
Concept explainers
Approximately 1.5 million high school students take the SAT each year and nearly 80% of the college and universities without open admissions policies use SAT scores in making admission decisions (College Board, March 2009). The current version of the SAT includes three parts: reading comprehension, mathematics, and writing. A perfect combined score for all three parts is 2400. A sample of SAT scores for the combined three-part SAT are as follows:
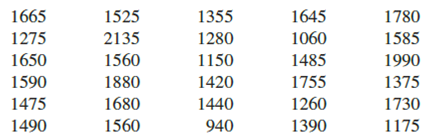
- a. Show a frequency distribution and histogram. Begin with the first class starting at 800 and use a class width of 200.
- b. Comment on the shape of the distribution.
- c. What other observations can be made about the SAT scores based on the tabular and graphical summaries?
a.
Construct the frequency distribution and histogram for the data.
Answer to Problem 44SE
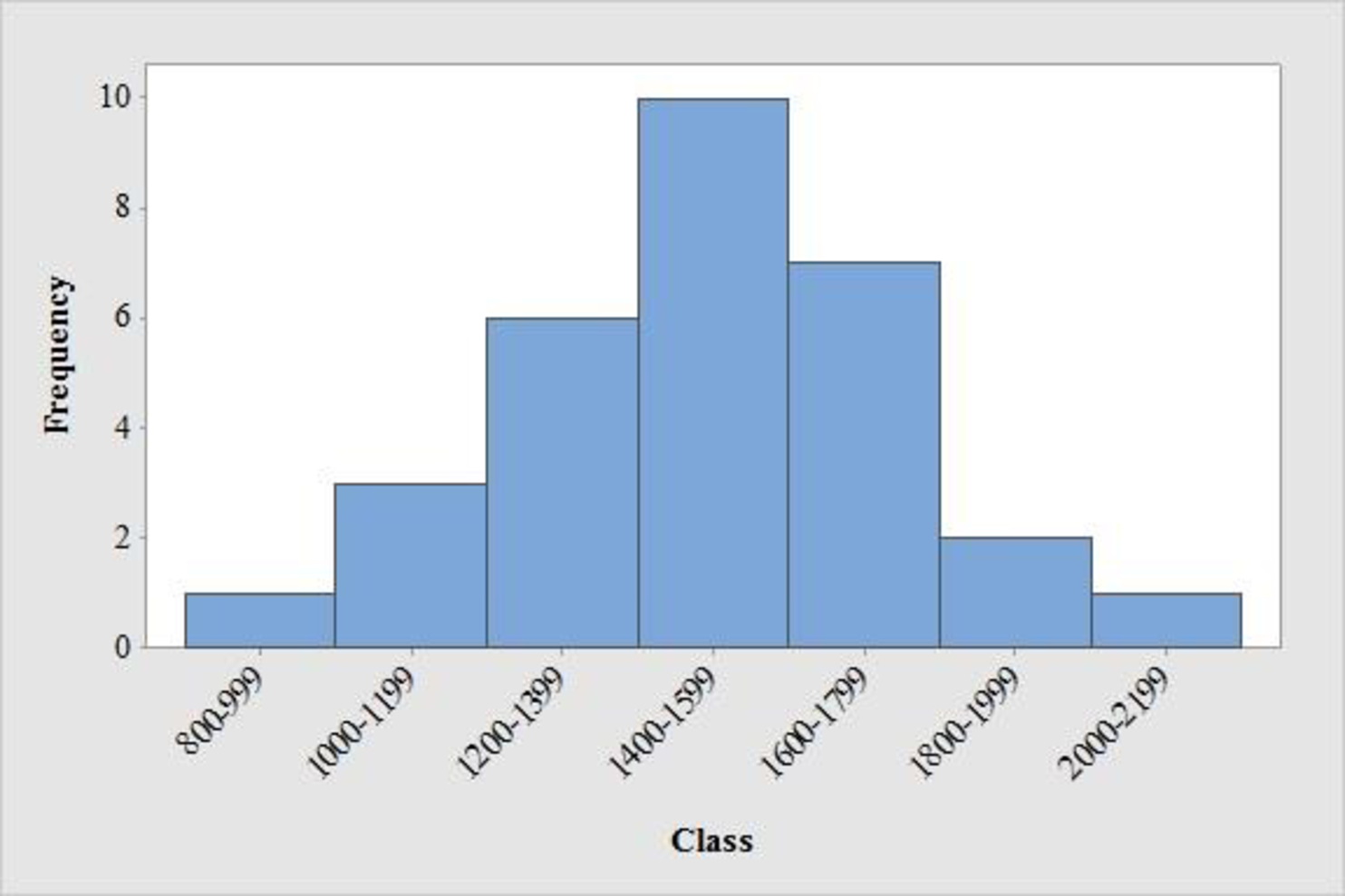
The frequency distribution is tabulated below:
| Class | Tally | Frequency |
| 800-999 | 1 | |
| 1000-1199 | 3 | |
| 1200-1399 | 6 | |
| 1400-1599 | 10 | |
| 1600-1799 | 7 | |
| 1800-1999 | 2 | |
| 2000-2199 | 1 | |
| Total | 30 |
- Output using MINITAB software is given below:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The data represents the sample of SAT scores for combined three part sat scores.
