
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399920
Author: Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 1LTL
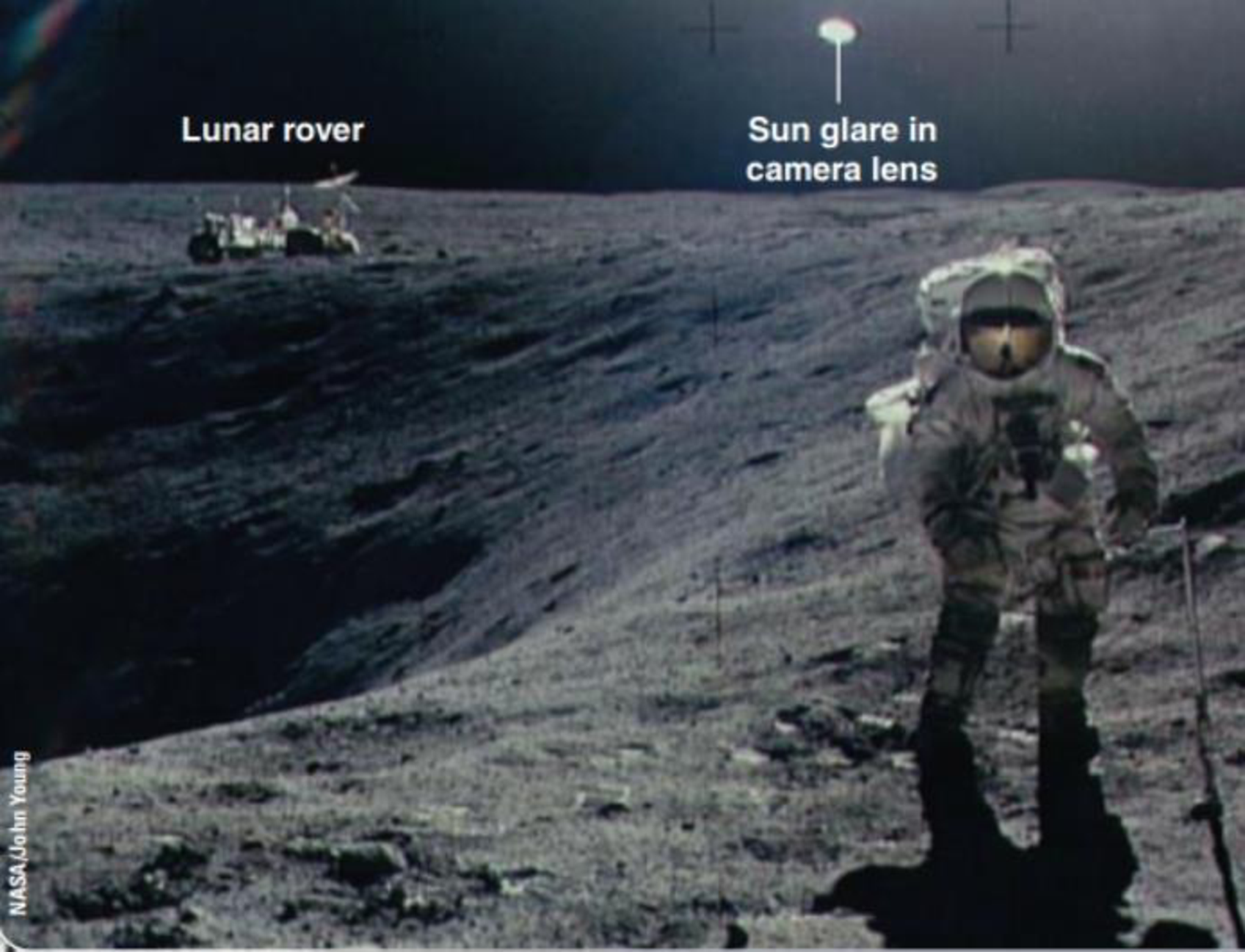
Look at the image of the astronaut on the Moon at the upper right of the right-hand page of the Concept Art: Impact Cratering. Can you tell whether the Sun's location is toward the upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left of the image? Is the relative time of day more like sunrise/sunset or high noon?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
please answer this asap!!!!
RT = 4.7E-30
18V
IT = 2.3E-3A+
12
38Ω
ли
56Ω
ли
r5
27Ω
ли
r3
28Ω
r4
> 75Ω
r6
600
0.343V
75.8A
Now figure out how much current in going through the r4
resistor.
|4 =
unit
And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r
resistor.
V4
=
unit
7
Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1
and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.
Chapter 20 Solutions
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 20 - How does the force of gravity cause tidal coupling...Ch. 20 - As viewed from Earth, how many times does the Moon...Ch. 20 - If the Moon is tidally coupled to Earth, is Earth...Ch. 20 - How can you determine the relative ages of the...Ch. 20 - From looking at images of the Moons near side, how...Ch. 20 - Why did the first Apollo missions land on the...Ch. 20 - Why do planetary scientists hypothesize that the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 8RQCh. 20 - Prob. 9RQCh. 20 - Prob. 10RQ
Ch. 20 - What is the most significant kind of erosion that...Ch. 20 - Provide evidence to support a hypothesis about...Ch. 20 - What evidence can you cite that the Moon had...Ch. 20 - What evidence would you expect to find on the Moon...Ch. 20 - How does the large-impact hypothesis explain the...Ch. 20 - Look at the Celestial Profiles for Earth, the...Ch. 20 - Look at the Celestial Profiles for the Moon and...Ch. 20 - Prob. 18RQCh. 20 - Look at the Celestial Profiles for Earth, the...Ch. 20 - Look at the Celestial Profiles for the Moon and...Ch. 20 - Why are features like the Moons maria not observed...Ch. 20 - What are the relative ages of the intercrater...Ch. 20 - What evidence can you give that Mercury has a...Ch. 20 - Why is it not surprising that there is no evidence...Ch. 20 - What evidence can you give that Mercury had...Ch. 20 - How are the histories of the Moon and Mercury...Ch. 20 - What property of the Moon and Mercury has resulted...Ch. 20 - Prob. 28RQCh. 20 - Look at the right top and bottom images in Figure...Ch. 20 - Calculate the escape velocity of the Moon from its...Ch. 20 - Prob. 3PCh. 20 - Why do small planets cool faster than large...Ch. 20 - The smallest detail visible through Earth-based...Ch. 20 - Prob. 6PCh. 20 - The trenches where Earths seafloor slips downward...Ch. 20 - An Apollo command module orbited the Moon about...Ch. 20 - Prob. 9PCh. 20 - What is the angular diameter of Mercury when it is...Ch. 20 - If you transmit radio signals to Mercury when...Ch. 20 - What is the wavelength of the most intense...Ch. 20 - Suppose you send a probe to land on Mercury, and...Ch. 20 - The smallest detail visible through Earth-based...Ch. 20 - Prob. 1SOPCh. 20 - Prob. 2SOPCh. 20 - Look at the image of the astronaut on the Moon at...Ch. 20 - In the photo shown here, astronaut Alan Bean works...Ch. 20 - Examine the shape of the horizon at the Apollo 17...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius cc and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What is the direction of the electric field for b<r<c? Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for c<r<d. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for r>d.arrow_forwardTICE D Conservation of Momentum 1. A 63.0 kg astronaut is on a spacewalk when the tether line to the shuttle breaks. The astronaut is able to throw a spare 10.0 kg oxygen tank in a direction away from the shuttle with a speed of 12.0 m/s, propelling the astronaut back to the shuttle. Assuming that the astronaut starts from rest with respect to the shuttle, find the astronaut's final speed with respect to the shuttle after the tank is thrown. 2. An 85.0 kg fisherman jumps from a dock into a 135.0 kg rowboat at rest on the west side of the dock. If the velocity of the fisherman is 4.30 m/s to the west as he leaves the dock, what is the final velocity of the fisher- man and the boat? 3. Each croquet ball in a set has a mass of 0.50 kg. The green ball, traveling at 12.0 m/s, strikes the blue ball, which is at rest. Assuming that the balls slide on a frictionless surface and all collisions are head-on, find the final speed of the blue ball in each of the following situations: a. The green…arrow_forwardThe 5.15 A current through a 1.50 H inductor is dissipated by a 2.15 Q resistor in a circuit like that in the figure below with the switch in position 2. 0.632/ C A L (a) 0.368/ 0+ 0 = L/R 2T 3r 4 (b) (a) What is the initial energy (in J) in the inductor? 0 t = L/R 2t (c) Эт 4t 19.89 ] (b) How long will it take (in s) the current to decline to 5.00% of its initial value? 2.09 S (c) Calculate the average power (in W) dissipated, and compare it with the initial power dissipated by the resistor. 28.5 1.96 x W X (ratio of initial power to average power)arrow_forward
- Imagine a planet where gravity mysteriously acts tangent to the equator and in the eastward directioninstead of radially inward. Would this force do work on an object moving on the earth? What is the sign ofthe work, and does it depend on the path taken? Explain by using the work integral and provide a sketch ofthe force and displacement vectors. Provide quantitative examples.arrow_forwardIf a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexamplearrow_forwardA futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their accelerationarrow_forward
- Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? 0.00897 × H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? 8.97 * ΜΩarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.212 cm from the center of a charged conducting sphere with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.598 cm from the center of the sphere? At a distance of 0.196 cmcm from the axis of a very long charged conducting cylinder with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.620 cm from the axis of the cylinder? At a distance of 0.202 cm from a large uniform sheet of charge, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 1.21 cm from the sheet?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399920
Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399944
Author:Michael A. Seeds
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Time Dilation - Einstein's Theory Of Relativity Explained!; Author: Science ABC;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuD34tEpRFw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY