
Concept explainers
Find the dead loads acting on the girder AE and beam CD.
Answer to Problem 6P
The dead load acting on the beam CD is
Dead load in Girder AE:
The dead load at C, A, and E are
The uniformly distributed load in the girder AE is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of the reinforced concrete slab is
The area of cross-section of the steel floor beam is
The area of cross-section of the steel girder is
The length, height, and thickness of the brick wall are
Calculation:
Show the floor systemof the building as shown in Figure 1.
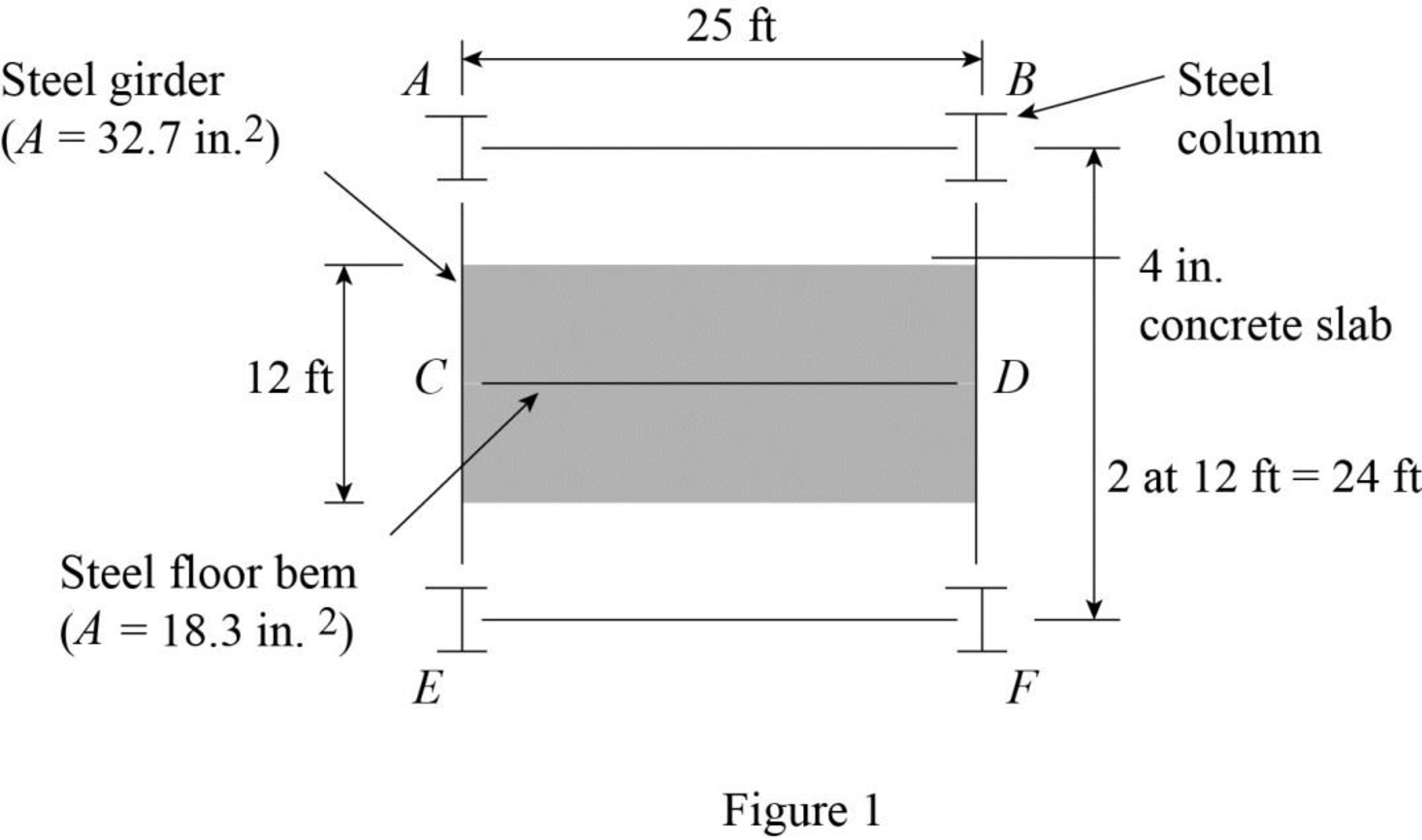
Refer Figure 1.
The tributary area of the beam CD is represented by the shaded region.
