
Concept explainers
Spreadsheet and Statement of
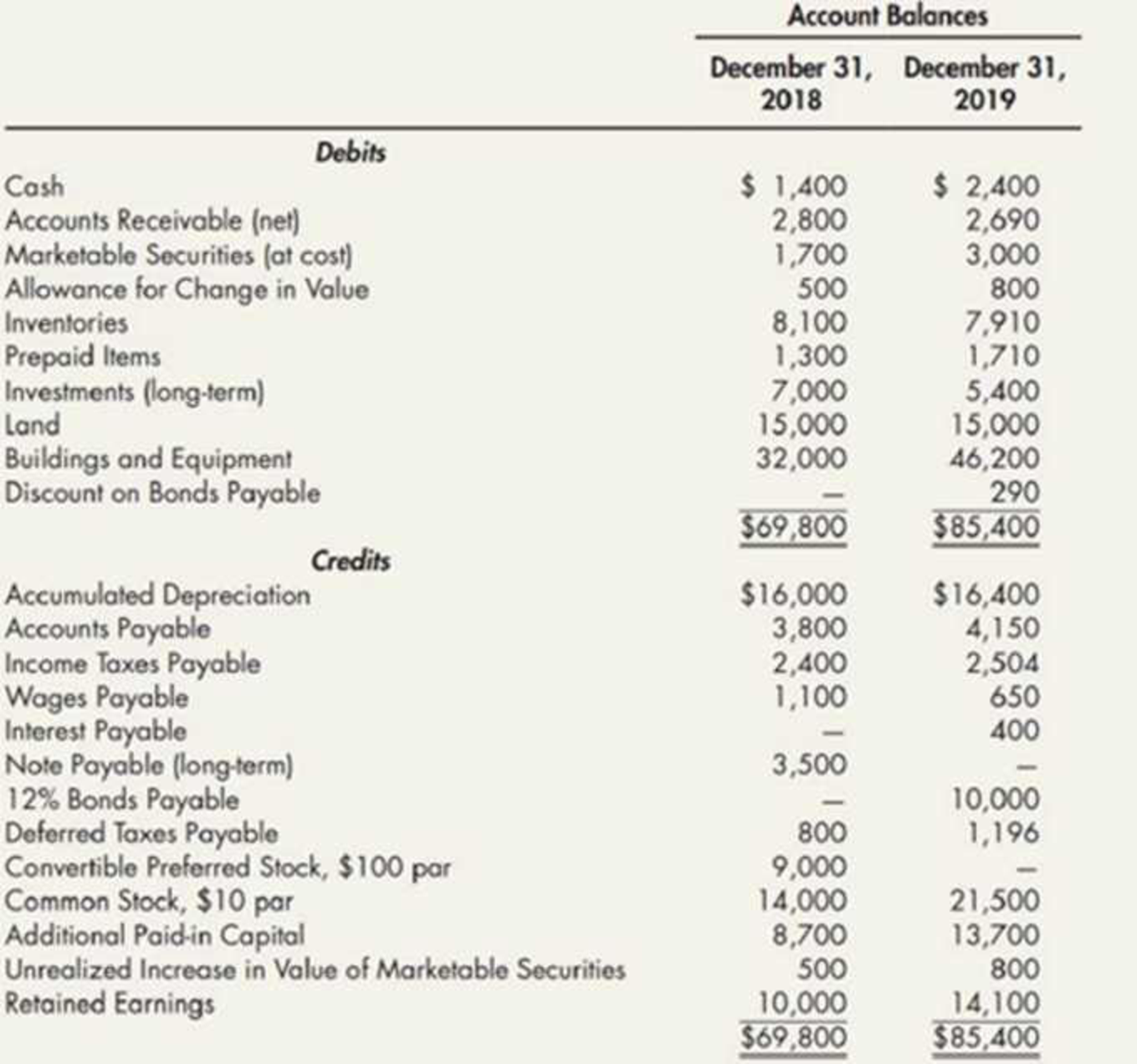
1.
Prepare a statement of cash flows using spreadsheet method.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
Worksheet: A worksheet is a spreadsheet used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
Prepare a statement of cash flows using spreadsheet method.
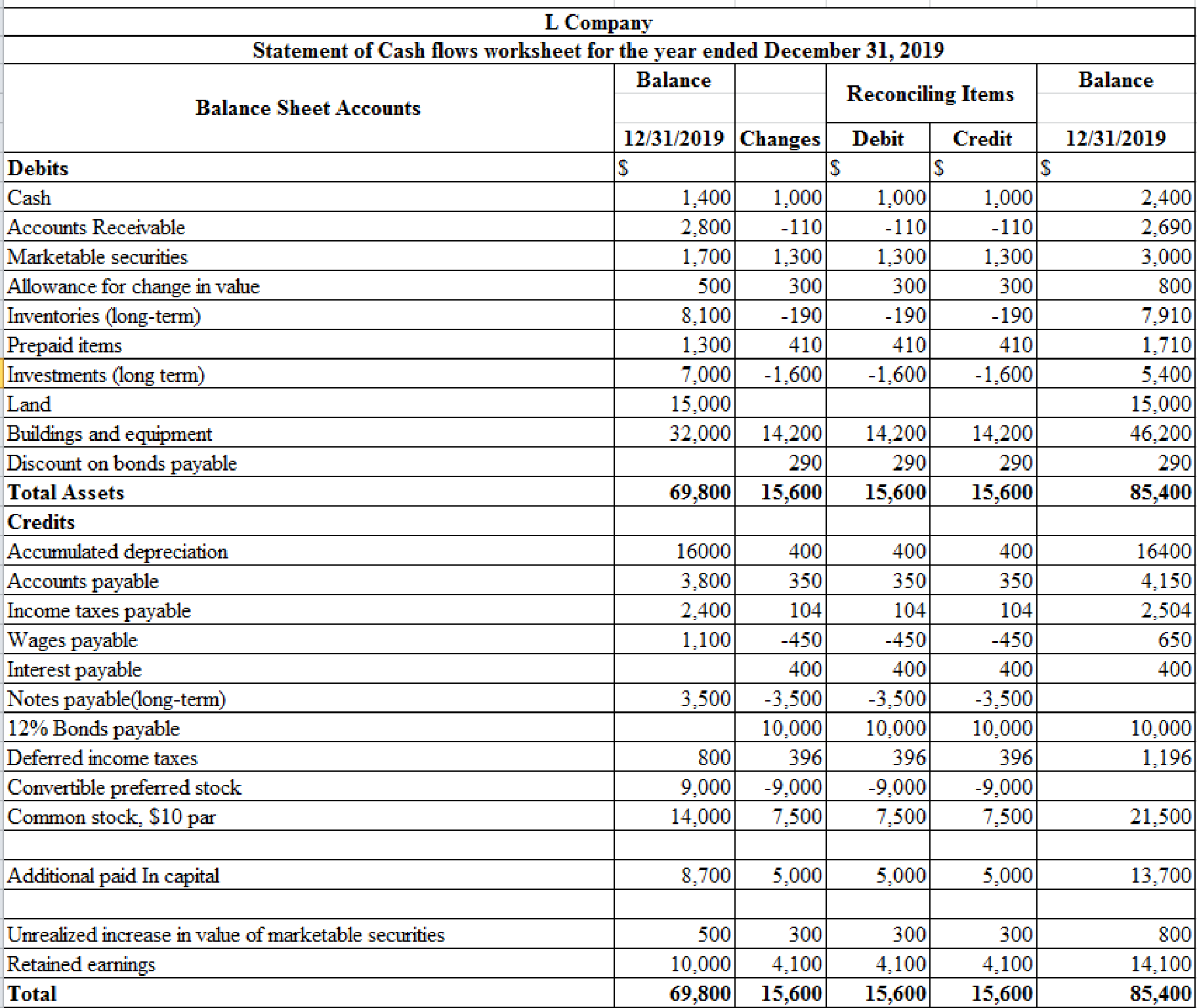
Table (1)
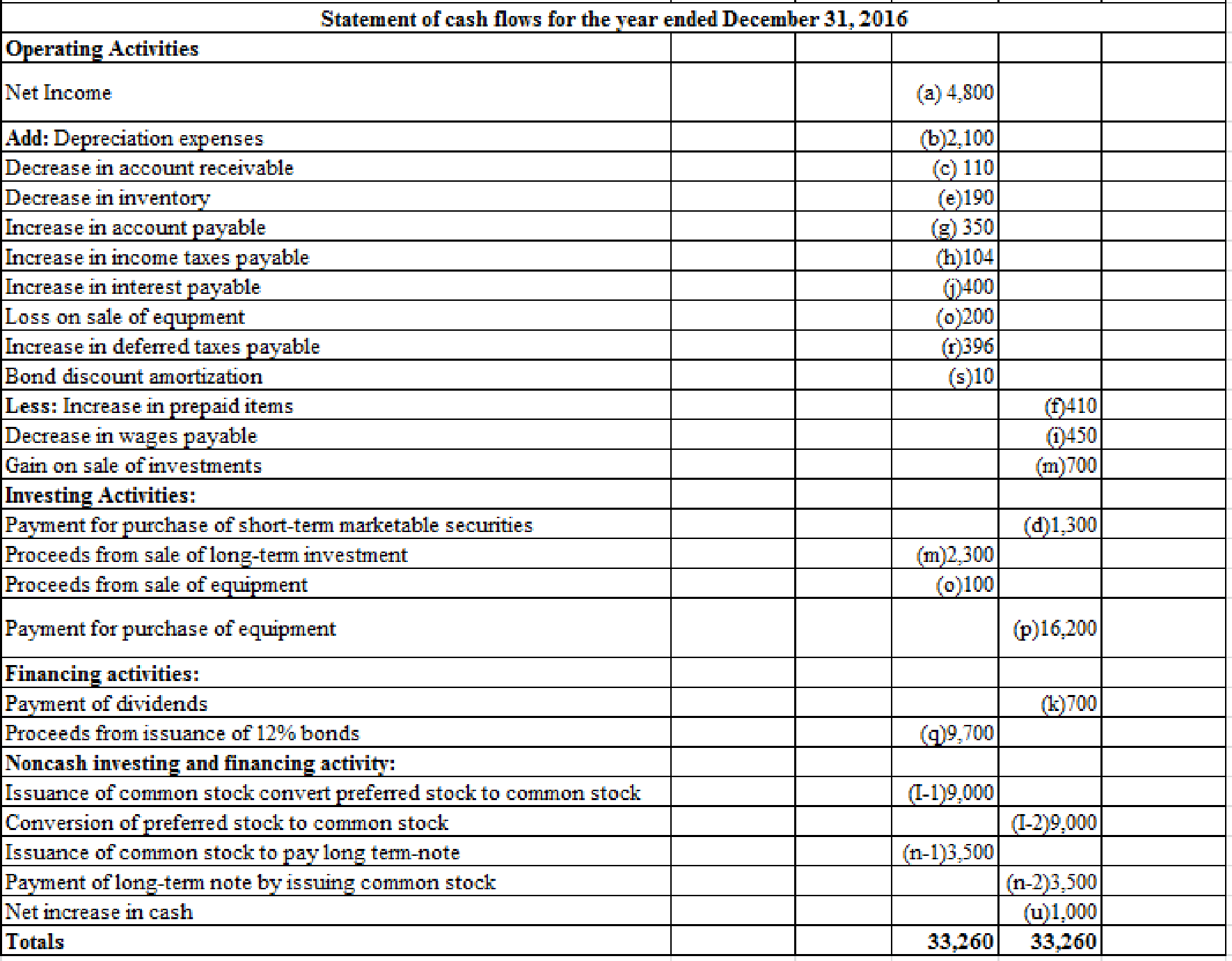
Table (1)
Notes:
a. Depreciation for the year ended is $2,100
b. Calculate accounts receivable.
c. Calculate the marketable securities.
d. Calculate the decrease in inventories.
e. Calculate the prepaid items.
f. Calculate the increase in accounts payable.
g. Calculate the income taxes payable.
h. Calculate the wages payable.
j. Interest payable for the year ended is $400.
k. Calculate the retained earnings.
l-1. Calculate the issuance of common stock to preferred stock.
