
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
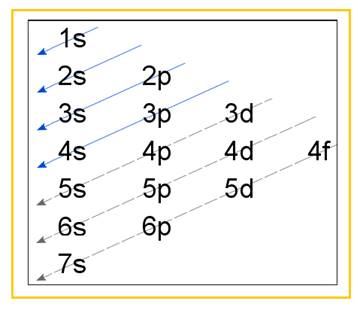
Figure 1
The terms
(a)
Answer to Problem 23E
Electronic configuration of Ti -
Electronic configuration of Ti2+ -
Electronic configuration of Ti4+ -
Explanation of Solution
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Argon till
Ti2+ is formed when Titanium loses two electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Ti2+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Argon till
Ti4+ is formed when Titanium loses four electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Ti4+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Argon till
(b)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
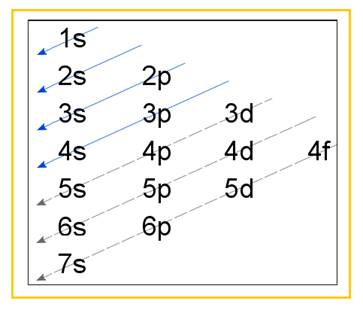
Figure 1
The terms
(b)
Answer to Problem 23E
Electronic configuration of Re -
Electronic configuration of Re2+ -
Electronic configuration of Re3+ -
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Rhenium is
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Re2+ is formed when Rhenium loses two electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Re2+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Re3+ is formed when Rhenium loses three electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Re2+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
(c)
Interpretation:
Electronic configuration of the following metals has to be written –
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom represents the arrangement of electrons in various energy levels. The electrons are arranged in increasing order of energy levels according to Aufbau principle. It is pictorially represented as –
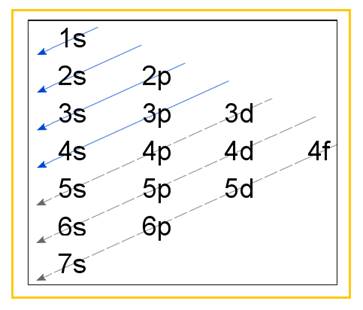
Figure 1
The terms
(c)
Answer to Problem 23E
Electronic configuration of Ir -
Electronic configuration of Ir2+ -
Electronic configuration of Ir3+ -
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Iridium is
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Ir2+ is formed when Iridium loses two electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Ir2+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Ir3+ is formed when Iridium loses three electrons. Accordingly the electronic configuration of Ir3+ is –
The above electronic configuration corresponds to that of Xenon till
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry (AP Edition)
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





