
Concept explainers
A manufacturer of a brand of inexpensive felt-tip pens maintains a production process that produces 10,000 pens per day, In order to maintain the highest quality of this product, the manufacturer guarantees free replacement of any defective pen sold, Each defective pen produced costs 20 cents for the manufacturer to replace, Based on past experience, four rates of producing defective pens are possible:
Very low-
Low-
Moderate-
High-
The manufacturer can reduce the late of defective pens produced by having a mechanic �x the machines at the end of each day. This mechanic can reduce the rate to
A payoff table based on the daily production of 10,000 pens, indicating the replacement costs
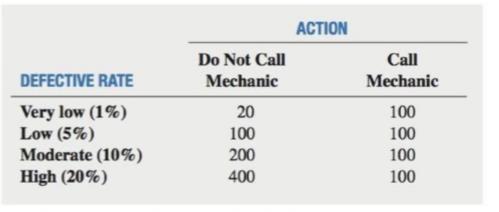
Based on past experience, each defective rate is assumed to be equally likely to occur.
a. Construct a decision tree.
b. Construct an opportunity loss table.
c. Compute the expected monetary value (EMV) for calling and for not calling the mechanic.
d. Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for calling and for not calling the mechanic.
e. Explain the meaning of the
f. Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for calling and not calling the mechanic.
g. Based on the results of (c), (d), and (f), should the company call the mechanic? Why?
h. At the end of a day’s production, a sample of 15 pens is selected, and 2 are defective. Revise the prior probabilities in light of this sample information.
i. Use the revised probabilities in (h) to repeat (c) through (g).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Basic Business Statistics Student Value Edition Plus NEW MyLab Statistics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (13th Edition)
- For context, the images attached below are a question from a June, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below (question and related graph) are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the images attached below are from a February 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- For context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image below is from a January 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forwardFor context, the image provided below is a question from a September, 2024 past paper in statistical modelingarrow_forward
- Section 2.2 Subsets 71 Exercise Set 2.2 Practice Exercises In Exercises 1-18, write or in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. 1. {1, 2, 5} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 2. {2, 3, 7} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} 3. {-3, 0, 3} {-4,-3,-1, 1, 3, 4} 4. {-4, 0, 4} 5. {Monday, Friday} {-3, -1, 1, 3} {Saturday, Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday} 6. {Mercury, Venus, Earth} {Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter} 7. {x/x is a cat} {xx is a black cat} {x|x is a pure-bred dog} ibrary mbers, ause the entire sual 8. {xx is a dog} 9. (c, o, n, v, e, r, s, a, t, i, o, n} {v, o, i, c, e, s, r, a, n, t, o, n} 10. [r, e, v, o, l, u, t, i, o, n} {t, o, l, o, v, e, r, u, i, n} 33. A = {x|x E N and 5 < x < 12} B = {x|x E N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 11} A_ B 34. A = {x|x = N and 3 < x < 10} B = A. {x|x = N and 2 ≤ x ≤ 8} B 35. Ø {7, 8, 9,..., 100} 36. Ø _{101, 102, 103, . . ., 200} 37. [7, 8, 9,...} 38. [101, 102, 103, ...} 39. Ø 40. { } { } e In Exercises 41-54, determine whether each statement is true or false. If…arrow_forwardA = 5.8271 ± 0.1497 = B 1.77872 ± 0.01133 C=0.57729 ± 0.00908 1. Find the relative uncertainty of A, B, and C 2. Find A-3 3. Find 7B 4. Find A + B 5. Find A B-B - 6. Find A * B 7. Find C/B 8. Find 3/A 9. Find A 0.3B - 10. Find C/T 11. Find 1/√A 12. Find AB²arrow_forwardWhy charts,graphs,table??? difference between regression and correlation analysis.arrow_forward
- You’re scrolling through Instagram and you notice that a lot of people are posting selfies. This piques yourcuriosity and you want to estimate the percentage of photos on Instagram that are selfies.(a) (5 points) Is there a “ground truth” for the percentage of selfies on Instagram? Why or why not?(b) (5 points) Is it possible to estimate the ground truth percentage of selfies on Instagram?Irrespective of your answer to the previous question, you decide to pull up n = 250 randomly chosenphotos from your friends’ Instagram accounts and find that 32% of these photos are selfies.(c) (15 points) Determine which of the following is an observation, a variable, a sample statistic (valuecalculated based on the observed sample), or a population parameter.• A photo on Instagram.• Whether or not a photo is a selfie.• Percentage of all photos on Instagram that are selfies.• 32%.(d) (5 points) Based on the sample you collected, do you think 32% is a reliable ballpark estimate for theground truth…arrow_forwardCan you explain this statement below in layman's terms? Secondary Analysis with Generalized Linear Mixed Model with clustering for Hospital Center and ICUvs Ward EnrolmentIn a secondary adjusted analysis we used generalized linear mixed models with random effects forcenter (a stratification variable in the primary analyses). In this analysis, the relative risk for the primaryoutcome of 90-day mortality for 7 versus 14 days of antibiotics was 0.90 (95% Confidence Interval [CI]0.78, 1.05).arrow_forwardIn a crossover trial comparing a new drug to a standard, π denotes the probabilitythat the new one is judged better. It is desired to estimate π and test H0 : π = 0.5against H1 : π = 0.5. In 20 independent observations, the new drug is better eachtime.(a) Find and plot the likelihood function. Give the ML estimate of π (Hint: youmay use the plot function in R)arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning




