
Prepare the transactions in general ledger accounts under the
Explanation of Solution
Prepare general ledger accounts under the accounting equation.
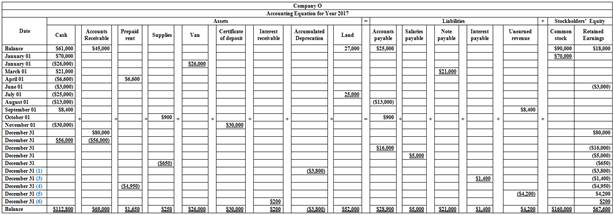
Table (1)
Working Note:
Determine the amount of
Determine the amount of total interest payable.
Determine the amount of interest payable on note that would be recognized.
Determine the amount of prepaid rent to be recognized.
Determine the amount of recognized revenue.
Determine the amount of interest earned:
a.
Identify the four additional adjustments.
a.
Explanation of Solution
The four additional adjustments are as follows:
- 1. Company O has acquired a delivery van on January 01, for that delivery van depreciation expense should be provided using
adjusting entry. - 2. On March 01, Company O issued note payable. Accrued interest expense on note payable should be recognized using adjusting entry.
- 3. On April 01, Company P paid rent in advance. Rent paid in advance should be recognized as rent expense for 9 months using adjusting entry.
- 4. On September 01, Company O received cash in advance. Unearned revenue should be recognized as revenue for 6 months using adjusting entry.
- 5. On November 1, purchased a certificate of deposit. Hence, interest revenue should be recognized.
b.
Identify the amount of interest expense that would be reported on the income statement.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of interest expense that would be reported on the income statement is $1,400 (3).
c.
Identify the amount of net cash flow from operating activities that would be reported on the statement of
c.
Explanation of Solution
The net cash flow from operating activities would be reported on the statement of cash flows amounts to $44,800 (6).
Determine the amount of net cash flow from operating activities.
d.
Identify the amount of rent expense that would be reported on the income statement.
d.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of rent expense would be reported on the income statement is $4,950 (4).
e.
Identify the amount of total liabilities that would be reported on the
e.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of total liabilities would be reported on the balance sheet $60,500
f.
Identify the amount of supplies expense that would be reported on the balance sheet.
f.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of supplies expense would be reported on the income statement is $650
g.
Identify the amount of unearned revenue that would be reported on the balance sheet.
g.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of unearned revenue that would be reported on the balance sheet is $4,200 (5).
h.
Identify the amount of net cash flow from investing activities that would be reported on the statement of cash flows.
h.
Explanation of Solution
The net cash flow from investing activities that would be reported on the statement of cash flows is ($81,000) (7).
Determine the amount of net cash flow from investing activities.
i.
Identify the amount of interest payable that would be reported on the balance sheet.
i.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of interest payable that would be reported on the balance sheet is $1,400 (3).
j.
Identify the amount of total expense that would be reported on the income statement.
j.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of total expense that would be reported on the income statement is $31,800
k.
Identify the amount of
k.
Explanation of Solution
The retained earnings that would be reported on the balance sheet amounts to $67,600 (8).
Determine the amount of retained earnings.
l.
Identify the amount of service revenue that would be reported on the income statement.
l.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of service revenue that would be reported on the income statement is $84,200
m.
Identify the amount of net cash flow from financing activities that would be reported on the statement of cash flows.
m.
Explanation of Solution
The net cash flow from financing activities that would be reported on the statement of cash flows is $88,000 (9).
Determine the amount of net cash flow from financing activities.
n.
Identify the amount of net income that would be reported on the income statement.
n.
Explanation of Solution
The net income that would be reported on the income statement is $52,600
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts, 9th Edition
- Compute the roc stockholders equityarrow_forwardWhat income will be earned if the investment generatesarrow_forwardDuring 2018, the band Maroon 5 is touring across the U.S. on its "Red Pill Blues Tour 2018." Two of those concerts, on October 14 and 15, will be held at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Madison Square Garden has a seating capacity for concerts of approximately 19,000. According to a Business Insider article in December 2016, Maroon 5 had an average concert ticket price of $165.Assume that these two Madison Square Garden concerts were sold out on the first day the tickets were available for sale to the public, November 4, 2017. Also assume, for the sake of simplicity, that all tickets are sold directly by Maroon5.Question:How will Maroon 5's balance sheet and income statement be impacted by the sale of the Madison Square Garden tickets on November 4, 2017 and what specific accounts will be impacted and will it be increased or decreased?arrow_forward
- During 2018, the band Maroon 5 is touring across the U.S. on its "Red Pill Blues Tour 2018." Two of those concerts, on October 14 and 15, will be held at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Madison Square Garden has a seating capacity for concerts of approximately 19,000. According to a Business Insider article in December 2016, Maroon 5 had an average concert ticket price of $165.Assume that these two Madison Square Garden concerts were sold out on the first day the tickets were available for sale to the public, November 4, 2017. Also assume, for the sake of simplicity, that all tickets are sold directly by Maroon 5.Question:How will Maroon 5's balance sheet and income statement be impacted by the performance of the October 14, 2018, concert at the Madison Square Garden tickets?arrow_forwardRequirement $1; During its first month of operation, the True Consulting Corporation, which specializes in management consulting, completed the following transactions. July 1 Gruod 15,000 shares of the company's commanstack in exchange for $15,000. July 3 Purchased a truck for $8,000. A down payment of $3,000 war made, with the balance on account. July 5 Paid $1,200 to cover rent from July 1 through September 30. July 7 Purcharod $2,000 af supplier an account. July 10 Billed customers for consulting servicos porfarmed, $3,700. July 14 Paid $500 toward the amount owed for the supplies purchased on July 7. July 15 Paid $1750 in cash for employee uages. July 19 Callected $1600 in cash from customers that were billed on July 10. July 21 Received $4,200 cash from customers for services performed. July 31 Paid $350 in cash for truck repairs. July 31 Declared and Paid $700 in cash dividends. Propuro journal entries to record the July transactions in the General Journal boluu. Ground Bote…arrow_forwardNeed To ask Right Expert for this solutionsarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