Tributary area of the beam CD:
The width of the tributary area of the beam CD is
The width of the tributary area of the beam CD is same as the length of the beam CD. Then,
The length of the tributary area of the beam CD is
The thickness of the concrete slab is
Refer Table 2.1 “Unit Weights of Construction Materials” in the text book.
The unit weight of the reinforced concrete is
The unit weight of the structural steel is
The unit weight of the brick wall is
Calculate the dead load per unit length of the beam CD as follows:
Concrete Slab:
Calculate the dead load of the concrete slab using the relation:
Substitute
Steel beam:
Calculate the dead load of the steel beam using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the dead load of the brick wall using the relation:
Calculate the dead load of the beam CD as follows:
The dead load of
Show the dead load acting on the beam as shown in Figure 2.
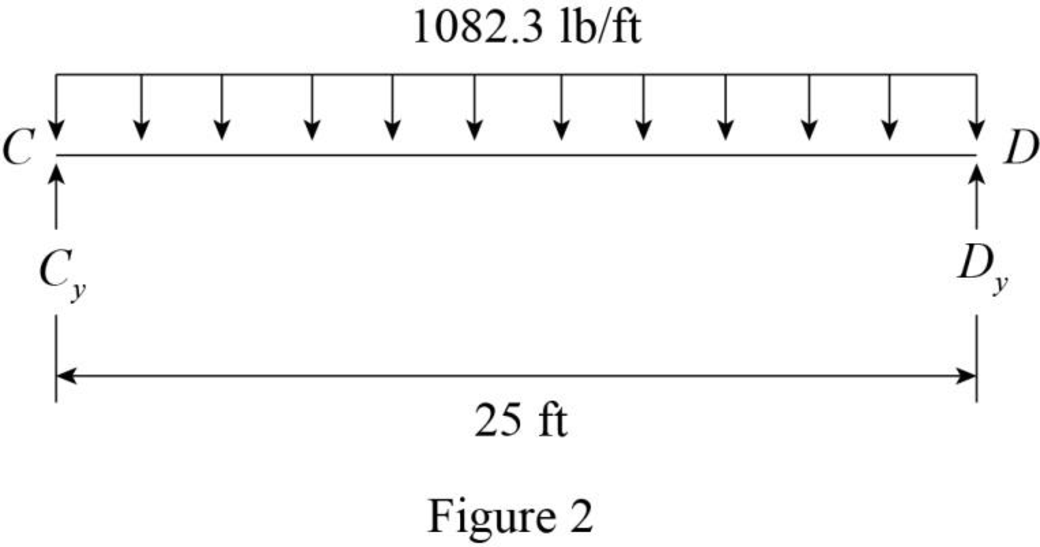
Refer Figure 2.
The reaction at C and D are denoted by
The dead load on the beam is symmetrical. Then,
Show the dead load acting on the beam as shown in Figure 3.
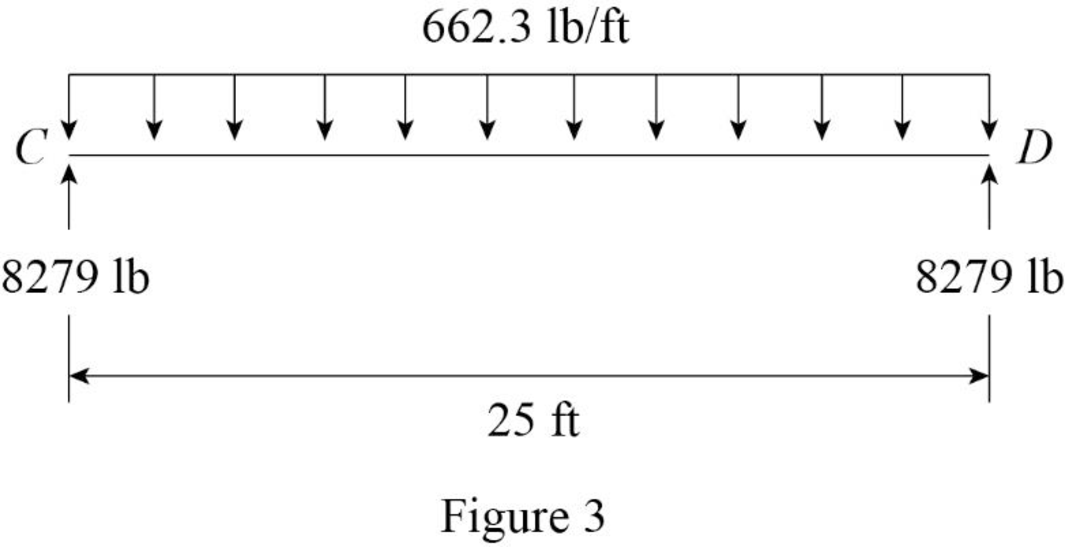
Refer Figure 3.
