
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the products are to be drawn for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 21.39P
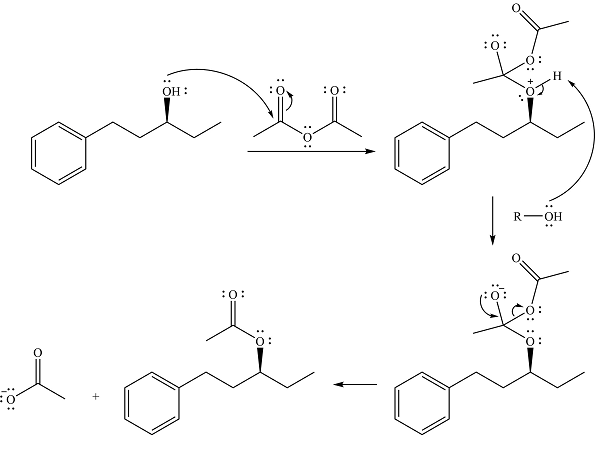
The complete mechanism is
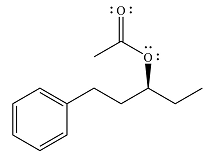
The product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
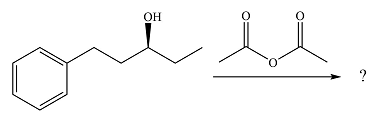
The given reaction is
Alcohol is a weak nucleophile and adds to one of the carbonyl carbons of acetic anhydride to produce a protonated ether linkage. The carbonyl oxygen becomes negatively charged as a result of the
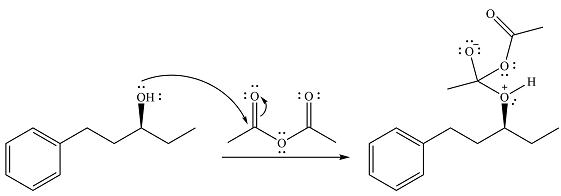
In the next step, the positively charged oxygen is deprotonated by another molecule of the alcohol.
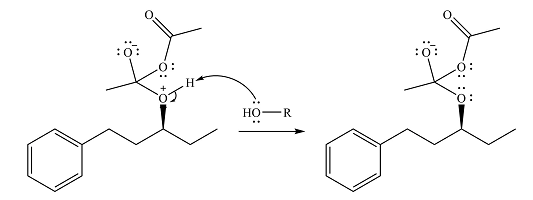
The final step is nucleophilic elimination of acetate anion as a result of the lone pair of the negatively charged oxygen moving to reform the carbonyl group.
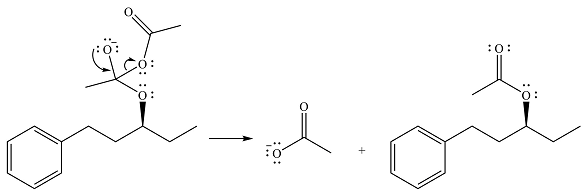
Thus, the complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as

The product of the reaction is

The product and mechanism of the given reaction are determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the products are to be drawn for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The complete mechanism is
The product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
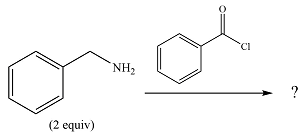
The
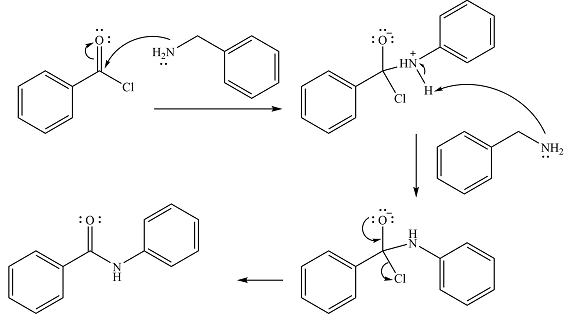
In the first step, it acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride to produce a protonated amine linkage. The
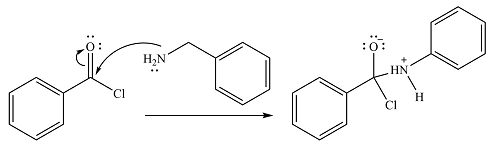
The protonated amine is then deprotonated by a second molecule of the amine.
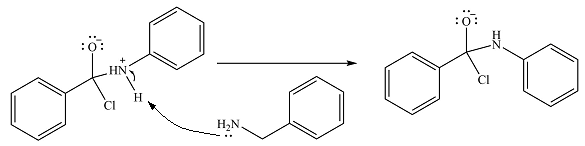
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the chloride and forming the product.
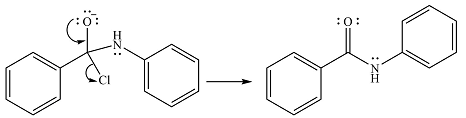
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

