
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 50PQ
Car A and car B travel in the same direction along a straight section of the interstate highway. For the entire interval shown on the velocity-versus-time graph (Fig. P2.50), car A is ahead of car B. a. At time t3, is the magnitude of the acceleration of car A greater than, less than, or equal to that of car B? Explain. b. From time t1 to time t2, does the distance between cars A and B increase, decrease, or remain constant? Explain.
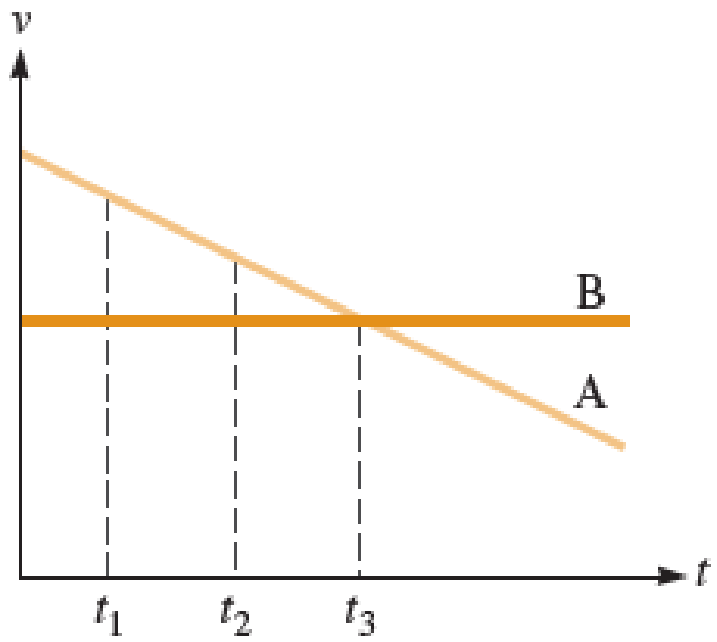
FIGURE P2.50
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
i need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearly
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Review the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle.
Equation: SF=ma
Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 2.2 - In each of the five motion diagrams shown in...Ch. 2.3 - For each of the following, give the vector...Ch. 2.5 - Figure 2.11 shows the motion of various objects:...Ch. 2.6 - The top marathon runners complete the race in...Ch. 2.6 - In our everyday experience, we sometimes use the...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 2.6CECh. 2.8 - Kinematics graphs are great for showing how a...Ch. 2 - Is the Moons motion around the Earth...Ch. 2 - An animals tracks are frozen in the snow (Fig....Ch. 2 - Problems 3 and 12 are paired. G A particle moves...
Ch. 2 - Prob. 4PQCh. 2 - For each of the following velocity vectors, give...Ch. 2 - In the traditional Hansel and Gretel fable, the...Ch. 2 - After a long and grueling race, two cadets, A and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8PQCh. 2 - Elisha Graves Otis invented the elevator brake in...Ch. 2 - As shown in Figure 2.9, Whipple chose a coordinate...Ch. 2 - Prob. 11PQCh. 2 - Prob. 12PQCh. 2 - A race car travels 825 km around a circular sprint...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14PQCh. 2 - A train leaving Albuquerque travels 293 miles, due...Ch. 2 - Prob. 16PQCh. 2 - The position of a particle attached to a vertical...Ch. 2 - Prob. 18PQCh. 2 - Prob. 19PQCh. 2 - Prob. 20PQCh. 2 - During a relay race, you run the first leg of the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 22PQCh. 2 - Prob. 23PQCh. 2 - Prob. 24PQCh. 2 - During a thunderstorm, a frightened child is...Ch. 2 - Scientists and engineers must interpret problems...Ch. 2 - Prob. 27PQCh. 2 - Prob. 28PQCh. 2 - A In attempting to break one of his many swimming...Ch. 2 - A The instantaneous speed of a particle moving...Ch. 2 - A particles velocity is given by vy(t)=atj, where...Ch. 2 - Prob. 32PQCh. 2 - Figure P2.33 shows the y-position (in blue) of a...Ch. 2 - A particles position is given by z(t) = (7.50...Ch. 2 - Prob. 35PQCh. 2 - Two sprinters start a race along a straight track...Ch. 2 - An electronic line judge camera captures the...Ch. 2 - During a bungee jump, a student (i) initially...Ch. 2 - Prob. 39PQCh. 2 - Prob. 40PQCh. 2 - Prob. 41PQCh. 2 - Prob. 42PQCh. 2 - Prob. 43PQCh. 2 - Prob. 44PQCh. 2 - A computer system, using a preset coordinate...Ch. 2 - In Example 2.6, we considered a simple model for a...Ch. 2 - A uniformly accelerating rocket is found to have a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 48PQCh. 2 - A driver uniformly accelerates his car such that...Ch. 2 - Car A and car B travel in the same direction along...Ch. 2 - Accelerating uniformly to overtake a slow-moving...Ch. 2 - An object that moves in one dimension has the...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the positive x axis with a...Ch. 2 - Case Study Crall and Whipple attached a fan to a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 55PQCh. 2 - The engineer of an intercity train observes a rock...Ch. 2 - A pebble is thrown downward from a 44.0-m-high...Ch. 2 - In a cartoon program, Peter tosses his baby,...Ch. 2 - Tadeh launches a model rocket straight up from his...Ch. 2 - Prob. 60PQCh. 2 - In the movie Star Wars: The Empire Strikes Back,...Ch. 2 - A worker tosses bricks one by one to a coworker on...Ch. 2 - A rock is thrown straight up into the air with an...Ch. 2 - Prob. 64PQCh. 2 - A sounding rocket, launched vertically upward with...Ch. 2 - Prob. 66PQCh. 2 - While strolling downtown on a Saturday Afternoon,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 68PQCh. 2 - A trooper is moving due south along the freeway at...Ch. 2 - A dancer moves in one dimension back and forth...Ch. 2 - The electrical impulse initiated by the nerves in...Ch. 2 - Two cars leave Seattle at the same time en route...Ch. 2 - An object begins to move along the y axis and its...Ch. 2 - Prob. 74PQCh. 2 - Prob. 75PQCh. 2 - Two carts are set in motion at t = 0 on a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 77PQCh. 2 - Cars A and B each move to the right with constant...Ch. 2 - Prob. 79PQCh. 2 - Prob. 80PQCh. 2 - Prob. 82PQCh. 2 - Prob. 83PQCh. 2 - A Write expressions for the average acceleration...Ch. 2 - Prob. 85PQCh. 2 - Prob. 86PQCh. 2 - In 1898, the world land speed record was set by...Ch. 2 - In Example 2.12, two circus performers rehearse a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 89PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY