
Concept explainers
Write the chemical formula and Lewis structure of the following each of which contains five carbon atoms:
(a) an
(b) an
(c) an
a)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula and Lewis structure of an alkane with five carbon atoms are to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The completely saturated hydrocarbon is known as an alkane.
The general molecular formula of alkane is
Answer to Problem 1E
Chemical formula:
Lewis structure:
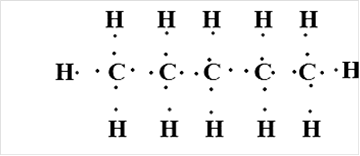
Pentane
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of alkane is
In case of five carbon atoms, the molecular formula of alkane is
- Lewis structures are the diagrams that show the bonding between the atoms of the molecules and existing lone pairs of electrons.
- Bonding electrons are those electrons which are shared between the atoms resulting in the formation of bond.
- Non-bonding electrons are the valence electrons of the atom which are not shared with another atom.
Number of valence electrons in a carbon atom = 4
Number of valence electrons in a hydrogen atom = 1
Total number of valence electrons =
= 32
Thus, Lewis structure of alkane having five carbon atoms is:
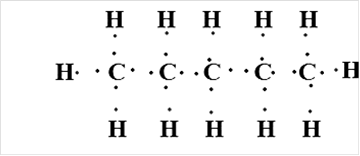 Or,
Or, 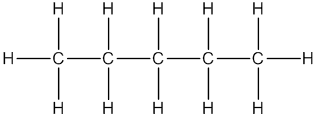
b)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula and Lewis structure of an alkene with five carbon atoms are to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The unsaturated hydrocarbon with one or more double bond is known as an alkene.
The general molecular formula of alkene is
Answer to Problem 1E
Chemical formula:
Lewis structure:
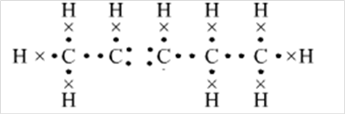
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of alkene is
In case of five carbon atoms, the molecular formula of alkene is
- Lewis structures are the diagrams that show the bonding between the atoms of the molecules and existing lone pairs of electrons.
- Bonding electrons are those electrons which are shared between the atoms resulting in the formation of bond.
- Non-bonding electrons are the valence electrons of the atom which are not shared with another atom.
Number of valence electrons in a carbon atom = 4
Number of valence electrons in a hydrogen atom = 1
Total number of valence electrons =
= 30
Thus, Lewis structure of alkene having five carbon atoms is:
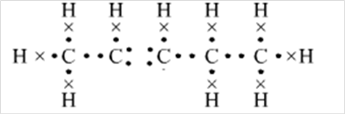 Or,
Or, 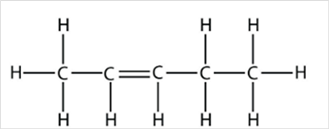
c)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula and Lewis structure of an alkyne with five carbon atoms are to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms.Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The unsaturated hydrocarbon with one or more triple bond is known as an alkyne.
The general molecular formula of alkyne is
Answer to Problem 1E
Chemical formula:
Lewis structure:
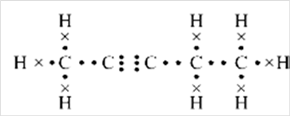
Explanation of Solution
The general formula of alkyne is
In case of five carbon atoms, the molecular formula of alkyne is
- Lewis structures are the diagrams that show the bonding between the atoms of the molecules and existing lone pairs of electrons.
- Bonding electrons are those electrons which are shared between the atoms resulting in the formation of bond.
- Non-bonding electrons are the valence electrons of the atom which are not shared with another atom.
Number of valence electrons in a carbon atom = 4
Number of valence electrons in a hydrogen atom = 1
Total number of valence electrons =
= 28
Thus, Lewis structure of alkyne having five carbon atoms is:
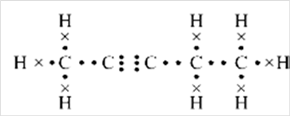 Or,
Or, 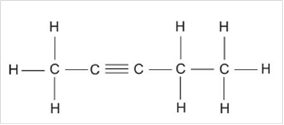
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- Which one? Ca2^- Na2^+ Si2^+ Mg2^- AI2^-arrow_forwardIn general, which is more polar, the stationary phase or the mobile phase? The stationary phase is always more polar The mobile phase is always more polar It depends on our choices for both stationary and mobile phase Their polarity doesn't really matter so we never consider itarrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism of aspirin synthesis in an basic medium and in a neutral medium, showing the attacks and the process for the formation of the product.arrow_forwardNa :S f. F NO2arrow_forwardQ1: For each molecule, assign each stereocenter as R or S. Circle the meso compounds. Label each compound as chiral or achiral. + CI OH woཡི།༠w Br H مه D CI ပ။ Br H, Br Br H₂N OMe R IN Ill N S H CI Br CI CI D OH H 1/111arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
