
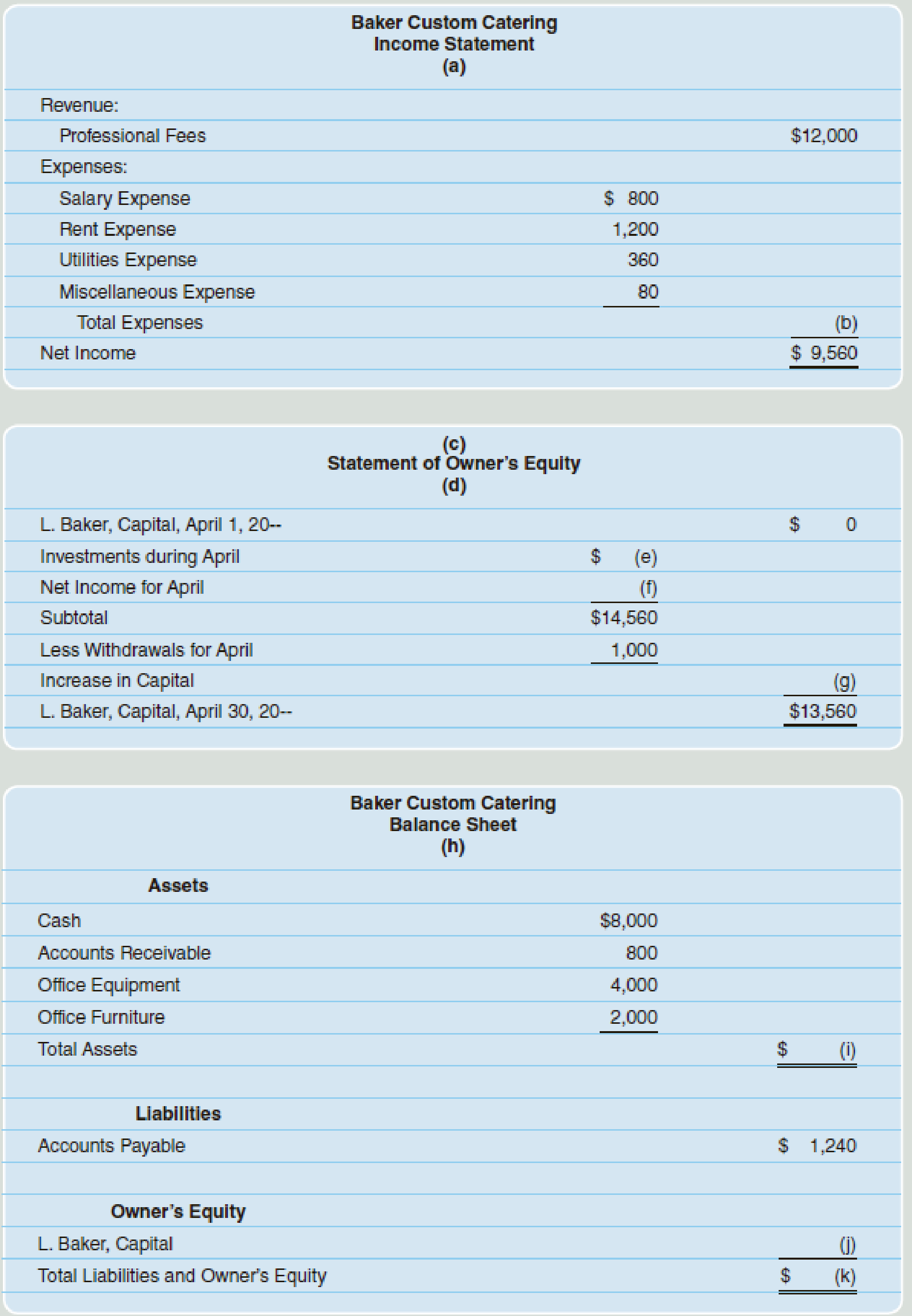
The financial statements for Baker Custom Catering for the month of April are presented below.
Required
Solve for the missing information.
Solve the missing information.
Answer to Problem 5PB
(a) For the year ended April 30.
(b) $2,440.
(c) Company B
(d) For the year ended April 30
(e) 5,000.
(f) 9,560.
(g) 13,560.
(h) For the year ended April 30.
(i) 14,800.
(j) 13,560.
(k) 14,800.
Explanation of Solution
Financial statement:
Financial statements are condensed summary of transactions communicated in the form of reports for the purpose of decision making. The financial statements reports, and shows the financial status of the business. The financial statements consist of the balance sheet, income statement, statement of retained earnings, and the cash flow statement.
Missing information (a):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended April 30) is missing in the income statement.
| Company B |
| Income Statement |
| (a) For the year ended April 30 |
Table (1)
Missing information (b):
The amount of total expense is missing in the income statement and it is calculated by adding all expenses:
| Company B | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| (a) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue: | ||
| Professional Fees | 12,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salary Expense | 800 | |
| Rent Expense | 1,200 | |
| Utilities Expense | 360 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 80 | |
| Total Expenses | (b) 2,440 | |
| Net income | 9,560 | |
Table (2)
Therefore, the amount of total expenses is (b) $2,440.
Missing information (c):
In this case, “Name of the Company “(Company B) is missing in the statement of owners’ equity.
| (c) Company B |
| Statement of Owners' equity |
| (d) For the year ended April 30 |
Table (3)
Missing information (d):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended April 30) is missing in the statement of owners’ equity.
| (c) Company B |
| Statement of Owners' equity |
| (d) For the year ended April 30 |
Table (4)
Missing information (e):
In this case, investments made during the month of April are missing and it is calculated as follows:
| (c) Company B | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, April 1 | ||
| Investments during April (1) | (e) 5,000 | |
| Net income for April | (f) 9,560 | |
| Subtotal | 14,560 | |
Table (5)
Therefore, the amount of investments during April are (e) $5,000.
Working note:
(1) Calculate the amount of investment made during April:
Missing information (f):
In this case, the net income mentioned in the income statement is recorded in the statement of owners’ equity. Therefore, amount of net income is (f) $9,560. The net income or net loss computed in the income statement is reported in the statement of owners’ equity for ascertaining the amount of ending capital balance.
| (c) Company B | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, April 1 | ||
| Investments during April (1) | (e) 5,000 | |
| Net income for April | (f) 9,560 | |
| Subtotal | 14,560 | |
Table (6)
Missing information (g):
In this case, the amount of increase in capital is (g) $13,560 and it is same as the Ending capital of Person L as on April 30, since the amount of beginning capital is given as zero. Suppose, If the amount of beginning capital is given, then the increase in capital is computed by deducting the ending capital from the beginning capital.
| (c ) Company B | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, April 1 | ||
| Investments during April | (e) 5,000 | |
| Net income for April | (f) 9,560 | |
| Subtotal | 14,560 | |
| Less: Withdrawals for April | 1,000 | |
| Increase in capital | (g) 13,560 | |
| Person L, Capital, April 30 | 13,560 | |
Table (7)
Note:
The net income or net loss computed in the income statement is reported in the statement of owners’ equity for ascertaining the amount of ending capital balance. Then, the balance of ending capital is reported in the balance sheet (owners’ equity section). Therefore, any transaction affecting the income statement eventually, affects the balance sheet through the balance of owners’ equity.
Missing information (h):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended April 30) is missing in the balance sheet.
| Company B |
| Balance Sheet |
| (h) For the year ended April 30 |
Table (8)
Missing information (i):
In this case, the amount of total assets is missing and it is calculated as follows;
| Company B | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 8,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 800 | |
| office Equipment | 4,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 2,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 14,800 | |
Table (9)
Therefore, the amount of total asset is (i) 14,800.
Missing information (j):
In this case, the amount of Person L, Capital is (j) $13,560 and it is the same as the amount of ending capital of Person L that is calculated in the statement of owners’ equity.
| Company B | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 8,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 800 | |
| office Equipment | 4,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 2,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 14,800 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 1,240 | |
| Owners' Equity | ||
| Person L, Capital | (j) 13,560 | |
Table (10)
Note:
The net income or net loss computed in the income statement is reported in the statement of owners’ equity for ascertaining the amount of ending capital balance. Then, the balance of ending capital is reported in the balance sheet (owners’ equity section). Therefore, any transaction affecting the income statement eventually, affects the balance sheet through the balance of owners’ equity.
Missing information (k):
In this case, the amount of total liabilities and owners’ equity is same as the amount of total assets ($14,800) and it is calculated as follows:
| Company B | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended April 30 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 8,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 800 | |
| office Equipment | 4,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 2,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 14,800 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 1,240 | |
| Owners' Equity | ||
| Person L, Capital | (j) 13,560 | |
| Total liabilities and owners’ equity (2) | (k)14,800 | |
Table (11)
Working note:
(2) Calculate the amount of total liabilities and owners’ equity:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Scott's College Accounting: A Career Approach, 13th
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
- need help this answerarrow_forwardFor each of the transactions above, indicate the amount of the adjusting entry on the elements of the balance sheet and income statement.Note: Enter negative amounts with a minus sign.arrow_forwardNeed help with this question solution general accountingarrow_forward
- Duo Corporation is evaluating a project with the following cash flows: Year 0 1 2 3 Cash Flow -$ 30,000 12,200 14,900 16,800 4 5 13,900 -10,400 The company uses an interest rate of 8 percent on all of its projects. a. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the discounting approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the reinvestment approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the combination approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. a. Discounting approach MIRR b. Reinvestment approach MIRR c. Combination approach MIRR % % %arrow_forwardHello tutor please provide this question solution general accountingarrow_forwardGet correct answer accounting questionsarrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