Thus, the dead load acting on the beam CD is
Show the floor system of the building as shown in Figure 4.
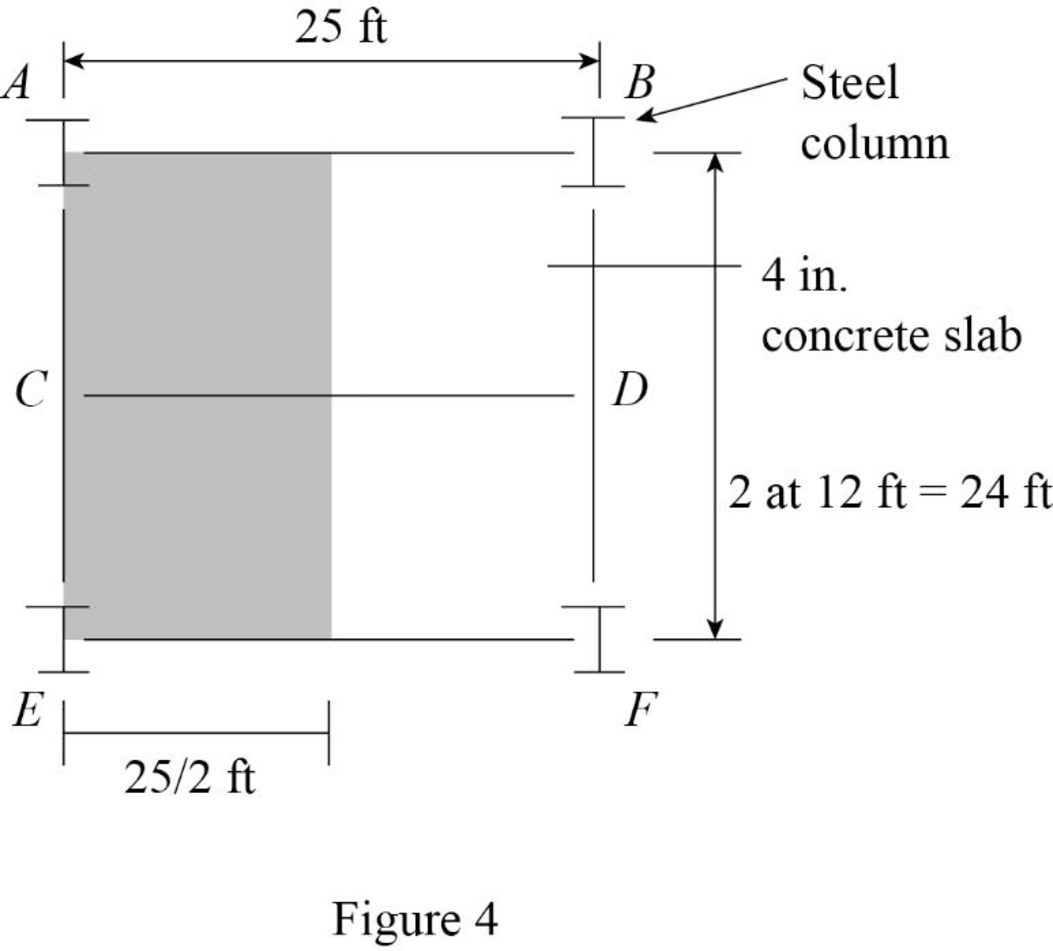
Refer Figure 4.
Tributary area of the girder AE:
The width of the tributary area of the girder AE is
The width of the tributary area of the girder AE is same as the length of the girder AE. Then,
The length of the tributary area of the girder AE is
The thickness of the reinforced concrete slab is
Calculate the dead load per unit length of the girder AE as follows:
Steel beam:
Calculate the dead load of the girder AE using the relation:
Substitute
Concentrated load at A and E.
Show the tributary area of column at A and E as shown in Figure 5.
