
Concept explainers
1.
To prepare:
The sales budget of D Company.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the sales budget of D Company as shown below.
| Sales Budget | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particulars | January ($) |
February ($) |
March ($) |
Total ($) |
| Sales unit (A) | 7,000 | 9,000 | 11,000 | 27,000 |
| Selling price per unit (B) | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 |
| Total sales |
385,000 | 495,000 | 605,000 | 1,485,000 |
Table (1)
2.
To prepare:
The purchase budget of D Company.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the purchase budget of D Company as shown below.
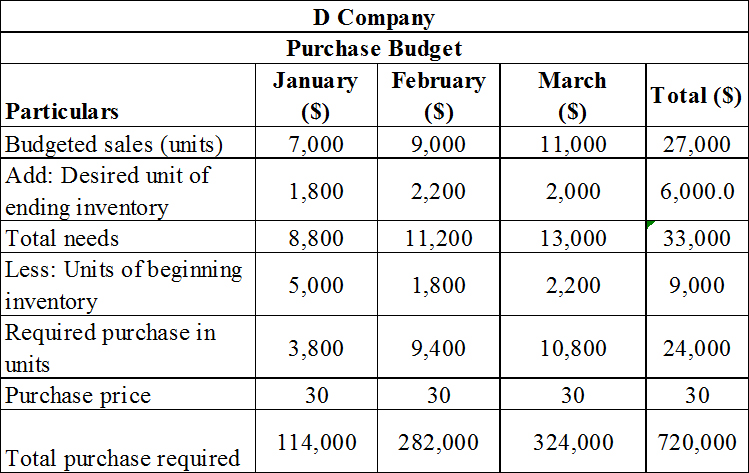
Table (2)
3.
To prepare:
The selling expense budget of D Company.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the selling expense budget of D Company as shown below.
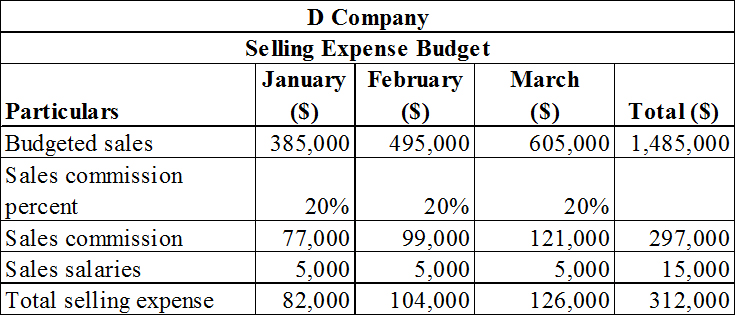
Table (3)
4.
To prepare:
The general and administrative expense budget of D Company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the general and administrative expense budget of D Company as shown below.
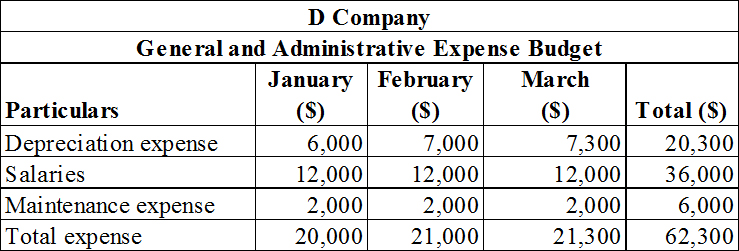
Table (4)
5.
To prepare:
The capital expenditure budget of D Company.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the capital expenditure budget of D Company as shown below.
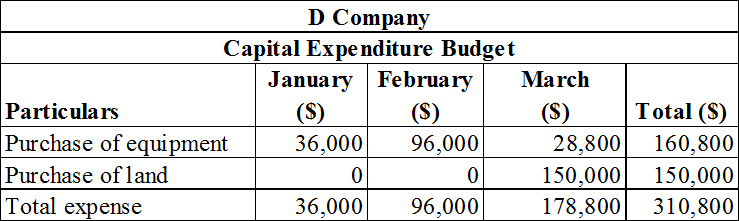
Table (5)
6.
To prepare:
The
6.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the cash budget of D Company as shown below.
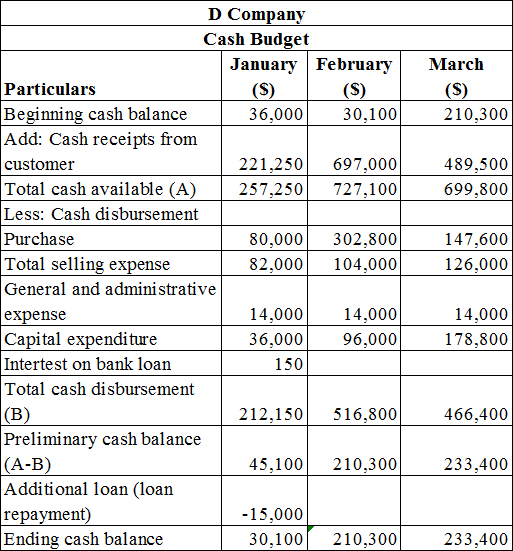
Table (6)
Working notes:
