
(a)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction:
Ocean acidification: The increase in concentration of carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere leads to ocean acidification. The amount is increasing day by day and this increase will lead to higher concentrations of dissolved
The concentration of hydronium ion is a key factor for many biochemical reactions. So variation may affect the organisms in the oceans.
The relationship between ocean
(a)
Answer to Problem 48GQ
The
Explanation of Solution
If the concentration of dissolved
The graph showing the fraction of species in the solution as a function of
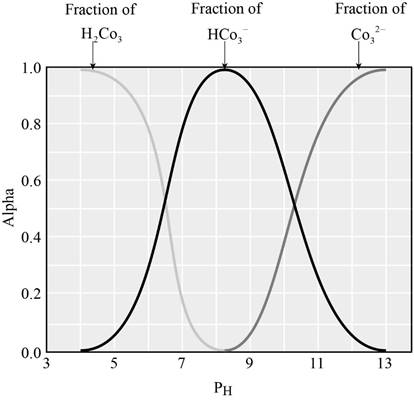
From the graph we can identify the
The fraction of dissociation will be 0.50 when the concentration of both the species will be equal.
The
(b)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction:
Ocean acidification: The increase in concentration of carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere leads to ocean acidification. The amount is increasing day by day and this increase will lead to higher concentrations of dissolved
The concentration of hydronium ion is a key factor for many biochemical reactions. So variation may affect the organisms in the oceans.
The relationship between ocean
(b)
Answer to Problem 48GQ
The
Explanation of Solution
If the concentration of dissolved
The graph showing the fraction of species in the solution as a function of
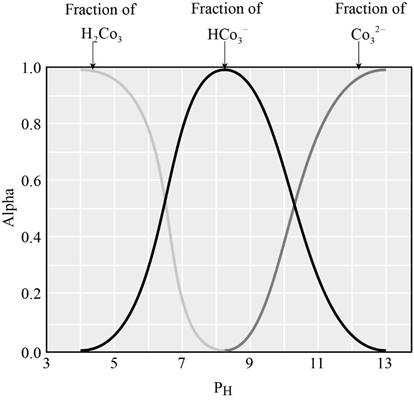
From the graph we can identify the
The fraction of dissociation will be 0.50 when the concentration of both the species will be equal.
The
(c)
Interpretation: The predominant species in the solution when the
Concept introduction:
Ocean acidification: The increase in concentration of carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere leads to ocean acidification. The amount is increasing day by day and this increase will lead to higher concentrations of dissolved
The concentration of hydronium ion is a key factor for many biochemical reactions. So variation may affect the organisms in the oceans.
The relationship between ocean
(c)
Answer to Problem 48GQ
The predominant species in the solution when the
Explanation of Solution
If the concentration of dissolved
The graph showing the fraction of species in the solution as a function of
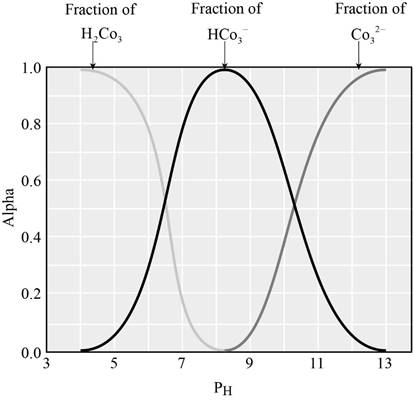
When the
From the graph it is clear that, the predominant species when the
(d)
Interpretation: The predominant species in the solution when the
Concept introduction:
Ocean acidification: The increase in concentration of carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere leads to ocean acidification. The amount is increasing day by day and this increase will lead to higher concentrations of dissolved
The concentration of hydronium ion is a key factor for many biochemical reactions. So variation may affect the organisms in the oceans.
The relationship between ocean
(d)
Answer to Problem 48GQ
The predominant species in the solution when the
Explanation of Solution
If the concentration of dissolved
The graph showing the fraction of species in the solution as a function of
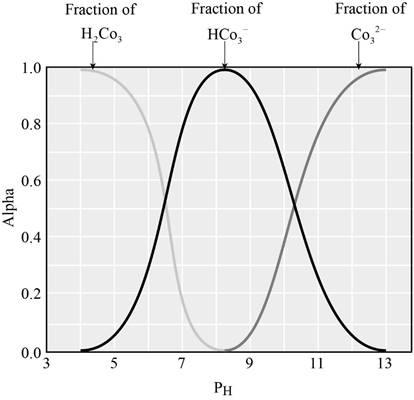
When the
From the graph it is clear that, the predominant species when the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
CHEMISTRY+CHEM...(LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction of XeF4 with H2O? Group of answer choices H2XeF2 H2XeF4 XeO3 H2XeOarrow_forwardWhile noble gas exerts the strongest London (dispersion) forces on neighboring atoms? Group of answer choices Xe Ar Kr Nearrow_forwardWhich of the following elements is corrosive to your skin due to that element breaking down C=C bonds? Group of answer choices fluorine iodine bromine chlorinearrow_forward
- What the best source of sulfide to use on a small scale in the lab? Group of answer choices thiourea H2S NaHS Na2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about sulfur is FALSE? Group of answer choices H2S is the product of an oxygen-depleted ecosystem. In the acid mine drainage reaction, FeS2 is a product. One allotrope of sulfur has the formula S20. In the environment, bacterial oxidation can convert S2− to elemental S or SO42−.arrow_forwardOf the following choices, which is the best reason that most materials DON'T spontaneously combust even though our atmosphere is about 21% oxygen? Group of answer choices The reduction of O2 in the gas phase (O2 + e− → O2−) is spontaneous. The reduction of O2 in acid solution (O2 + H+ + e− → HO2(aq)) is spontaneous. O2 is not a reactant in combustion. The O2 bond dissociation energy is 494 kJ/mol, leading to a high activation energy for combustion.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning