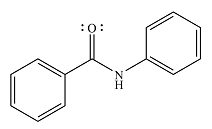
And the product of the reaction will be

The product and mechanism of the given reaction are determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the products are to be drawn for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
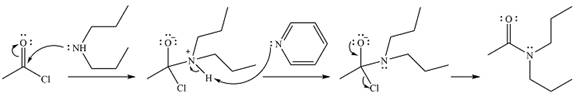
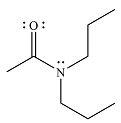
The product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
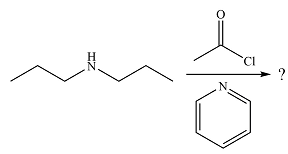
The amine will act as a nucleophile and add to the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride in the first step to form a protonated amine linkage. The
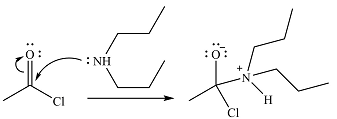
The protonated amine is deprotonated in the second step by the added base, pyridine.
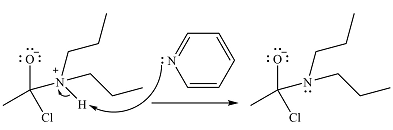
Finally, one lone pair on the negatively charged oxygen moves back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the leaving group chloride and forming the final product.
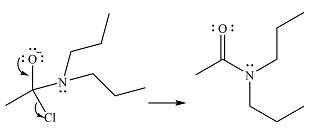
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

And the product of the reaction will be

The product and mechanism of the given reaction are determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the products are to be drawn for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), particularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.39P
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
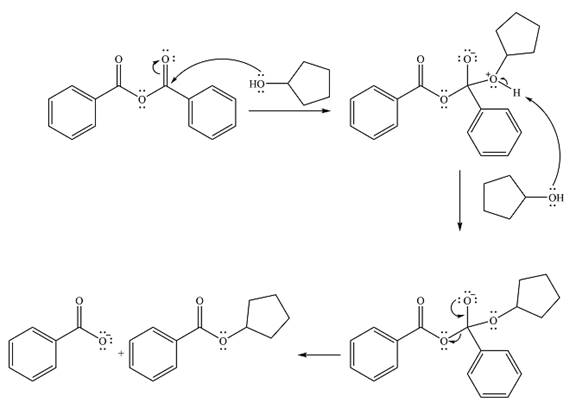
The product of the reaction is
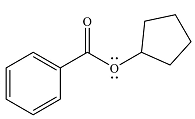
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
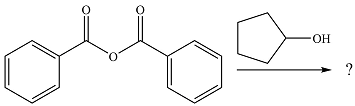
The alcohol is a weak nucleophile. It will add to one of the carbonyl carbons in the anhydride to produce a protonated intermediate.
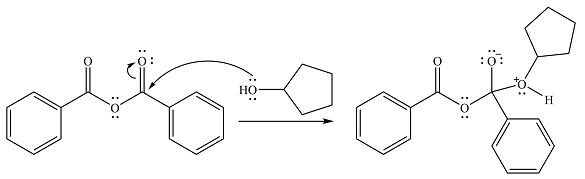
In the seconds step, this intermediate will be deprotonated by a second molecule of the alcohol.
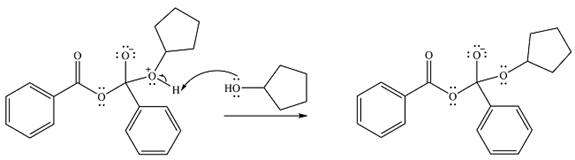
Finally, one lone pair from the negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl, eliminating the leaving group benzoate in the process and forming the product.
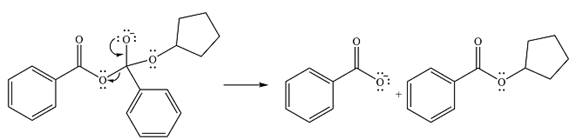
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

And the product of the reaction will be
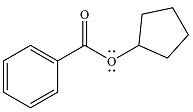
The product and mechanism of the given reaction are determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward
- 1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forwardLi+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