1-2. Conversion of preferred stock to common stock is $9,000.
m. Calculate the proceeds from sale of long-term investments
n-1. Calculate the Issuance of common stock to pay long-term note.
n-2. Long- term notes payable is $3,500.
o. Calculate the sale of building and equipment.
- Cost of the equipment is $2,000.
- Loss on sale of equipment is $200.
- Proceeds from sale of equipment is $100.
p. Calculate the payment for purchase of equipment.
q. Calculate the proceeds from issuance of bonds.
r. Calculate the increase in deferred tax.
s. Calculate the bond discount amortization.
t. Calculate the allowance for change in value.
u. Calculate net increase in cash.
2.
Prepare the statement of cash flows of L Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the statement of cash flows of L Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
| L Company | ||
| Statement of cash flows for the year 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Operating Activities: | ||
| Net income | 4,800 | |
| Adjustment for non-cash income items: | ||
| Add: Depreciation expenses | 2,100 | |
| Bound discount amortization | 10 | |
| Loss on sale of equipment | 200 | |
| Increase in deferred taxes payable | 396 | |
| Less: Gain on sale of equipment | (700) | |
| Adjustments for cash flow effects from working capital items: | ||
| Decrease in accounts receivable | 110 | |
| Decrease in inventories | 190 | |
| Increase in prepaid items | (410) | |
| Increase in accounts payable | 350 | |
| Decrease in wages payable | (450) | |
| Increase in income taxes payable | 104 | |
| Increase in interest payable | 400 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 7,100 | |
| Investing Activities: | ||
| Payment for purchase of short-term marketable securities | (1,300) | |
| Proceeds from sale of long-term investments | 2,300 | |
| Proceeds from sale of equipment | 100 | |
| Payment for purchase of equipment | (16,200) | |
| Net cash used for investing activities | (15,100) | |
| Financing Activities: | ||
| Proceeds from issuance of 12% bonds | 9,700 | |
| Payment of dividends | (700) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 9,000 | |
| Net increase in cash( schedule 1) | 1,000 | |
| Cash on January 1, 2016 | 1,400 | |
| Cash on December 31,2016 | 2,400 | |
| Schedule 1: Investing and Financial Activities Not Affecting Cash | ||
| Financing Activities: | ||
| Conversion of preferred stock to common stock | (9,000) | |
| Issuance of common stock to convert preferred stock | 9,000 | |
| Payment of long-term note by issuing common stock | (3,500) | |
| Issuance of common stock to pay long- term note | 3,500 | |
Table (2)
3.
Determine the difference in cash flow from operation to sales ratio and profit margin ratio of L Company for the year 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Cash flow to sales ratio: The cash flow to sales ratio reveals the ability of a business to generate cash flow in proportion to its sales volume. It is calculated by dividing operating cash flows by net sales.
Formula for Formula for to sales ratio:
Profit margin ratio: The profit margin ratio, also called the return on sales ratio or gross profit ratio, is a profitability ratio that measures the amount of net income earned with each dollar of sales generated by comparing the net income and net sales of a company.
Formula for Formula for to profit margin ratio
The primary reason for the difference is depreciation expenses ($2,100), which was deducted to determine the net income, which did not involve an operating cash outflow.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Hii expert please given correct answer general Accounting questionarrow_forwardOn 1st May, 2024 you are engaged to audit the financial statement of Giant Pharmacy for the period ending 30th December 2023. The Pharmacy is located at Mgeni Nani at the outskirts of Mtoni Kijichi in Dar es Salaam City. Materiality is judged to be TZS. 200,000/=. During the audit you found that all tests produced clean results. As a matter of procedures you drafted an audit report with an unmodified opinion to be signed by the engagement partner. The audit partner reviewed your file in October, 2024 and concluded that your audit complied with all requirements of the international standards on auditing and that; sufficient appropriate audit evidence was in the file to support a clean audit opinion. Subsequently, an audit report with an unmodified opinion was issued on 1st November, 2024. On 18th January 2025, you receive a letter from Dr. Fatma Shemweta, the Executive Director of the pharmacy informing you that their cashier who has just absconded has been arrested in Kigoma with TZS.…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