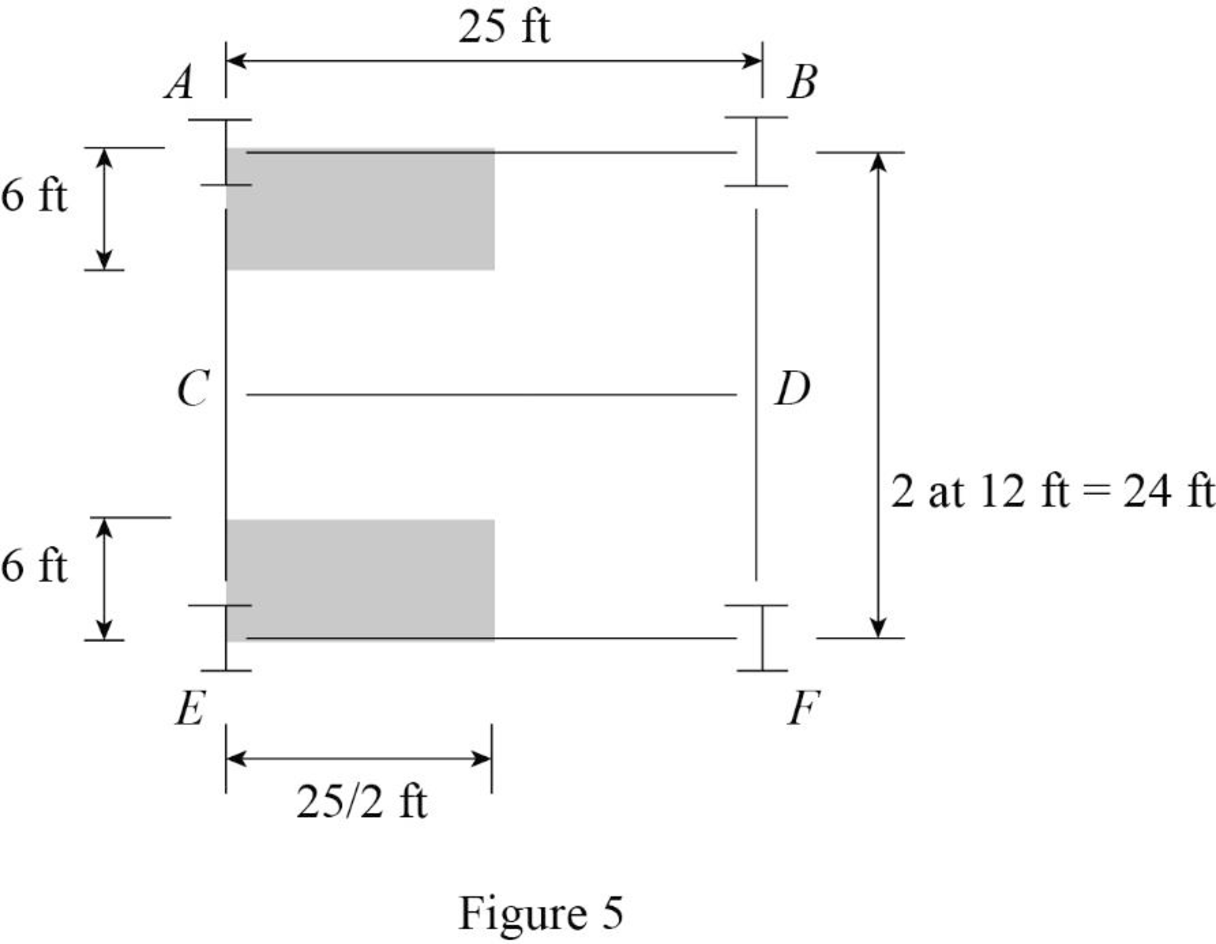
Refer Figure 5.
The tributary area of column at A and E are Equal.
The tributary area of column at A and E are
Calculate the concentrated load (P) at the column A and E the using the relation:
Substitute
Refer Figure 3.
The concentrated load at the column C is
Show the loading on the girder AE as shown in Figure 6.
