
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Name of the given organic compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to at least one hydrogen is said to be an
In order to give the name to the aldehyde group, the following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest)
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -al for an aldehyde group. The carbonyl group of an aldehyde appear at the end of the carbon chain so, the numbering start with carbon having aldehyde group.
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1meth
Carbon-2eth
Carbon-3prop
Carbon-4but
Carbon-5pent
Carbon-6hex
Carbon-7hept
Carbon-8oct
Carbon-9non
Carbon-10dec.
Answer to Problem 145CP
Name of the given compound is:
Heptanal.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
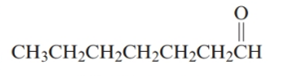
The parent chain in the given structure is heptane. Numbering is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets number 1.
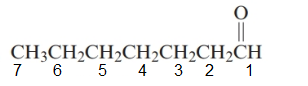
So, the name will be: heptanal.
(b)
Interpretation:
Name of the given organic compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to at least one hydrogen is said to be an aldehyde group, general representation of an aldehyde group is RCH=O or RCHO. Whereas the group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to two carbon atoms is said to be a ketone group, general representation of a ketone group is RCOR’.
In order to give the name to the aldehyde group, the following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -al for an aldehyde group. The carbonyl group of an aldehyde appear at the end of the carbon chain so, the numbering start with carbon having aldehyde group.
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1meth
Carbon-2eth
Carbon-3prop
Carbon-4but
Carbon-5pent
Carbon-6hex
Carbon-7hept
Carbon-8oct
Carbon-9non
Carbon-10dec.
Answer to Problem 145CP
Name of the given compound is:
3-ethyl-5-methylhexanal.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
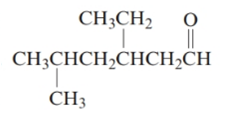
The parent chain in the given structure is hexane. Numbering is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets number 1.
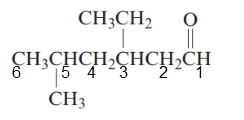
The substituent on 3 position is ethyl and on 5 position is methyl.
So, the name will be: 3-ethyl-5-methylhexanal.
(c)
Interpretation:
Name of the given organic compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to at least one hydrogen is said to be an aldehyde group, general representation of an aldehyde group is RCH=O or RCHO. Whereas the group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to two carbon atoms is said to be a ketone group, general representation of a ketone group is RCOR’.
In order to give the name to the ketone group, the following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -one for a ketone group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1meth
Carbon-2eth
Carbon-3prop
Carbon-4but
Carbon-5pent
Carbon-6hex
Carbon-7hept
Carbon-8oct
Carbon-9non
Carbon-10dec.
Answer to Problem 145CP
Name of the given compound is:
Hexan-3-one.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
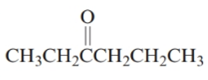
The parent chain in the given structure is hexane. Numbering is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets lower number that is 3.
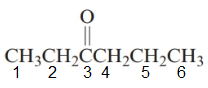
So, the name will be: Hexan-3-one.
(d)
Interpretation:
Name of the given organic compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to at least one hydrogen is said to be an aldehyde group, general representation of an aldehyde group is RCH=O or RCHO. Whereas the group that contains carboxyl group which is attached to two carbon atoms is said to be a ketone group, general representation of a ketone group is RCOR’.
In order to give the name to the ketone group, the following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -one for a ketone group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1meth
Carbon-2eth
Carbon-3prop
Carbon-4but
Carbon-5pent
Carbon-6hex
Carbon-7hept
Carbon-8oct
Carbon-9non
Carbon-10dec.
Answer to Problem 145CP
Name of the given compound is:
4, 5-dimethylhexan-3-one.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
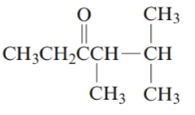
The parent chain in the given structure is hexane. Numbering is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets lower number that is 3.
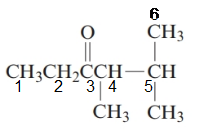
The substituent on 4 and 5 position is methyl.
So, the name will be: 4, 5-dimethylhexan-3-one.
(e)
Interpretation:
Name of the given organic compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which carboxy
In order to give the name to the carboxylic acid group, the following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1meth
Carbon-2eth
Carbon-3prop
Carbon-4but
Carbon-5pent
Carbon-6hex
Carbon-7hept
Carbon-8oct
Carbon-9non
Carbon-10dec.
Answer to Problem 145CP
Name of the given compound is:
3, 4-dimethylhexanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
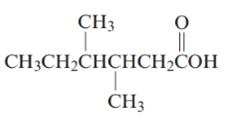
The parent chain in the given structure is hexane. Numbering is done in such a way that carboxyl group gets number 1.
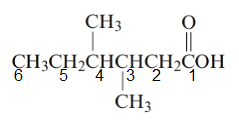
The substituent on 3 and 4 position is methyl.
So, the name will be: 3, 4-dimethylhexanoic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/DeCoste's Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 9th
- ΌΗ 1) V2 CO 3 or Nalt In منهarrow_forward6. The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HBr (g) → H2(g) + Br2(g) Can be expressed by the empirical formula 11790 K In K-6.375 + 0.6415 In(T K-¹) - T Use this formula to determine A,H as a function of temperature. Calculate A,-H at 25 °C and at 100 °C.arrow_forward3. Nitrosyl chloride, NOCI, decomposes according to 2 NOCI (g) → 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) Assuming that we start with no moles of NOCl (g) and no NO(g) or Cl2(g), derive an expression for Kp in terms of the equilibrium value of the extent of reaction, Seq, and the pressure, P. Given that K₂ = 2.00 × 10-4, calculate Seq/ of 29/no when P = 0.080 bar. What is the new value по ƒª/ at equilibrium when P = 0.160 bar? Is this result in accord with Le Châtelier's Principle?arrow_forward
- Consider the following chemical equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2SO3(g) • Write the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. Now compare it to the equilibrium constant expression for the related reaction: • . 1 SO2(g) + O2(g) = SO3(g) 2 How do these two equilibrium expressions differ? What important principle about the dependence of equilibrium constants on the stoichiometry of a reaction can you learn from this comparison?arrow_forwardGiven Kp for 2 reactions. Find the Kp for the following reaction: BrCl(g)+ 1/2 I2(g) ->IBr(g) + 1/2 Cl2(g)arrow_forwardFor a certain gas-phase reaction at constant pressure, the equilibrium constant Kp is observed to double when the temperature increases from 300 K to 400 K. Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction, Ah, using this information.arrow_forward
- Hydrogen bonding in water plays a key role in its physical properties. Assume that the energy required to break a hydrogen bond is approximately 8 kJ/mol. Consider a simplified two-state model where a "formed" hydrogen bond is in the ground state and a "broken" bond is in the excited state. Using this model: • Calculate the fraction of broken hydrogen bonds at T = 300 K, and also at T = 273 K and T = 373 K. • At what temperature would approximately 50% of the hydrogen bonds be broken? • What does your result imply about the accuracy or limitations of the two-state model in describing hydrogen bonding in water? Finally, applying your understanding: • Would you expect it to be easier or harder to vaporize water at higher temperatures? Why? If you were to hang wet laundry outside, would it dry more quickly on a warm summer day or on a cold winter day, assuming humidity is constant?arrow_forward(3 pts) Use the Kapustinskii equation to calculate the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2 anddiscuss any differences between this result and that from #4.arrow_forward(3 pts) Silver metal adopts a fcc unit cell structure and has an atomic radius of 144 pm. Fromthis information, calculate the density of silver. Show all work.arrow_forward
- 4. (3 pts) From the information below, determine the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2. Show all work. AH/(kJ mol-¹) Sublimation of Mg(s) +148 lonization of Mg(g) +2187 to Mg2+(g) Vaporization of Br₂(1) +31 Dissociation of Br,(g) +193 Electron gain by Br(g) -331 Formation of MgBr₂(s) -524arrow_forward1. (4 pts-2 pts each part) Consider the crystal structures of NaCl, ZnS, and CsCl (not necessarily shown in this order). a. For one of the three compounds, justify that the unit cell is consistent with stoichiometry of the compound. b. In each of the crystal structures, the cations reside in certain holes in the anions' packing structures. For each compound, what type of holes are occupied by the cations and explain why those particular types of holes are preferred.arrow_forward(2 pts) What do you expect to happen in a Na2O crystal if a Cl− ion replaces one of the O2−ions in the lattice?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning  Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





