
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 51P
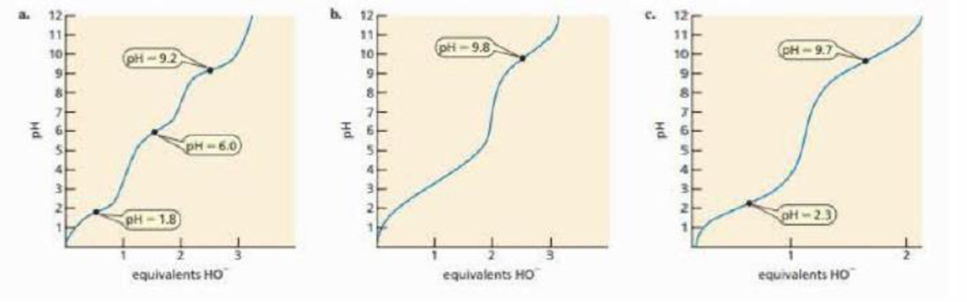
A titration curve is a plot of the pH of a solution as a function of added equivalents of hydroxide ion. As hydroxide ion is added to the aqueous solution, the pH increases because hydroxide ion removes protons from the solution. The pH flattens out when hydroxide ion can remove a proton from an ionziable group of an amino acid rather than a proton from the solution. Identify the amino acids that give the titration curves below.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
b.
H3C
Br
-CEN
H3C
Draw the most likely mechanism for the following
Draw the most likely mechanism for the following
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 21.1 - a. Explain why, when the imidazole ring of...Ch. 21.2 - a. Which isomer(R)-alanine or (S)-alanineis...Ch. 21.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 21.3 - Draw the predominant form for glutamate in a...Ch. 21.3 - a. Why is the pKa of the glutamate side chain...Ch. 21.4 - Calculate the pI of each of the following amino...Ch. 21.4 - a. Which amino acid has the lowest pI value? b....Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 12P
Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 21.4 - Explain why the pI of lysine is the average of the...Ch. 21.5 - What aldehyde is formed when valine is treated...Ch. 21.5 - Prob. 16PCh. 21.5 - Prob. 17PCh. 21.5 - Prob. 18PCh. 21.5 - Prob. 19PCh. 21.6 - Why is excess ammonia used in the preceding...Ch. 21.6 - Prob. 21PCh. 21.6 - What amino acid is formed using the...Ch. 21.6 - Prob. 23PCh. 21.6 - What amino acid is formed when the aldehyde used...Ch. 21.7 - Esterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the...Ch. 21.8 - Draw the tetrapeptide Ala-Thr-Asp-Asn and indicate...Ch. 21.8 - Draw the resonance contributors of the peptide...Ch. 21.8 - Which bonds in the backbone of a peptide can...Ch. 21.9 - An opioid pentapeptide has the following...Ch. 21.9 - What is the configuration about each of the...Ch. 21.9 - Glutathione is a tripeptide whose function is to...Ch. 21.10 - What dipeptides would be formed by heating a...Ch. 21.10 - Suppose you are trying to synthesize the dipeptide...Ch. 21.10 - Show the steps in the synthesis of the...Ch. 21.10 - a. Calculate the overall yield of bradykinin when...Ch. 21.11 - Show the steps in the synthesis of the...Ch. 21.13 - Prob. 37PCh. 21.13 - In determining the primary structure of insulin,...Ch. 21.13 - A decapeptide undergoes partial hydrolysis to give...Ch. 21.13 - Explain why cyanogen bromide does not cleave on...Ch. 21.13 - Indicate the peptides produced from cleavage by...Ch. 21.14 - Prob. 43PCh. 21.14 - Three peptides were obtained from a trypsin...Ch. 21.14 - Prob. 45PCh. 21.15 - How would a protein that resides in the nonpolar...Ch. 21.16 - a. Which would have the greatest percentage of...Ch. 21.17 - When apples that have been cut are exposed to...Ch. 21 - Glycine has pK2 values of 2.34 and 9.60. At what...Ch. 21 - Prob. 50PCh. 21 - A titration curve is a plot of the pH of a...Ch. 21 - Prob. 52PCh. 21 - Aspartame (its structure is on page 1007) has a pl...Ch. 21 - Draw the form of aspartate that predominates at...Ch. 21 - Show how phenylalanine can be prepared by...Ch. 21 - A professor was preparing a manuscript for...Ch. 21 - What aldehydes are formed when the following amino...Ch. 21 - Prob. 58PCh. 21 - Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide...Ch. 21 - Prob. 60PCh. 21 - Prob. 61PCh. 21 - Which is the more effective buffer at...Ch. 21 - Identify the location and type of charge on the...Ch. 21 - Draw the product obtained when a lysine side chain...Ch. 21 - After the polypeptide shown below was treated with...Ch. 21 - Treatment of a polypeptide with 2-mercaptoethanol...Ch. 21 - Show how aspartame can be synthesized using DCCD.Ch. 21 - -Amino acids can be prepared by treating an...Ch. 21 - Reaction of a polypeptide with carboxypeptidase A...Ch. 21 - a. How many different octapeptides can be made...Ch. 21 - Glycine has pKa values of 2.3 and 9.6. Do you...Ch. 21 - A mixture of 15 amino acids gave the fingerprint...Ch. 21 - Write the mechanism for the reaction of an amino...Ch. 21 - Prob. 74PCh. 21 - Show how valine can be prepared by a. a...Ch. 21 - The primary structure of -endorphin, a peptide...Ch. 21 - A chemist wanted to test his hypothesis that the...Ch. 21 - Propose a mechanism for the rearrangement of the...Ch. 21 - A normal polypeptide and a mutant of the...Ch. 21 - Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Biomolecules - Protein - Amino acids; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySNVPDHJ0ek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY