
a.
Indicate each event affecting the Year 1 and Year 2 accounting periods as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE) or claims exchange (CE). Record the effects of each event under the appropriate general ledger account headings of the
a.
Answer to Problem 43AP
Indicate each event affecting the Year 1 and Year 2 accounting periods as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE) or claims exchange (CE) and record the effects of each event under the appropriate general ledger account headings of the
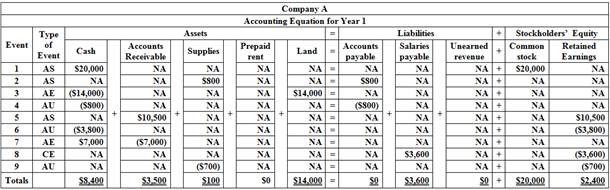
Table (1)
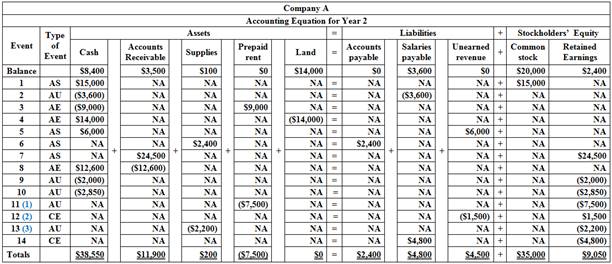
Table (2)
Note:
AE refers to asset exchange.
AS refer to asset source.
AU refers to asset used.
CE refers to claims exchange.
NA refers to does not affected.
Explanation of Solution
Asset source transactions are the transactions that results in an increase of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset use transactions are the transactions that results in a decrease of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset exchange transactions are the transactions that results in increase in one asset and decrease in the other asset.
Claim exchange transactions are the transactions that results in decrease of one claim and increase of other claims; thereby the total claims remains unchanged.
Working Note:
Determine the amount of prepaid rent recognized at the end of year 2.
Determine the amount of unearned revenue realized at the end of year.
Determine the amount of supplies used at the end of year.
b.
Prepare the statement of income, statement of changes in
b.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions involves for inflow and outflow of cash, and the result of these transactions is reported as an ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of income of Company A for the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of income | ||
| For the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Service revenue | $10,500 | $26,000 |
| Total revenue (A) | $10,500 | $26,000 |
| Expenses | ||
| Operating expenses | ($3,800) | ($2,850) |
| Supplies expenses | ($700) | ($2,200) |
| Salaries expense | ($3,600) | ($4,800) |
| Rent expense | $0 | ($7,500) |
| Total expenses (B) | ($8,100) | ($17,350) |
| Net income |
$2,400 | $8,650 |
Table (3)
Hence, the net income of Company A for the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 are $2,400 and $8,650 respectively.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity of Company A for the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders' equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Beginning Common Stock | $0 | $20,000 |
| Add: Stock Issued | $20,000 | $15,000 |
| Ending Common Stock (A) | $20,000 | $35,000 |
| Beginning |
$0 | $2,400 |
| Add/Less: Net Income (Loss) | $2,400 | $8,650 |
| Less: Dividends | $0 | ($2,000) |
| Ending Retained Earnings (B) | $2,400 | $9,050 |
| Total stockholder's equity |
$22,400 | $44,050 |
Table (4)
Hence, the total stockholders’ equity of Company A for the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 are $22,400 and $44,050 respectively.
Prepare the Balance sheet of Company A as on December 31, Year 1 and Year 2.
| Company A | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As on December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 | ||
| Assets | Year 1 | Year 2 |
| Cash | $8,400 | $38,550 |
| Accounts Receivable | $3,500 | $15,400 |
| Supplies | $100 | $300 |
| Prepaid Rent | $0 | $1,500 |
| Land | $14,000 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $26,000 | $55,750 |
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $2,400 |
| Salaries Payable | $3,600 | $4,800 |
| Unearned Revenue | $0 | $4,500 |
| Total Liabilities | $3,600 | $11,700 |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | $20,000 | $35,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $2,400 | $9,050 |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $22,400 | $44,050 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $26,000 | $55,750 |
Table (5)
Hence, the assets and liabilities of Company A as on December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 are $26,000 and $55,750 respectively.
Prepare the statement of cash flows of Company A for the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of cash flows | ||
| For the year ended December 31, Year 1 and Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers (4) | $20,000 | $35,000 |
| Cash payments for expenses (5) | (5) ($4,600) | (6) ($15,450) |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $2,400 | $3,150 |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| Cash Payment for Land | ($14,000) | $0 |
| Cash Proceeds from Sale of Land | $0 | $14,000 |
| Net Cash Flow From Investing Activities | ($14,000) | $14,000 |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Stock Issue | $20,000 | $15,000 |
| Cash Payment for Dividends | $0 | ($2,000) |
| Net Cash Flow From Financing Activities | $20,000 | $13,000 |
| Net Change in Cash | $8,400 | $30,150 |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | $0 | $8,400 |
| Ending Cash Balance | $8,400 | $38,550 |
Table (6)
Hence, the net change in the cash during the Year 1 and Year 2 are $8,400 and $38,550.
Working Note:
Determine the amount of cash receipts from customers for Year 2.
Determine the amount of cash paid for operating expense for Year 1
Determine the amount of cash paid for operating expense for Year 2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose-Leaf Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts
- Need Solution: A company has the following data: Cash: $50,000Accounts Receivable: $30,000Inventory: $60,000Current Liabilities: $70,000a) What is the company’s acid-test ratio?b) Is the company in a strong liquidity position based on this ratio?arrow_forwardHii teacher please provide for general accounting question answer do fastarrow_forwardPlease give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Explanation: Question:A company has the following information: Beginning Inventory: $50,000Purchases: $120,000Ending Inventory: $60,000The company uses the periodic inventory system. What is the cost of goods sold (COGS) for the period?arrow_forward✓ Unit Price $12.51 $35.39 $34.98 $12.13 $43.98 A B D E F G H K 1 Product Order Quantity ✓ Product ID ✓ Unit Price Gross Sales Formulas for Columns C, D, & E Product Product ID 2 Carry-on Suitcase 3 Carry-on Suitcase 4 Bluetooth Headphones 5 Carry-on Suitcase 6 Travel Pillow 7 Travel Umbrella 8 Battery Pack 9 Travel Pillow 10 Travel Pillow 11 Battery Pack 12 Battery Pack 13 Travel Pillow 14 Bluetooth Headphones 15 Battery Pack 16 Bluetooth Headphones 17 Travel Umbrella 18 Carry-on Suitcase 19 Bluetooth Headphones 20 Travel Umbrella 21 Bluetooth Headphones 22 Travel Umbrella 23 #N/A #N/A #N/A Travel Umbrella B07NQKQ19S #N/A #N/A #N/A Bluetooth Headphones B01NAJGGA2 10 #N/A #N/A #N/A Battery Pack B00Z9QVE4Q 9 23 27 27 23 6 1 #N/A #N/A #N/A Travel Pillow B00GXBZM5I #N/A #N/A #N/A Carry-on Suitcase B07PB3P1N8 #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A Pivot Table #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A 19 23 Battery Pack 25 24 Bluetooth Headphones 25 Carry-on Suitcase 26 Travel Pillow 27 Battery…arrow_forwardA company sold a piece of equipment that originally cost $55,000 for $20,000 when accumulated depreciation on the equipment was $40,000. What is the amount of gain or loss recorded on the sale of this equipment?arrow_forward
- Financial Accounting Questionarrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardOn August 31, 20X1, the balance in the checkbook and the Cash account of the Dry Creek Bed and Breakfast was $12,831. The balance shown on the bank statement on the same date was $13,677. Notes a. The firm's records indicate that a $1,700 deposit dated August 30 and a $701 deposit dated August 31 do not appear on the bank statement. b. A service charge of $35 and a debit memorandum of $250 covering an NSF check have not yet been entered in the firm's records. (The check was issued by Andrew Corollo, a credit customer) c. The following checks were issued but have not yet been paid by the bank Check 712, Check 713, Check 716, $125 $ 130 $ 245 Check 736, $ 577 Check 739, Check 741, $187 $ 118 d. A credit memorandum shows that the bank collected a $2,095 note receivable and interest of $55 for the firm. These amounts have not yet been entered in the firm's records. Required: 1. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement for the firm as of August 31. 2. Record general journal entries for items…arrow_forward
- I need help finding the correct solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the accurate steps for solving this financial accounting problem with valid procedures?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