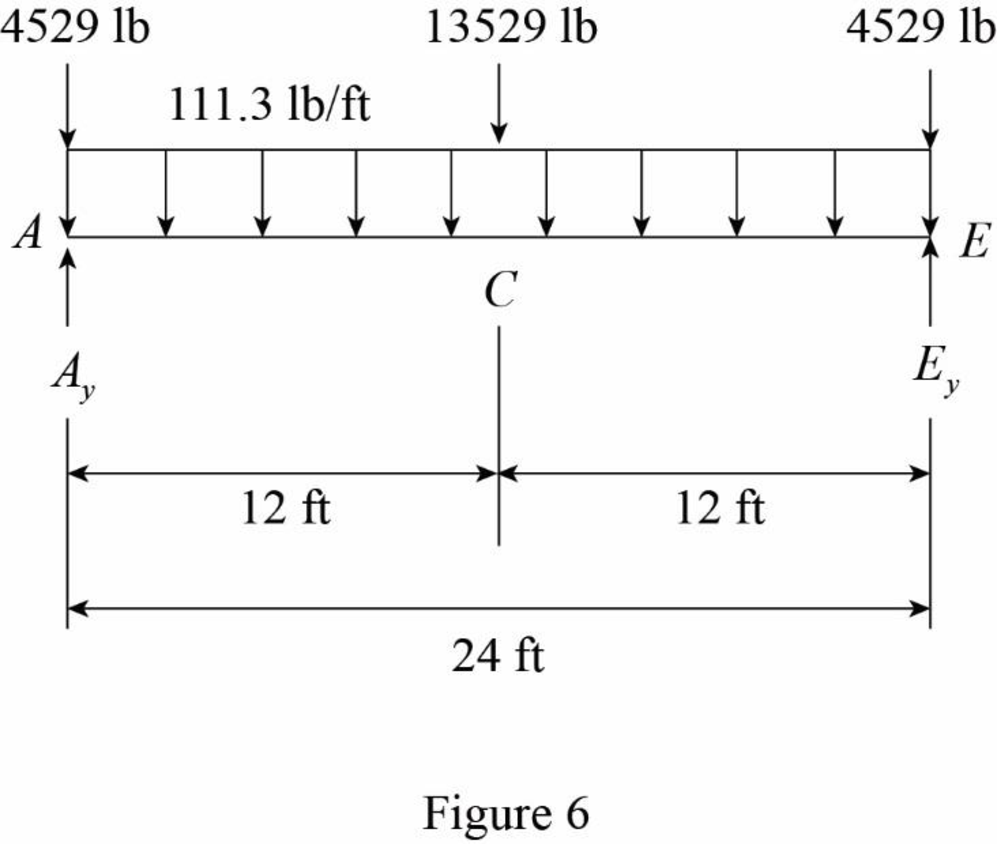
Refer Figure 6.
The reaction at A and E are denoted by
The dead load on the beam is symmetrical. Then,
Show the loading on the girder AE as shown in Figure 7.
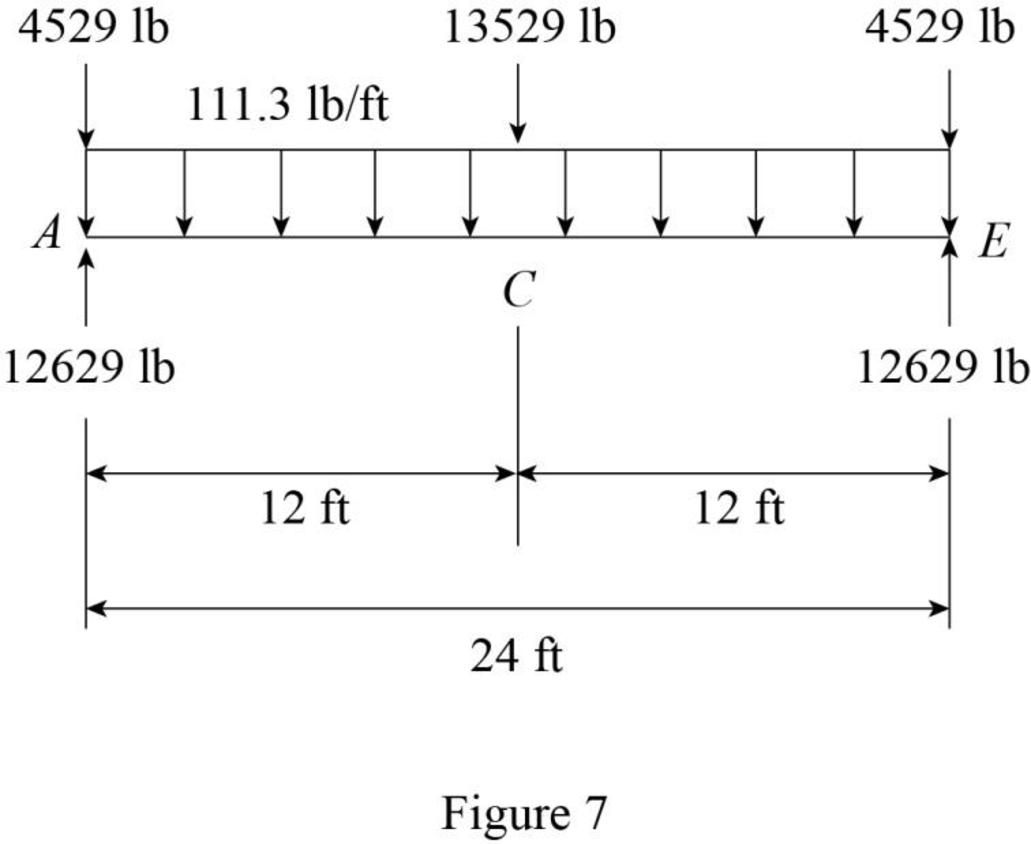
Refer Figure 7.