1. Calculate the expected cash collection.
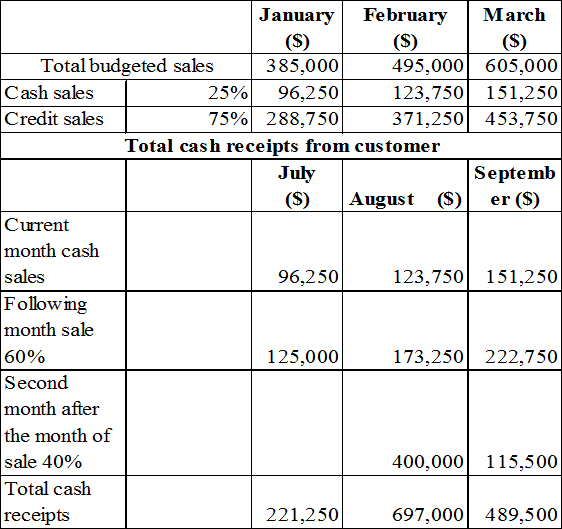
Table (7)
2. Calculate the cash payment from purchase.
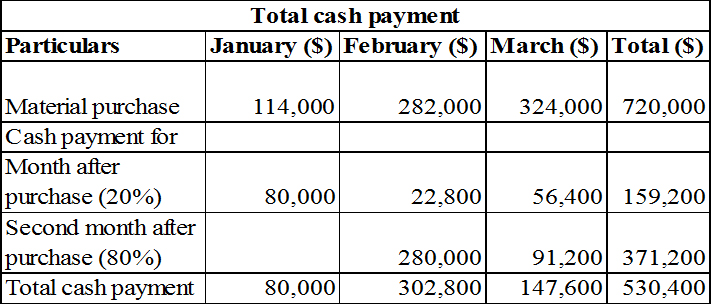
Table (8)
7.
To prepare:
The
7.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the income statement as shown below.
| Income Statement | ||
|---|---|---|
| For three months ended March 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Sales | 1,485,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold |
810,000 | |
| Gross profit | 675,000 | |
| Less: Operating expenses | ||
| Total selling expense | 312,000 | |
| General administrative salary | 62,300 | |
| Interest on bank loan | 150 | |
| Total operating expense | 374,450 | |
| Earnings before taxes (A) | 300,550 | |
| Less: Income tax | 120,220 | |
| Net income | 180,330 | |
Table (9)
Thus, the budgeted net income of D Company is $180,330.
8.
To prepare:
The budgeted
8.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the balance sheet for the first quarter as shown below.
| Balance sheet | ||
|---|---|---|
| For three months ended March 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | 233,400 | |
| Accounts receivable | 602,250 | |
| Inventory | 60,000 | |
| Total current assets | 895,650 | |
| Equipment | 523,000 | |
| Land | 150,000 | |
| Net equipment | ||
| Total Assets | 1,568,650 | |
| Liabilities and |
||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | 549,600 | |
| Income tax payable | 120,220 | |
| Total liabilities | 669,820 | |
| Stockholder’s Equity | ||
| Common Stock | 472,500 | |
| 426,330 | ||
| Total stockholders’ equity | 898,830 | |
| Total Liabilities and stockholder’s equity | 1,568,650 | |
Table (10)
Working note:
Calculate the retained earnings.
Hence, the total amount appearing on the balance sheet of D Company as on March 31, 2016 is $1,568,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting: Information for Decisions
- Please show me the valid approach to solving this financial accounting problem with correct methods.arrow_forwardI need guidance in solving this financial accounting problem using standard procedures.arrow_forwardCan you help me find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem using valid principles?arrow_forward
- Jazz Corporation owns 50 percent of the Vanderbilt Corporation stock. Vanderbilt distributed a $10,000 dividend to Jazz Corporation. Jazz Corporation's taxable income before the dividend was $100,000. What is the amount of Jazz's dividends received deduction on the dividend it received from Vanderbilt Corporation?arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardBillie Bob purchased a used camera (five-year property) for use in his sole proprietorship in the prior year. The basis of the camera was $2,400. Billie Bob used the camera in his business 60 percent of the time during the first year. During the second year, Billie Bob used the camera 40 percent for business use. Calculate Billie Bob’s depreciation deduction during the second year, assuming the sole proprietorship had a loss during the year. (Billie Bob did not place the asset in service in the last quarter.arrow_forwardAccording to the income tax of Jamaica, a person is a resident if he (a) lives in the country, (b) resides in the country for not more than 183 days, (c) lives in a country 183 days or longer in any one year, or (d) lives in a country for 3 consecutive months in any one year.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





