
Concept explainers
Credit Policy at Howlett Industries
Sterling Wyatt, the president of Howlett Industries, has been exploring ways of improving the company’s financial performance. Howlett manufactures and sells office equipment to retailers. The company’s growth has been relatively slow in recent years, but with an expansion in the economy, it appears that sales may increase more rapidly in the future. Sterling has asked Andrew Preston, the company’s treasurer, to examine Howlett’s credit policy to see if a change can help increase profitability.
The company currently has a policy of net 30. As with any credit sales, default rates are always of concern. Because of Howlett’s screening and collection process, the default rate on credit is currently only 1.6 percent. Andrew has examined the company’s credit policy in relation to other vendors, and he has found three available options.
The first option is to relax the company’s decision on when to grant credit. The second option is to increase the credit period to net 45, and the third option is a combination of the relaxed credit policy and the extension of the credit period to net 45. On the positive side, each of the three policies under consideration would increase sales. The three policies have the drawbacks that default rates would increase, the administrative costs of managing the firm’s receivables would increase, and the receivables period would increase. The effect of the credit policy change would impact all four of these variables to different degrees. Andrew has prepared the following table outlining the effect on each of these variables:
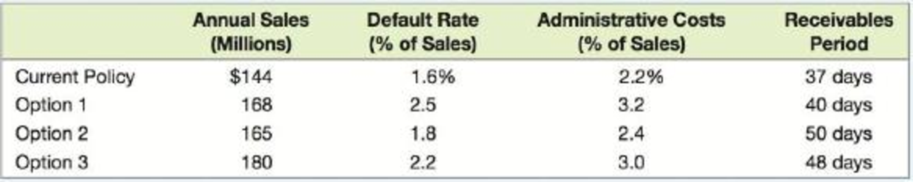
Howlett’s variable costs of production are 45 percent of sales, and the relevant interest rate is a 6 percent effective annual rate.
1. Which credit policy should the company use?
To evaluate: The credit policy of the firm.
Introduction:
Credit policy refers to a set of procedures that include the terms and conditions for providing goods on credit and principles for making collections.
Answer to Problem 1M
Company H should select Option 1, because it has the highest net present value (NPV) of $34,226,117.98 compared to other two options.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average sales under current policy is $394,520.55.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under current policy:
Hence, the variable costs under current policy is $177,534.25.
The formula to calculate the average daily default under current policy:
Hence, the average daily default under current policy is $6312.33.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under current policy:
Hence, the average administrative costs under current policy is $8,679.45.
The formula to calculate the interest rate for the collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.61%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under current policy:
Hence, the NPV under current policy is $32,936,321.48.
Option 1:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 1:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 1 is $460,273.97.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 1:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 1 is $207,123.29.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 1:
Hence, average daily default under option 1 is $11,506.85.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 1:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 1 is $14,728.77.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.659%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under option 1:
Hence, the NPV under option 1 is $34,226,117.98.
Option 2:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 2:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 2 is $452,054.79.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 2:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 2 is $203,424.66.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 2:
Hence, the average daily default under option 2 is $8,136.99.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 2:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 2 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.852%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 2:
Hence, the NPV under option 2 is $27,632,189.89.
Option 3:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 3 is $493,150.68.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 3:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 3 is $221,917.81.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 3:
Hence, the average daily default under option 3 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 3:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 3 is $14,794.52.
The formula to calculate interest rate for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.792%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 3:
Hence, the NPV under option 3 is $30,786,798.099.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance
- Nataro, Incorporated, has sales of $698,000, costs of $344,000, depreciation expense of $89,000, interest expense of $54,000, and a tax rate of 21 percent. What is the net income for this firm? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32. Net incomearrow_forwardGreenland is a small country with only listed stocks on its stock exchange. Using the following data create a market capitalisation index. Stock Price on Index Creation Number of Shares issued Day $45 300 B $70 500 C $18 600 D $11 900 If the value of the stock index is set at 100 on the index creation date, what will be the value of the index when stock prices are the following: Stock A Stock Price $35 B $78 C $15 D $9arrow_forwardLight Sweet Petroleum, Inc., is trying to evaluate a generation project with the following cash flows. If the company requires a return of 12 percent on its investments, what is the project's NPV? What are the IRRS for the project? Year 0 $ (45,000,000) Year 1 $ 71,000,000 Year 2 $ (15,000,000) Required return 12% Complete the following analysis. Do not hard code values in your calculations. Use a "Guess" of .99 to calculate the higher IRR and -.99 to calculate the lower IRR. You must use the built-in Excel functions to answer this question. NPV Higher IRR Lower IRRarrow_forward
- Bethesda Mining Company reports the following balance sheet information for 2021 and 2022: Assets Current assets 2021 BETHESDA MINING COMPANY Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2021 and 2022 Liabilities and Owners' Equity Current liabilities Accounts payable Notes payable 2021 $ 190,422 85,520 2022 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory $ 47,858 61,781 124,912 $ 60,783 82,139 190,747 Total $ 275,942 Total $ 234,551 $ 333,669 Long-term debt $ 238,000 Owners' equity Fixed assets Common stock and paid-in surplus Accumulated retained earnings $ 217,000 161,656 Net plant and equipment Total assets $ 658,047 $ 589,628 $ 378,656 $ 892,598 $ 923,297 Total liabilities and owners' equity $ 892,598 Total 2022 $ 198,111 137,088 $ 335,199 $ 174,750 $ 217,000 196,348 $ 413,348 $ 923,297 Based on the balance sheets given, calculate the following financial ratios for each year: Calculate the following financial ratios for each year: a. Current ratio. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round…arrow_forwardMary decides to buy a Treasury note futures contract for delivery of $100,000 face amount in September, at a price of 120′24.0. At the same time, Eric decides to sell a Treasury note futures contract if he can get a price of 120′24.0 or higher. The exchange, in turn, agrees to sell one Treasury note contract to Mary at 120′24.0 and to buy one contract from Eric at 120′24.0. The price of the Treasury note decreases to 120′10.5. Calculate Eric's balance on margin account. Assume that initial margin is $1,890. Please note that loss should be entered with minus sign. Round the answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- (2x76m A = + S) Waterfront Inc. wishes to borrow on a short-term basis without reducing its current ratio below 1.25. At present its current assets and current liabilities are $1,600 and $1,000 respectively. How much can Waterfront Inc. borrow?arrow_forwardExpected Standard Stock Return Beta Deviation A B 12% 16 0.75 1.25 28% 37 The market index has a standard deviation of 22% and the risk-free rate is 9%. Required: a. What are the standard deviations of stocks A and B? b. Suppose that we were to construct a portfolio with proportions: Stock A Stock B T-bills 0.25 0.50 0.25 Compute the expected return, beta, nonsystematic standard deviation, and standard deviation of the portfolio. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B What are the standard deviations of stocks A and B? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Stock A 0.33 % Stock B 0.46 %arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Could you explain what are the Biblical principles researchers that can follow to mitigate researcher bias? How to use of Biblical ethics to synthesize the literature to avoid misrepresentation of the literature? How researchers can demonstrate Biblical ethics when collecting and analyzing data?arrow_forwardThe manager of company A is thinking about adding an air conditioner to the office. The AC will cost $1630 to buy and install. The manager plans to use the AC for 5 years and each year's depreciation rate is 18% of the purchase price. The manager expects to sell the AC in 5 years for $880.The tax rate is 15% and the company's WACC is 15%. If the manager considers this purchase of AC as an investment, what is the NPV (keep two decimal places and assume that the AC will not affect the operations of the company)?arrow_forwardProblem 5-5 Calculating IRR A firm has a project with the following cash flows: Year Cash Flow 0 -$27,700 1 23 11,700 14,700 10,700 The appropriate discount rate is 18 percent. What is the IRR for this project? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) IRR %arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