The dead load at C, A, and E are
The uniformly distributed load in the girder AE is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- 7.69 Assume that the head loss in the pipe is given by h₁ = 0.014(L/D) (V²/2g), where L is the length of pipe and D is the pipe diameter. Assume α = 1.0 at all locations. a. Determine the discharge of water through this system. b. Draw the HGL and the EGL for the system. c. Locate the point of maximum pressure. d. Locate the point of minimum pressure. e. Calculate the maximum and minimum pressures in the system. Elevation 100 m Water T = 10°C L = 100 m D = 60 cm Elevation 95 m Elevation 100 m L = 400 m D = 60 cm Elevation = 30 m Nozzle 30 cm diameter jet Problem 7.69arrow_forwardA rectangular flume of planed timber (n=0.012) slopes 0.5 ft per 1000 ft. (i)Compute the discharge if the width is 7 ft and the depth of water is 3.5 ft. (ii) What would be thedischarge if the width were 3.5 ft and depth of water is 7 ft? (iii) Which of the two forms wouldhave greater capacity and which would require less lumber?arrow_forwardFigure shows a tunnel section on the Colorado River Aqueduct. The area of the water cross section is 191 ft 2 , and the wetted perimeter is 39.1 ft. The flow is 1600 cfs. If n=0.013 for the concrete lining, find the slope.arrow_forward
- 7.48 An engineer is making an estimate for a home owner. This owner has a small stream (Q= 1.4 cfs, T = 40°F) that is located at an elevation H = 34 ft above the owner's residence. The owner is proposing to dam the stream, diverting the flow through a pipe (penstock). This flow will spin a hydraulic turbine, which in turn will drive a generator to produce electrical power. Estimate the maximum power in kilowatts that can be generated if there is no head loss and both the turbine and generator are 100% efficient. Also, estimate the power if the head loss is 5.5 ft, the turbine is 70% efficient, and the generator is 90% efficient. Penstock Turbine and generator Problem 7.48arrow_forwarddesign rectangular sections for the beam and loads, and p values shown. Beam weights are not included in the loads given. Show sketches of cross sections including bar sizes, arrangements, and spacing. Assume concrete weighs 23.5 kN/m'. fy= 420 MPa, and f’c= 21 MPa.Show the shear and moment diagrams as wellarrow_forwardDraw as a 3D object/Isometricarrow_forward
- Post-tensioned AASHTO Type II girders are to be used to support a deck with unsupported span equal to 10 meters. Two levels of Grade 250, 10 x 15.2 mm Ø 7-wire strand are used to tension the girders with 5 tendons per level, where the tendons on top stressed before the ones on the bottom. The girder is simply supported at both ends. The anchors are located 100 mm above the neutral axis at the supports while the eccentricity is measured at 400 mm at the midspan. The tendon profile follows a parabolic shape using a rigid metal sheathing. A concrete topping (slab) 130 mm thick is placed above the beam with a total tributary width of 4 meters. Use maximum values for ranges (table values). Assume that the critical section of the beam is at 0.45LDetermine the losses (friction loss, anchorage, elastic shortening, creep, shrinkage, relaxation). Determine the stresses at the top fibers @ critical section before placing a concrete topping, right after stress transfer. Determine the stress at the…arrow_forwardPlease solve this question in hand writting step by step with diagram drawingarrow_forwardSolve this question pleasearrow_forward
- Please draw shear and moment diagrams with provided information.arrow_forwardShow step by step solutionarrow_forwardDraw the shear and the moment diagrams for each of the frames below. If the frame is statically indeterminate the reactions have been provided. Problem 1 (Assume pin connections at A, B and C). 30 kN 2 m 5 m 30 kN/m B 60 kN 2 m 2 m A 22 CO Carrow_forward

 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning





