
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The reagents that are used to make the given compound of aldol condensation have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Retro synthetic analysis:
It is the analysis of the synthetic starting materials for a given compound through its precursors or fragments which are known as synthons. The synthons can be obtained by logical cleavage of the
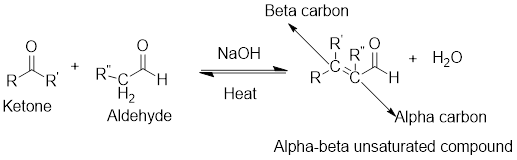
Crossed aldol condensation:
Crossed aldol condensation reaction occurs, when an
General scheme:
Retro aldol analysis:
To obtain the reactants of the given aldol product, the alpha beta unsaturated bond has to be cleaved using water molecule as shown here:
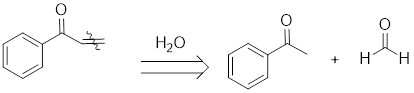
(b)
Interpretation: The reagents that are used to make the given compound of aldol condensation have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Retro synthetic analysis:
It is the analysis of the synthetic starting materials for a given compound through its precursors or fragments which are known as synthons. The synthons can be obtained by logical cleavage of the chemical bonds in the compounds. The resulted synthons will be therefore known as logical synthons.
Crossed aldol condensation:
Crossed aldol condensation reaction occurs, when an aldehyde and a ketone are heated in aqueous sodium hydroxide. The resulted product will be an
General scheme:

Retro aldol analysis:
To obtain the reactants of the given aldol product, the alpha beta unsaturated bond has to be cleaved using water molecule as shown here:
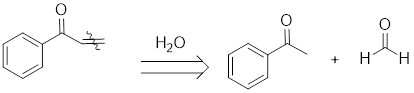
(c)
Interpretation: The reagents that are used to make the given compound of aldol condensation have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Retro synthetic analysis:
It is the analysis of the synthetic starting materials for a given compound through its precursors or fragments which are known as synthons. The synthons can be obtained by logical cleavage of the chemical bonds in the compounds. The resulted synthons will be therefore known as logical synthons.
Crossed aldol condensation:
Crossed aldol condensation reaction occurs, when an aldehyde and a ketone are heated in aqueous sodium hydroxide. The resulted product will be an
General scheme:

Retro aldol analysis:
To obtain the reactants of the given aldol product, the alpha beta unsaturated bond has to be cleaved using water molecule as shown here:
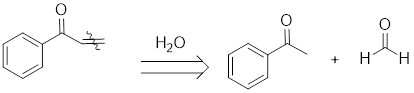
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRYPKGDRL+MLCRL MDL
- 8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward
- 7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forwardWhat is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions using the data I included. 1&2arrow_forwardAssign all the Protons in HNMRarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





