
Concept explainers
Why the acceleration of a freely falling body is less in the Galapagos island at the equator and more a Oslo, Norway?
Answer to Problem 7C
The acceleration of free fall is different at different latitudes because of the following reasons:
(i) The radius of the earth is greatest at the equator and the acceleration of free fall at points close to the surface of the earth is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of earth at the point.
(ii) Due to rotation of the earth, the points on the surface of the earth experience an outward force depending on the latitude.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Acceleration of free fall is the acceleration experienced by a body due to the force of gravitation acting on it. This is given by the expression,
Here, G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth and R is the radius of the earth.
(i) Earth is not a perfect sphere. It is bulged at the equator and flattened at the poles. The equatorial radius is estimated to be 6378 km and the polar radius is around 6357 km. The difference between the equatorial and polar radius is about 21 km.
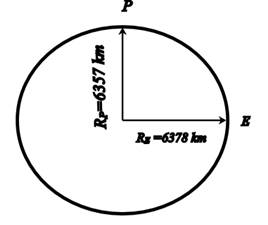
Since
(ii) The earth rotates from west to east with an
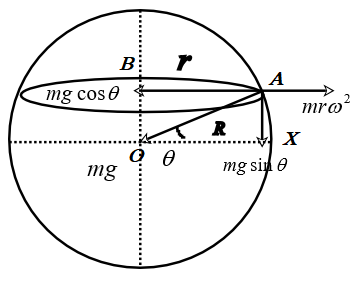
Consider a point A located at a latitude
Resolve the gravitational force mg into two components,
The net force along AB is given by,
From the triangle OBA,
Therefore,
The force along AX is given by,
The net force acting on the mass is given by,
From Newtons second law,
Here,
From equations (1),(2), (3) and (4),
Simplify the expression.
The value of
Hence,
Using binomial expansion and neglecting all higher powers of
At equator the latitude is zero,
At the poles, the latitude is 90°, the acceleration of free fall at poles is given by,
It can be seen that the value of
Conclusion:
Thus, the acceleration of free fall is different at different latitudes because of the following reasons:
(i) The radius of the earth is greatest at the equator and the acceleration of free fall at points close to the surface of the earth is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of earth at the point.
(ii) Due to rotation of the earth, the points on the surface of the earth experience an outward force depending on the latitude.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Inquiry Into Physics
- Give a more general expression for the magnitude of the torque τ. Rewrite the answer found in Part A in terms of the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of the current loop m. Define the angle between the vector perpendicular to the plane of the coil and the magnetic field to be ϕ, noting that this angle is the complement of angle θ in Part A. Give your answer in terms of the magnetic moment mm, magnetic field B, and ϕ.arrow_forwardCalculate the electric and magnetic energy densities at thesurface of a 3-mm diameter copper wire carrying a 15-A current. The resistivity ofcopper is 1.68×10-8 Ω.m.Prob. 18, page 806, Ans: uE= 5.6 10-15 J/m3 uB= 1.6 J/m3arrow_forwardA 15.8-mW laser puts out a narrow beam 2.0 mm in diameter.Suppose that the beam is in free space. What is the rms value of E in the beam? What isthe rms value of B in the beam?Prob. 28, page 834. Ans: Erms= 1380 V/m, Brms =4.59×10-6 Tarrow_forward
- A 4.5 cm tall object is placed 26 cm in front of a sphericalmirror. It is desired to produce a virtual image that is upright and 3.5 cm tall.(a) What type of mirror should be used, convex, or concave?(b) Where is the image located?(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?(d) What is the radius of curvature of the mirror?Prob. 25, page 861. Ans: (a) convex, (b) di= -20.2 cm, i.e. 20.2 cm behind the mirror,(c) f= -90.55 cm, (d) r= -181.1 cm.arrow_forwardA series RCL circuit contains an inductor with inductance L=3.32 mH, and a generator whose rms voltage is 11.2 V. At a resonant frequencyof 1.25 kHz the average power delivered to the circuit is 26.9 W.(a) Find the value of the capacitance.(b) Find the value of the resistance.(c) What is the power factor of this circuit?Ans: C=4.89 μF, R=4.66 Ω, 1.arrow_forwardA group of particles is traveling in a magnetic field of unknown magnitude and direction. You observe that a proton moving at 1.70 km/s in the +x-direction experiences a force of 2.06×10−16 N in the +y-direction, and an electron moving at 4.40 km/s in the −z-direction experiences a force of 8.10×10−16 N in the +y-direction. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on an electron moving in the −y-direction at 3.70 km/s ? What is the direction of this the magnetic force? (in the xz-plane)arrow_forward
- A particle with a charge of −5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of B =−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be F=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the x component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardIs it possible for average velocity to be negative?a. Yes, in cases when the net displacement is negative.b. Yes, if the body keeps changing its direction during motion.c. No, average velocity describes only magnitude and not the direction of motion.d. No, average velocity describes only the magnitude in the positive direction of motion.arrow_forwardTutorial Exercise An air-filled spherical capacitor is constructed with an inner-shell radius of 6.95 cm and an outer-shell radius of 14.5 cm. (a) Calculate the capacitance of the device. (b) What potential difference between the spheres results in a 4.00-μC charge on the capacitor? Part 1 of 4 - Conceptualize Since the separation between the inner and outer shells is much larger than a typical electronic capacitor with separation on the order of 0.1 mm and capacitance in the microfarad range, we expect the capacitance of this spherical configuration to be on the order of picofarads. The potential difference should be sufficiently low to avoid sparking through the air that separates the shells. Part 2 of 4 - Categorize We will calculate the capacitance from the equation for a spherical shell capacitor. We will then calculate the voltage found from Q = CAV.arrow_forward
- I need help figuring out how to do part 2 with the information given in part 1 and putting it in to the simulation. ( trying to match the velocity graph from the paper onto the simulation to find the applied force graph) Using this simulation https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/cheerpj/forces-1d/latest/forces-1d.html?simulation=forces-1d.arrow_forwardI need help running the simulation to get the result needed.arrow_forwardHow can I remember this Formula: p = m × v where m is in kg and v in Meter per second in the best way?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





