Problem 1CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. Any set of ordered pairs is called a/an... Problem 2CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. A set of ordered pairs in which each... Problem 3CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. The notation f (x) describes the value... Problem 4CVC: True or false: y=x21 1 defines y as a function of x ____ Problem 5CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true.
5. True or false: defines y as a... Problem 6CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. If f(x)=x25x+4, we can find f(x+6) by... Problem 7CVC: Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true.
7. The graph of a function is the graph... Problem 8CVC: 8. If any vertical line intersects a graph____ the graph does not define y as a/an ____ of x.
Problem 9CVC: The shaded set of numbers shown on the x-axis can be expressed in interval notation as____. This set... Problem 10CVC Problem 11CVC Problem 12CVC: 12. True or false: A function can have more than one y-intercept.____
Problem 1E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 2E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 3E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 4E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 5E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 6E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 7E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 8E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 9E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 10E: In Exercises 1-10, determine whether each relation is a function. Give the domain and range for each... Problem 11E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x+y=16 Problem 12E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x+y=25 Problem 13E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x2+y=16 Problem 14E: In Exercises 11-26. determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x2+y=25 Problem 15E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x2+y2=16 Problem 16E: In Exercises 11-26. determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x2+y2=25 Problem 17E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x.
17.
Problem 18E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x.
18.
Problem 19E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. y=x+4 Problem 20E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. y=x+4 Problem 21E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x.
21.
Problem 22E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x+y3=27 Problem 23E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. xy+2y=1 Problem 24E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. xy5y=1 Problem 25E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. xy=2 Problem 26E: In Exercises 11-26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x.
26.
Problem 27E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 28E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 29E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 30E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 31E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 32E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 33E: In Exercises 27-38 evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 34E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 35E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 36E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given value. the independent variable and... Problem 37E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 38E: In Exercises 27-38, evaluate each function at the given values of the independent variable and... Problem 39E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 40E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system... Problem 41E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 42E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system... Problem 43E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 44E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g. In the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 45E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 46E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 47E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 48E Problem 49E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 50E: In Exercises 39-50, graph the given functions, f and g, in the same rectangular coordinate system.... Problem 51E Problem 52E: In Exercises 51-54, graph the given square root functions, f and g, in the same rectangular... Problem 53E: In Exercises 51-54, graph the given square root functions, f and g, in the same rectangular... Problem 54E Problem 55E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x.
55.... Problem 56E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 57E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 58E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of... Problem 59E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 60E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 61E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 62E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x.
Problem 63E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x. Problem 64E: In Exercises 55-64, use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x.
Problem 65E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value.
65.
Problem 66E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value.
66. f(2)
Problem 67E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value.
67. f(4)
Problem 68E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value. f(4) Problem 69E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value.
69.
Problem 70E: In Exercises 65-70, use the graph of f to find each indicated function value. f(1) Problem 71E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76. Find g(4). Problem 72E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76. Find g (2). Problem 73E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76.
73. Find .
Problem 74E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76.
74. Find g (10).
Problem 75E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76. For what value of x is g(x)=1? Problem 76E: Use the graph of g to solve Exercises 71-76.
76. For what value of x is
Problem 77E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 78E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 79E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 80E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 81E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 82E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 83E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 84E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 85E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 86E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 87E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 88E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 89E Problem 90E: In Exercises 77-92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b, the function's range: c.... Problem 91E Problem 92E Problem 93E Problem 94E: In Exercises 93-94,let and
94. Find and .
Problem 95E Problem 96E Problem 97E Problem 98E Problem 99E Problem 100E Problem 101E: The bar graph shows your chances of surviving to various ages once you reach 60.
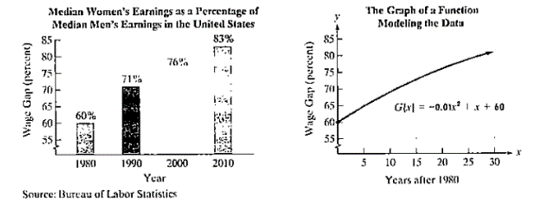
The... Problem 102E: The bar graph shows your chances of surviving to various ages once you reach 60. The functions... Problem 103E Problem 104E: The wage gap is used to compare the status of women's comings relative to men's. The wage gap is... Problem 105E: In Exercises 105-108, you will be developing functions that model given conditions. A company that... Problem 106E: In Exercises 105-108, you will be developing functions that model given conditions.
106. A car was... Problem 107E: In Exercises 105-108, you will be developing functions that model given conditions.
107. You commute... Problem 108E Problem 109E Problem 110E Problem 111E Problem 112E Problem 113E Problem 114E Problem 115E: Explain how to identify the domain and range of a function from its graph. Problem 116E Problem 117E Problem 118E: Make Sense? In Exercises 118-121, determine whether each statement makes sense or does not make... Problem 119E Problem 120E Problem 121E Problem 122E Problem 123E Problem 124E Problem 125E Problem 126E: 126. If find .
Problem 127E Problem 128E: If f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y) and f(1)=3, find f(2), f(3), and f(4). Is f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y) for all functions? Problem 129E Problem 130E: ACHIEVING SUCCESS
According to the Ebbinghaus relention model, you forget 50% of what you learn... Problem 131E: ACHIEVING SUCCESS
According to the Ebbinghaus retention model, you forget 50% of what you learn... Problem 132E Problem 133E Problem 134E: Exercises 132-134 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Simplify... format_list_bulleted


 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning




