
Concept explainers
Segment variable costing income statement and effect on operating income of change in operations
Valdespin Company manufactures three sizes of camping tents—small (S), medium (M), and large (L). The income statement has consistently indicated a net loss for the M size, and management is considering three proposals: (1) continue Size M, (2) discontinue Size M and reduce total output accordingly, or (3) discontinue Size M and conduct an advertising campaign to expand the sales of Size S so that the entire plant capacity can continue to be used.
If Proposal 2 is selected and Size M is discontinued and production curtailed, the annual fixed production costs and fixed operating expenses could be reduced by $46,080 and $32,240, respectively. If Proposal 3 is selected, it is anticipated that an additional annual expenditure of $34,560 for the rental of additional warehouse space would yield an additional 130% in Size S sales volume. It is also assumed that the increased production of Size S would utilize the plant facilities released by the discontinuance of Size M.
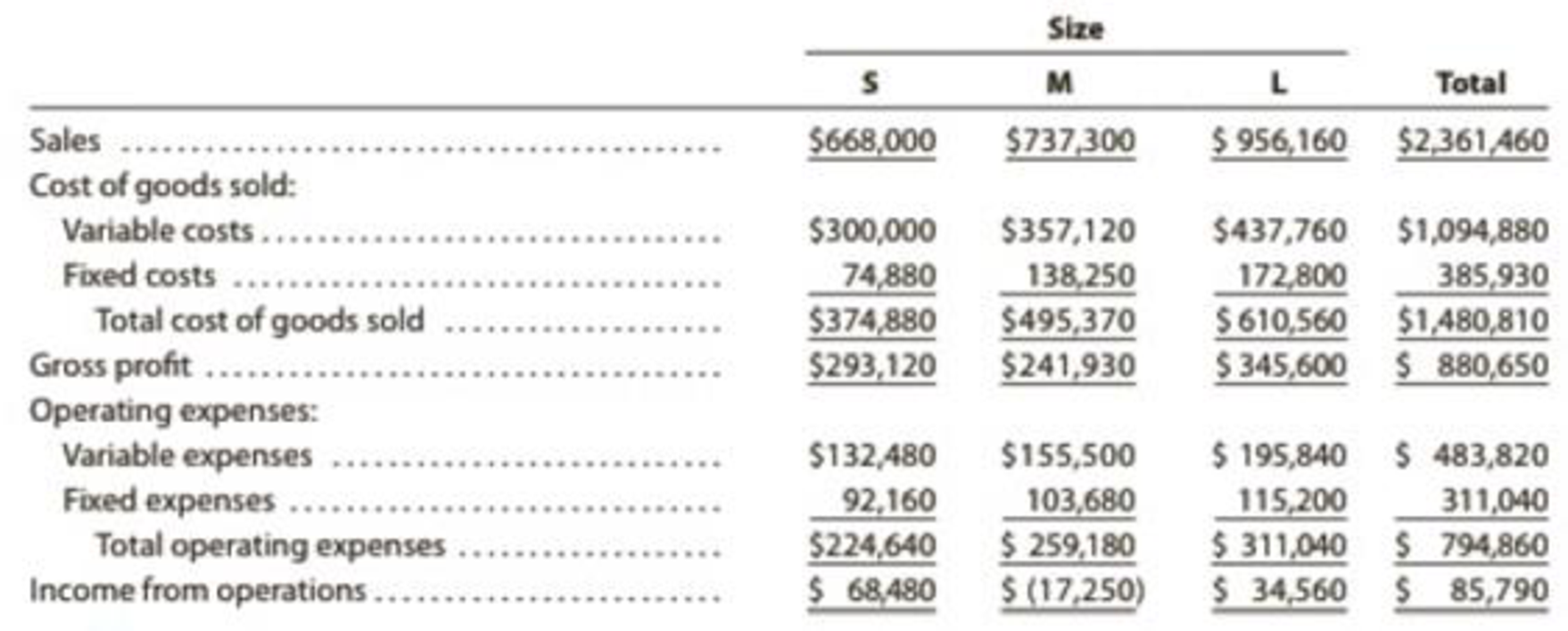
The sales and costs have been relatively stable over the past few years, and they are expected to remain so for the foreseeable future. The income statement for the past year ended June 30, 20Y9, is as follows:
Instructions
- 1. Prepare an income statement for the past year in the variable costing format. Use the following headings:

Data for each size should be reported through contribution margin. The fixed costs should be deducted from the total contribution margin, as reported in the “Total” column, to determine operating income.
- 2. Based on the income statement prepared in (1) and the other data presented, determine the amount by which total annual operating income would be reduced below its present level if Proposal 2 is accepted.
- 3. Prepare an income statement in the variable costing format, indicating the projected annual operating income if Proposal 3 is accepted. Use the following headings:

Data for each style should be reported through contribution margin. The fixed costs should be deducted from the total contribution margin as reported in the “Total” column. For purposes of this problem, the expenditure of $34,560 for the rental of additional warehouse space can be added to the fixed operating expenses.
- 4. By how much would total annual operating income increase above its present level if Proposal 3 is accepted? Explain.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 21 Solutions
Financial And Managerial Accounting
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