The frequencies are calculated by using the tally mark and the method of grouping is used because, range of the data is from 800 to 2,199. Here, the number of times each class levels repeats is the frequency of that particular class.
- From the given data set it is given that the class should be from approximately started with the class of 800 with class width of about 200.
- Make a tally mark for each value in the corresponding class and continue for all values in the data.
- The number of tally marks in each class represents the frequency, f of that class.
Similarly, the frequency of remaining classes for the data set is given below:
| Class | Tally | Frequency |
| 800-999 | 1 | |
| 1000-1199 | 3 | |
| 1200-1399 | 6 | |
| 1400-1599 | 10 | |
| 1600-1799 | 7 | |
| 1800-1999 | 2 | |
| 2000-2199 | 1 | |
| Total | 30 |
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to draw the frequency histogram chart by using MINITAB software.
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple, and then click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the corresponding column of data.
- In scale on y-axis, make click on frequency.
- Click on ok.
b.
Comment the shape of the distribution.
Answer to Problem 44SE
The distribution of sat score is approximately symmetric.
Explanation of Solution
Symmetric distribution:
When the left and right sides of the distribution are approximately equal or mirror images of each other and three distributions will fall under symmetric distribution that is bell shaped, triangular and uniform or rectangular and then it is symmetric distribution.
From the graph, it is observed that the left and right side of the histogram is approximately equal. Hence, the shape of the distribution is bell-shaped curve.
Thus, it can be concluded that the distribution is approximately symmetric.
c.
Comment the observations of sat scores based on the tabular and graphical summary.
Explanation of Solution
From the data and the histogram, it is observed that approximately 33 percent of sat score (frequency about 10 of 30) will lie between 1400 and 1599.
- Moreover, the score less than 800 or greater than 2,200 are unusual and the average value of sat scores is over 1,500.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Statistics for Business & Economics, Revised (MindTap Course List)
- Please help me with the following question on statisticsFor question (e), the drop down options are: (From this data/The census/From this population of data), one can infer that the mean/average octane rating is (less than/equal to/greater than) __. (use one decimal in your answer).arrow_forwardHelp me on the following question on statisticsarrow_forward3. [15] The joint PDF of RVS X and Y is given by fx.x(x,y) = { x) = { c(x + { c(x+y³), 0, 0≤x≤ 1,0≤ y ≤1 otherwise where c is a constant. (a) Find the value of c. (b) Find P(0 ≤ X ≤,arrow_forwardNeed help pleasearrow_forward7. [10] Suppose that Xi, i = 1,..., 5, are independent normal random variables, where X1, X2 and X3 have the same distribution N(1, 2) and X4 and X5 have the same distribution N(-1, 1). Let (a) Find V(X5 - X3). 1 = √(x1 + x2) — — (Xx3 + x4 + X5). (b) Find the distribution of Y. (c) Find Cov(X2 - X1, Y). -arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward6. [10] Let X, Y and Z be random variables. Suppose that E(X) = E(Y) = 1, E(Z) = 2, V(X) = 1, V(Y) = V(Z) = 4, Cov(X,Y) = -1, Cov(X, Z) = 0.5, and Cov(Y, Z) = -2. 2 (a) Find V(XY+2Z). (b) Find Cov(-x+2Y+Z, -Y-2Z).arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward== 4. [10] Let X be a RV. Suppose that E[X(X-1)] = 3 and E(X) = 2. (a) Find E[(4-2X)²]. (b) Find V(-3x+1).arrow_forward2. [15] Let X and Y be two discrete RVs whose joint PMF is given by the following table: y Px,y(x, y) -1 1 3 0 0.1 0.04 0.02 I 2 0.08 0.2 0.06 4 0.06 0.14 0.30 (a) Find P(X ≥ 2, Y < 1). (b) Find P(X ≤Y - 1). (c) Find the marginal PMFs of X and Y. (d) Are X and Y independent? Explain (e) Find E(XY) and Cov(X, Y).arrow_forward32. Consider a normally distributed population with mean μ = 80 and standard deviation σ = 14. a. Construct the centerline and the upper and lower control limits for the chart if samples of size 5 are used. b. Repeat the analysis with samples of size 10. 2080 101 c. Discuss the effect of the sample size on the control limits.arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothesis test. The following results are for two independent samples taken from the two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n 1 = 80 n 2 = 70 x 1 = 104 x 2 = 106 σ 1 = 8.4 σ 2 = 7.6 What is the value of the test statistic? If required enter negative values as negative numbers (to 2 decimals). What is the p-value (to 4 decimals)? Use z-table. With = .05, what is your hypothesis testing conclusion?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt





