point can be illustrated as point B and it can be represented as follows:
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (c):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
The initial price of cup o' soup was $1.5, and the new price after the increase is $2. The initial quantity demanded of cup o' soup was 20 units; whereas after the increased price of the commodity, the quantity demanded is 21 units. This shows that the
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (d):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
The initial price of cup o' soup was $1.5, and the new price after the increase is $2. The initial quantity demanded of cup o' soup was 20 units denoted by point A; whereas after the increased price of the commodity, the quantity demanded is 21 units denoted by point B. This shows that the demand for the commodity will increase, when the price of the commodity increases. Thus, these two points can be graphically illustrated as follows:
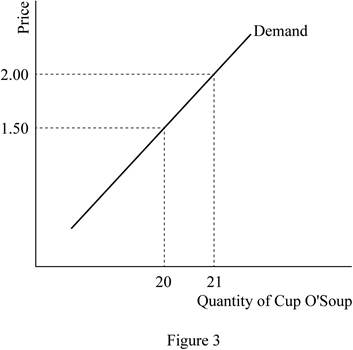
Here, the demand for the cup o' soup increases, when its price increases, which means that the commodity is an inferior good. However at the same time, the income effect overweighs the substitution effect for the commodity, which is a special case of inferior goods, known as the Giffen goods. Thus, the cup o' soup is a Giffen good.
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Principles of Microeconomics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
- Everything is in the attached picture. 22arrow_forwardEverything is in attached picture. 23arrow_forward1) Use the supply and demand schedules to graph the supply and demand functions. Find and show on the graph the equilibrium price and quantity, label it (A). P Q demanded P Q supplied 0 75 0 0 5 65 5 0 10 55 10 0 15 45 15 10 20 35 20 20 25 25 25 30 30 15 30 40 35 40 5 0 35 40 50 60 2) Find graphically and numerically the consumers and producers' surplus 3) The government introduced a tax of 10$, Label the price buyers pay and suppliers receive. Label the new equilibrium for buyers (B) and Sellers (S). How the surpluses have changed? Give the numerical answer and show on the graph. 4) Calculate using midpoint method the elasticity of demand curve from point (A) to (B) and elasticity of the supply curve from point (A) to (C).arrow_forward
- Four heirs (A, B, C, and D) must divide fairly an estate consisting of three items — a house, a cabin and a boat — using the method of sealed bids. The players' bids (in dollars) are: In the initial allocation, player D Group of answer choices gets no items and gets $62,500 from the estate. gets the house and pays the estate $122,500. gets the cabin and gets $7,500 from the estate. gets the boat and and gets $55,500 from the estate. none of thesearrow_forwardJack and Jill are getting a divorce. Except for the house, they own very little of value so they agree to divide the house fairly using the method of sealed bids. Jack bids 140,000 and Jill bids 160,000. After all is said and done, the final outcome is Group of answer choices Jill gets the house and pays Jack $80,000. Jill gets the house and pays Jack $75,000. Jill gets the house and pays Jack $70,000. Jill gets the house and pays Jack $65,000. none of thesearrow_forwardThe problem statement never defines whether the loan had compound or simple interest. The readings indicate that the diference in those will be learned later, and the formula used fro this answer was not in the chapter. Should it be assumbed that a simple interest caluclaton should be used?arrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





